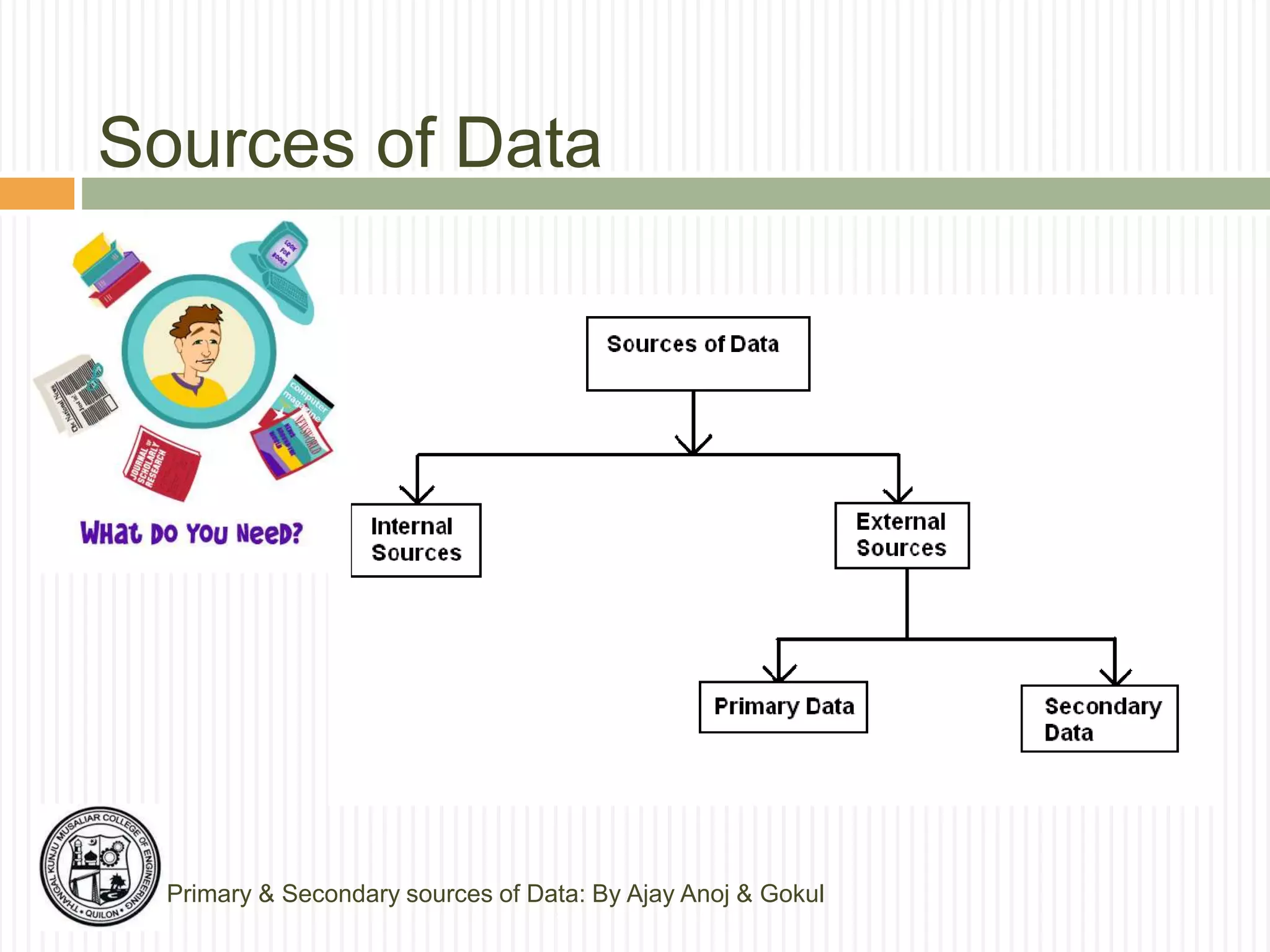
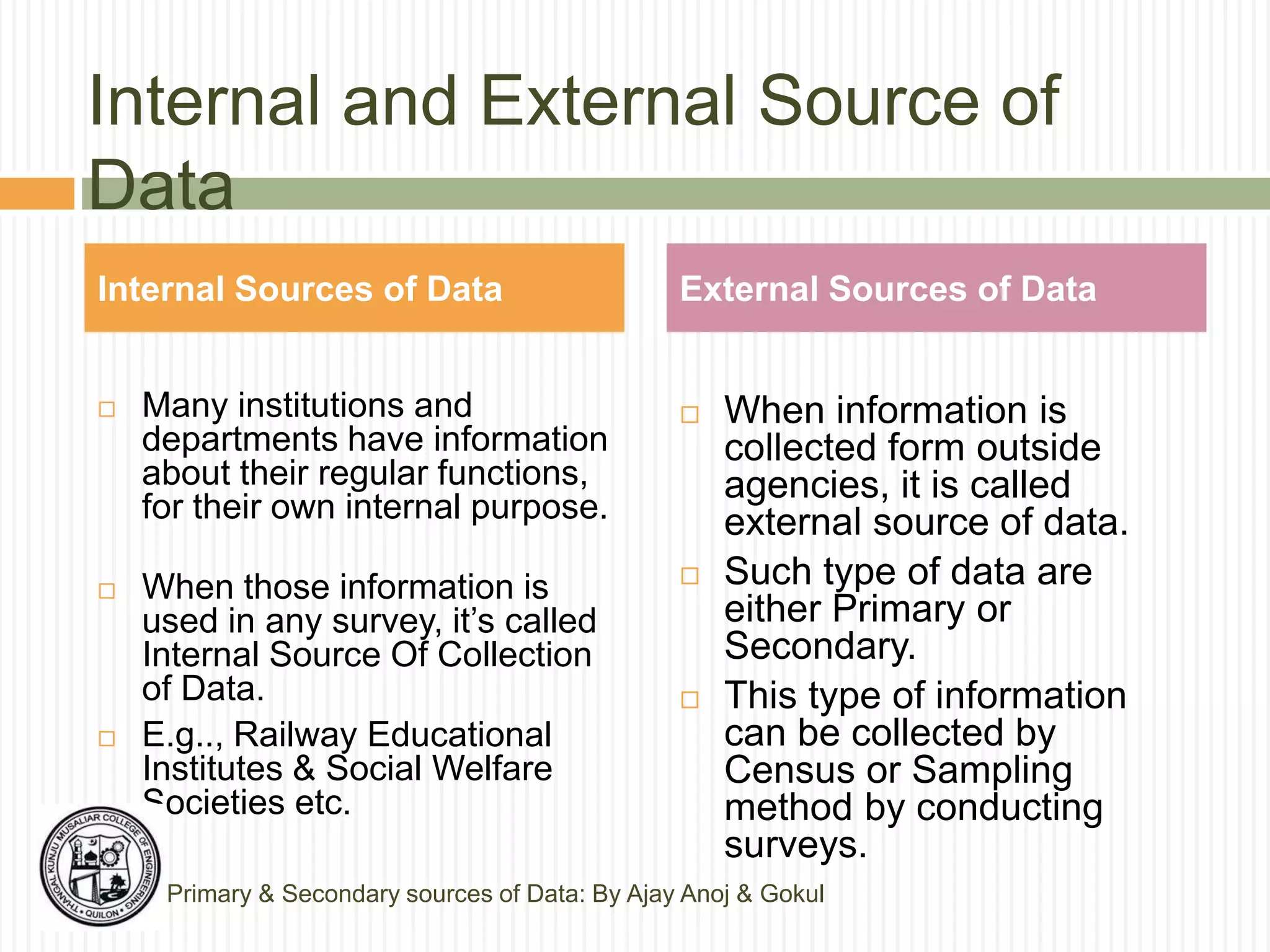
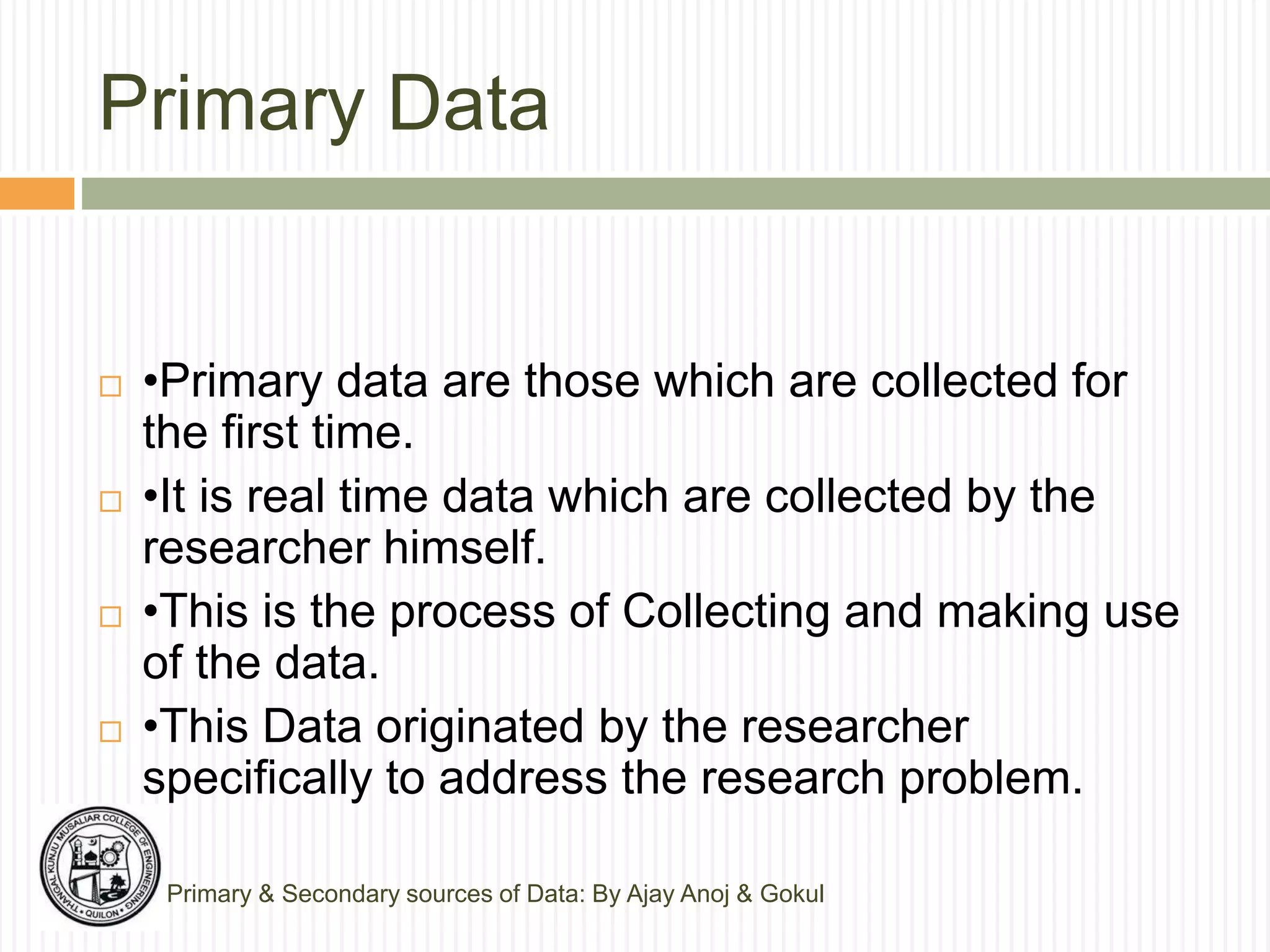
