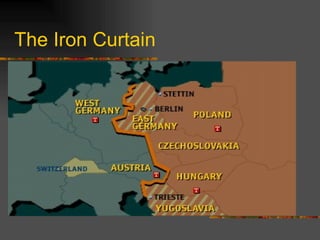
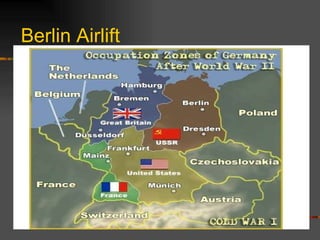
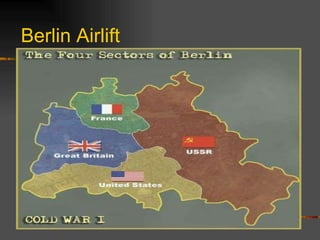
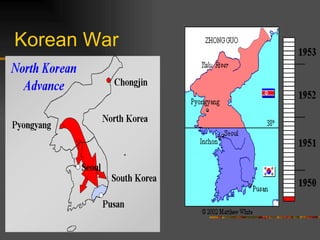
The document discusses the origins of the Cold War following World War II. It describes the Yalta and Potsdam conferences where the fate of Eastern Europe was left unclear. It then discusses the increasing tensions between the US and USSR, including the Truman Doctrine, Marshall Plan, NATO alliance, and Warsaw Pact that divided Europe into western and eastern spheres of influence. Key events that escalated Cold War tensions included the Berlin Airlift and blockade, and the Korean War.