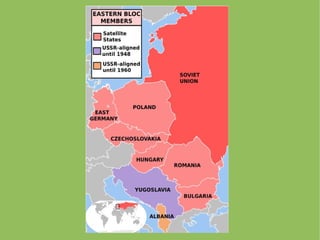
The Cold War was an ideological struggle between capitalist democracy led by the US and communist authoritarianism led by the USSR from 1945 to 1991. Each sought global influence through alliances, aid, and propaganda, dividing the world into two hostile camps without direct military conflict. Nationalism and imperialism differed from traditional forms, focusing on loyalty to ideologies and using influence rather than colonies. Both superpowers spread their spheres of influence while fearing encirclement and revolution from the other.