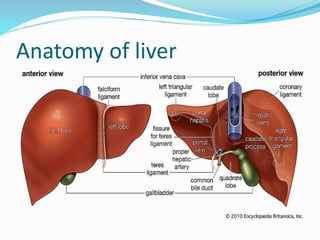
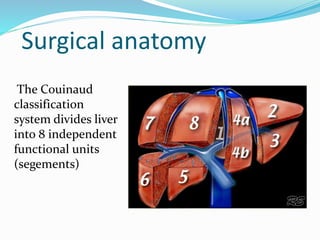
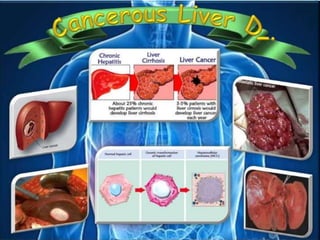
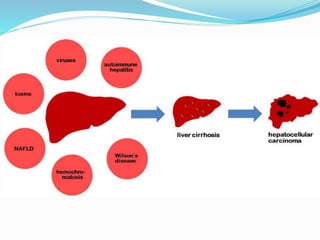
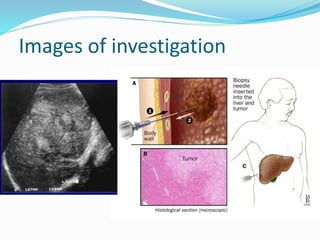
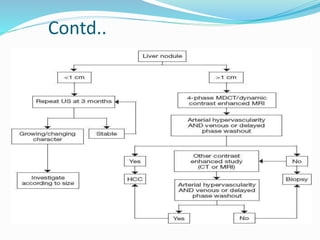
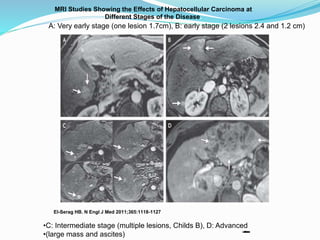
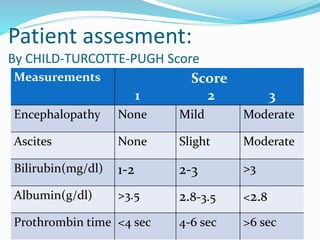
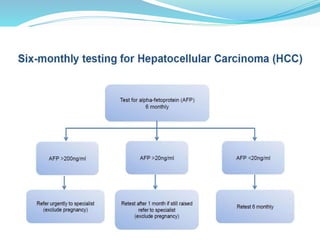
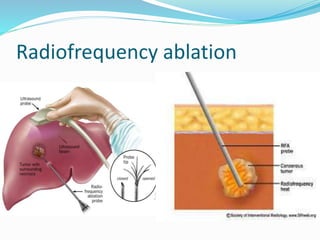
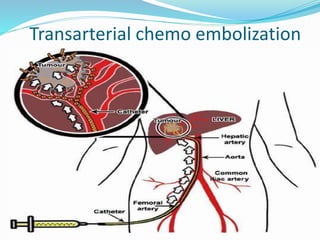
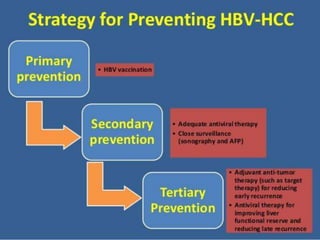
The document discusses the anatomy of the liver, particularly the Couinaud classification that segments the liver into eight functional units. It addresses the increasing incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), its risk factors, clinical presentations, diagnostic methods, staging systems, and treatment strategies. Emphasis is placed on prevention through managing viral hepatitis and lifestyle changes to mitigate the risk of liver cancer.