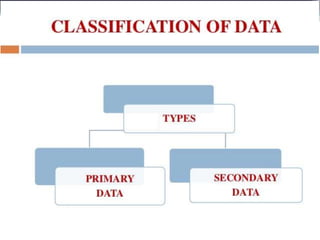
This document defines key terms related to data collection and research methods. It discusses what constitutes primary and secondary data, as well as the advantages of each. Primary data is gathered directly from original sources like individuals, groups, documents, and objects, while secondary data is collected from secondary sources like published books and articles. The document also outlines different categories of data that can be collected from respondents, including facts, attitudes, judgements, and test results. Finally, it lists several research instruments and tools that can be used to gather data, such as questionnaires, interviews, observations, and mechanical devices like microscopes.