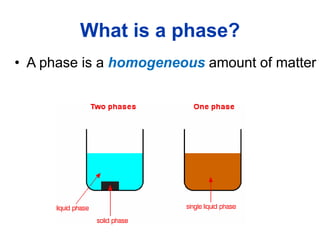
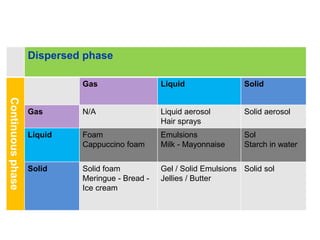
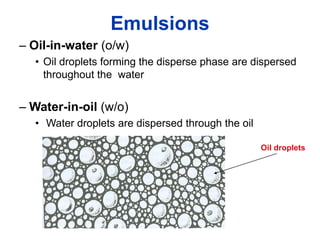
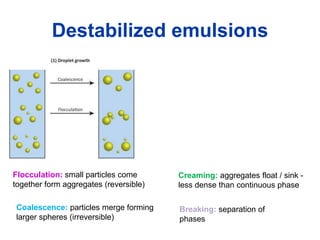
The document provides an overview of food colloids, focusing on their definitions, classifications, and functionalities, including emulsions, gels, and foams. It discusses the structural components of food colloids, their formation processes, and the role of emulsifiers and stabilizers in achieving desired textures and consistency in various food products. Understanding these colloidal systems is crucial for food technologists to manipulate and enhance the properties of food.