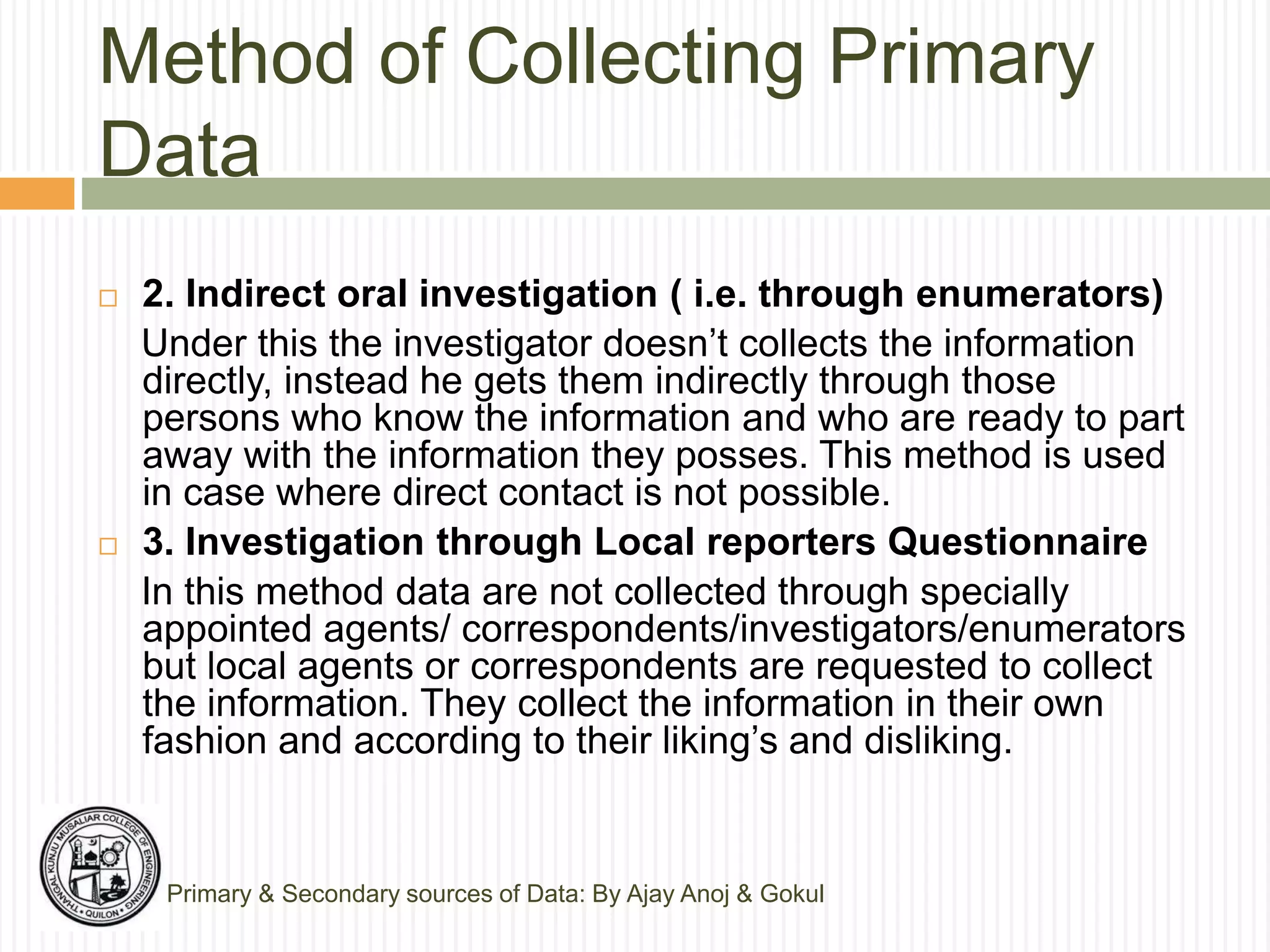
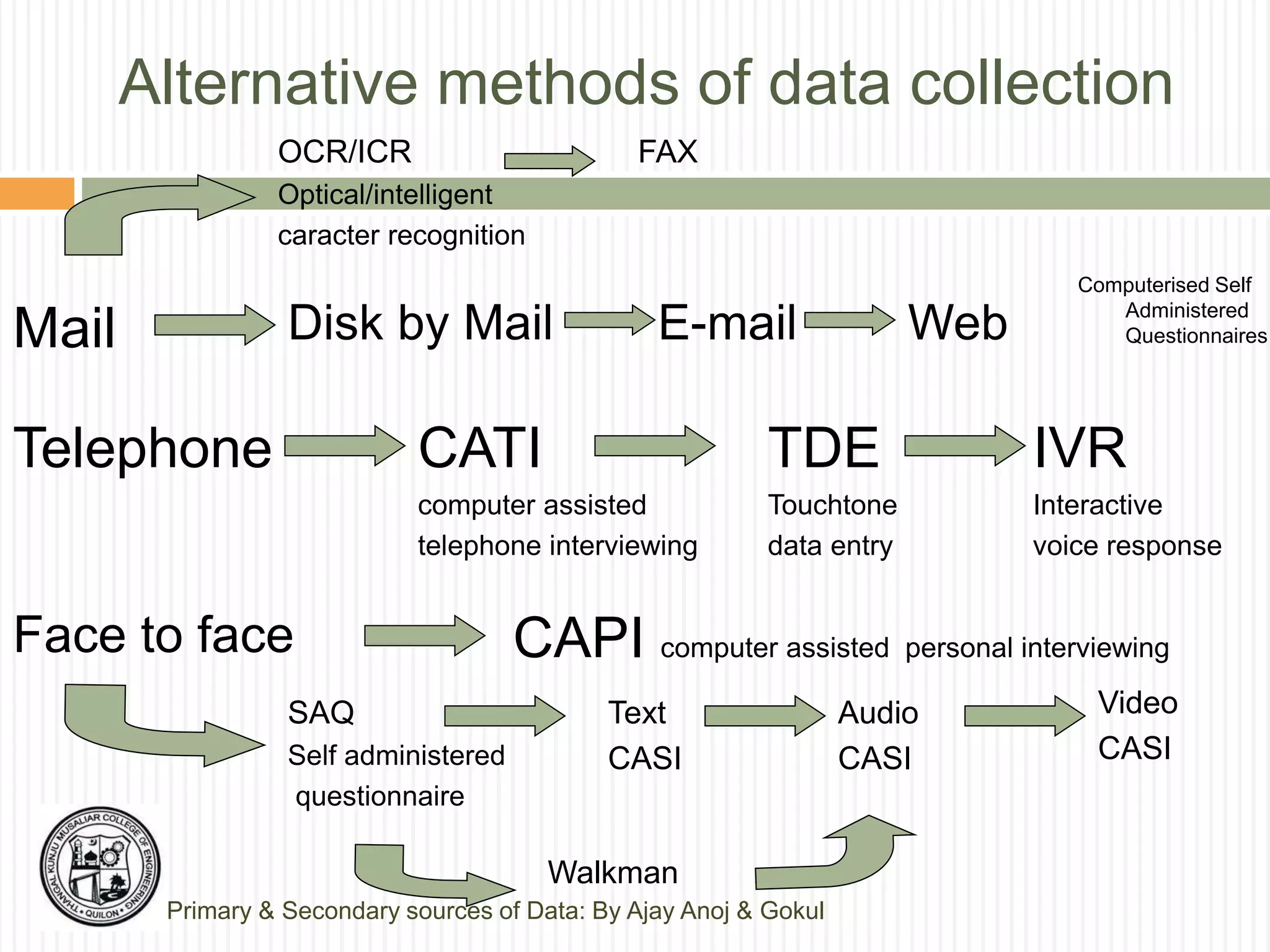
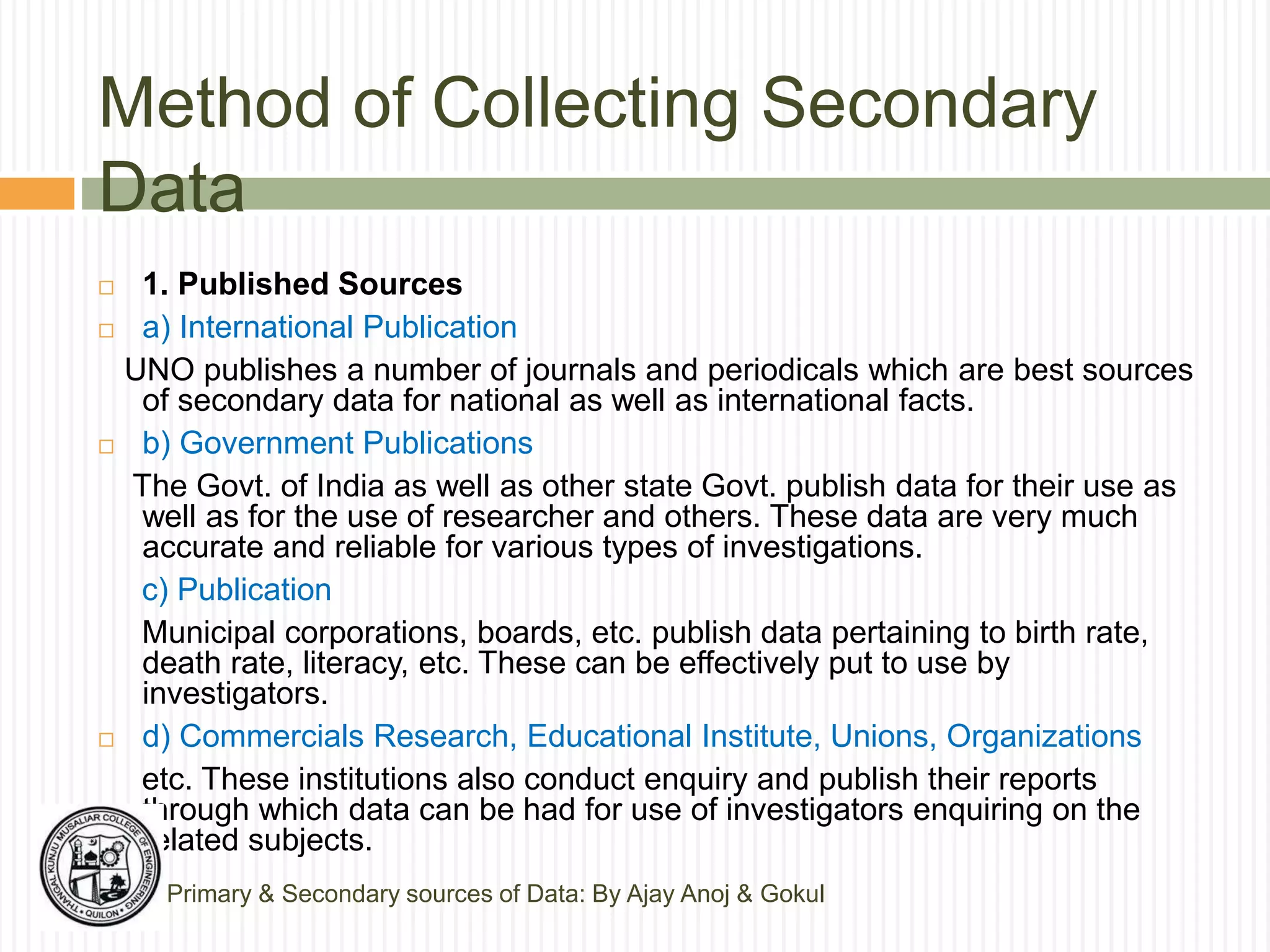
