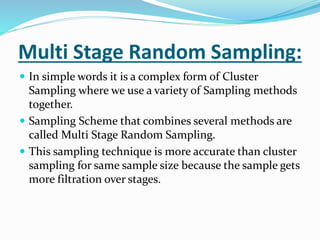
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of individuals from within a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. It is done because examining the entire population would be impossible or impractical in terms of time, cost, and effort. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every member of the population has a chance of being selected; and non-probability sampling, which does not use random selection. Some common sampling techniques include simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling, and systematic random sampling. Issues to consider with sampling include sampling error and sampling bias.