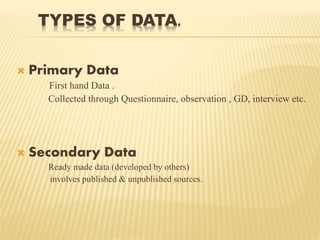
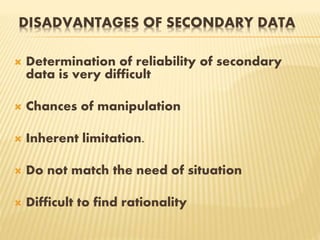
The document discusses considerations for data collection plans including objectives, scope, sources, methods, units of measurement, and accuracy levels. It defines primary and secondary data, as well as qualitative and quantitative data. Sources of primary data include interviews, questionnaires, and observation, while published/unpublished sources and databases are sources of secondary data. Secondary data has advantages like being easy to generalize from, economical, and quick, but reliability can be difficult to determine and inherent limitations may exist. Questionnaires should be clearly written following principles like being precise, unbiased, and pilot tested.