1. Data can come from various sources like numbers, words, images, facts or ideas. It is needed to answer queries and forms the basis of analysis.
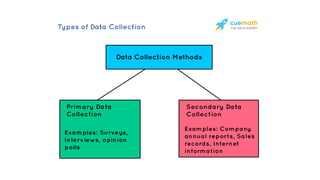
2. Primary data is original and collected specifically for a purpose, while secondary data already exists and is collected economically.
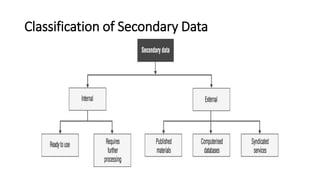
3. Key primary collection methods include observation, questionnaires, experiments, stimulation, interviews, and projective techniques. Secondary data comes from internal company sources or external personal and public sources.