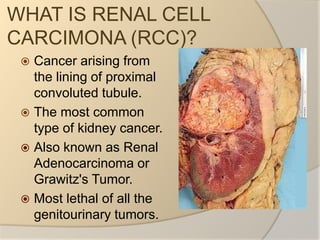
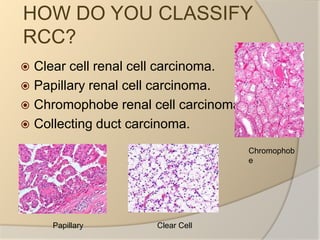
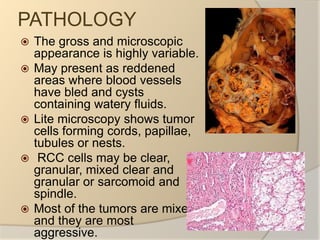
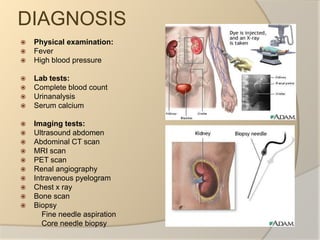
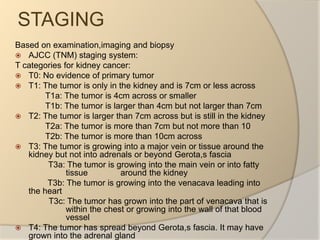
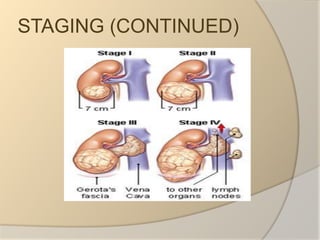
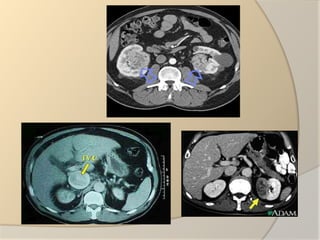
Renal cell carcinoma arises from the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule in the kidney. It is the most common and lethal type of kidney cancer. RCC can be classified into several subtypes including clear cell and papillary. The incidence is rising and risk factors include smoking, obesity, and family history. Imaging tests such as CT scans and biopsies are used for diagnosis and staging. Surgery is the primary treatment if the cancer is confined to the kidneys, while targeted drug therapies may be options for advanced cases. Prognosis depends on staging, with 5-year survival rates ranging from 90% for small localized tumors to less than 5% if the cancer has metastasized to other organs.