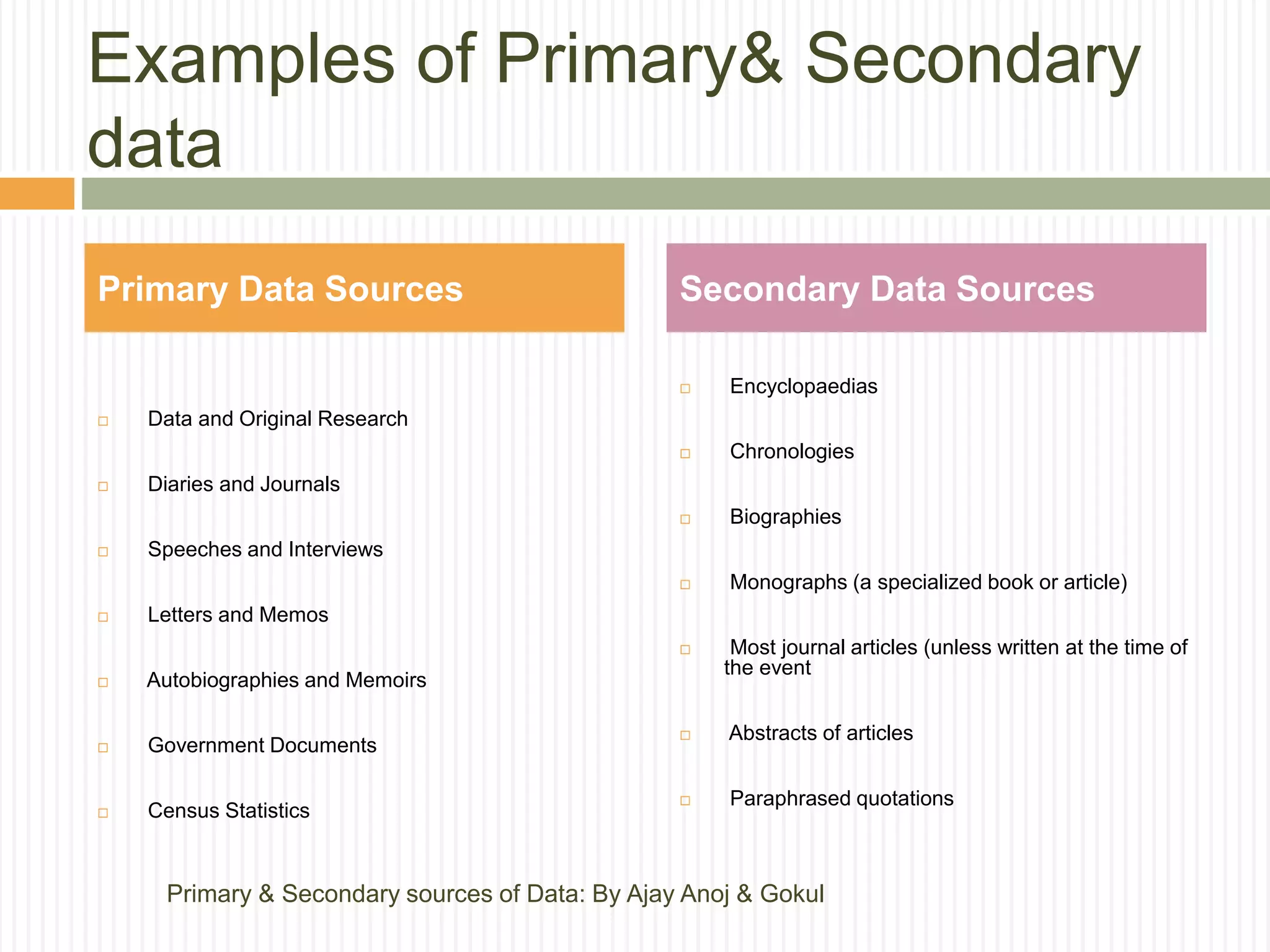
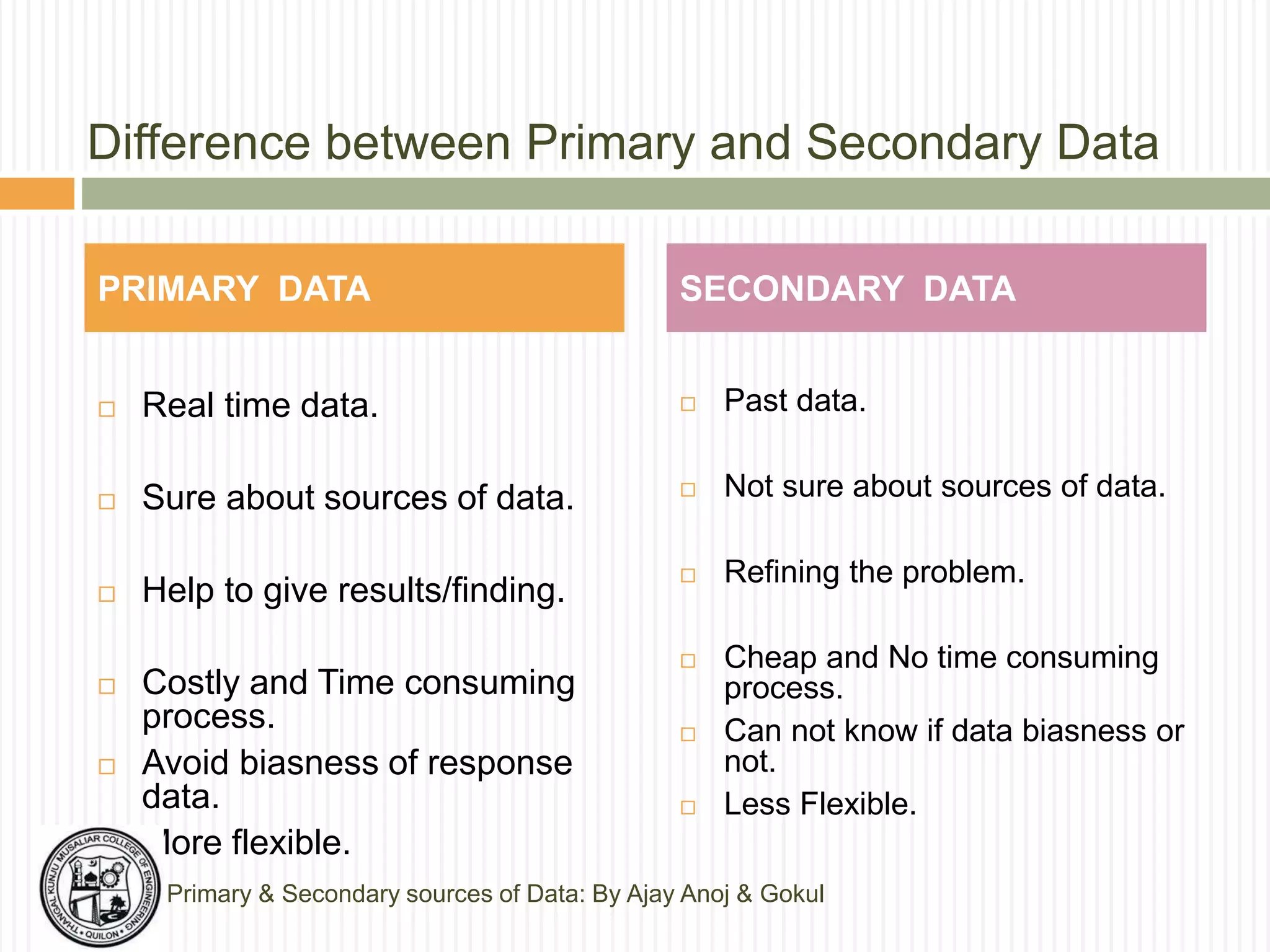
The document discusses primary and secondary sources of data collection for research. It defines primary data as data collected directly by the researcher for the purposes of the research project. Secondary data is defined as data that was previously collected by others. The document outlines various methods for collecting both primary and secondary data, including surveys, interviews, observation, and reviewing published sources. It also compares primary and secondary data and discusses best practices for selecting an appropriate data collection method based on factors like the research objective, availability of funds, and required precision.