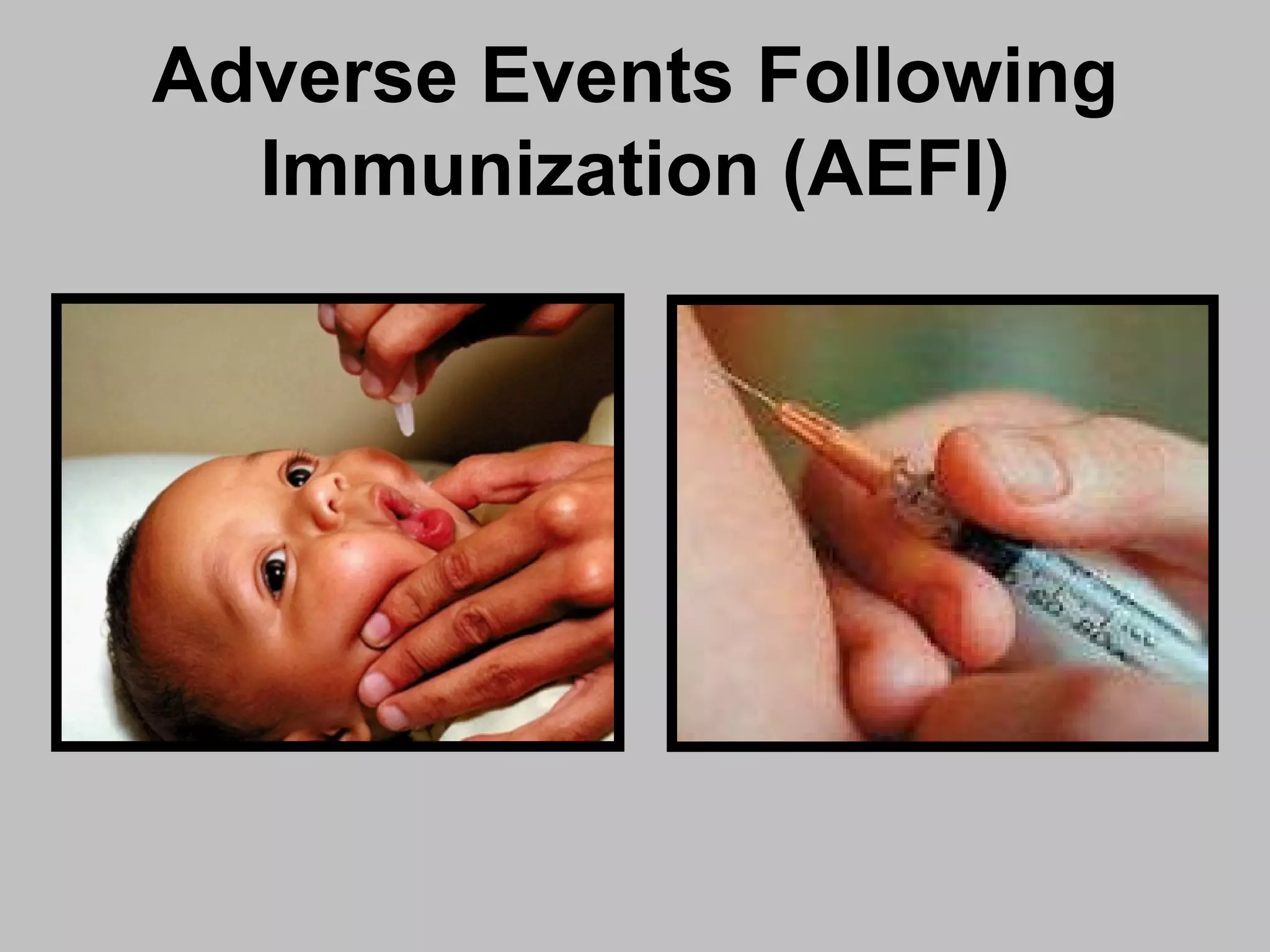
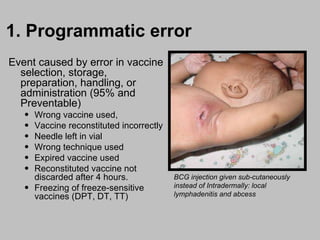
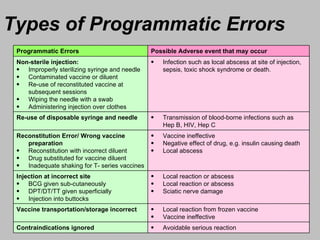
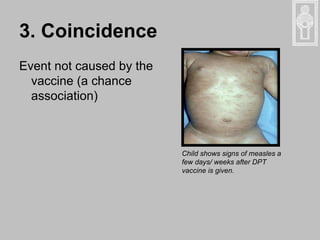
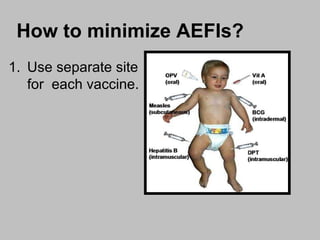
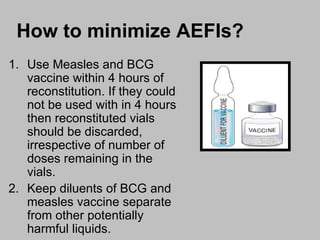
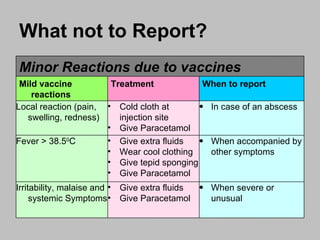
An adverse event following immunization (AEFI) is a medical event that occurs after immunization and causes concern that it may be related to the vaccine. AEFIs can range from mild side effects like fever and swelling to rare but life-threatening illnesses. Common AEFIs include mild reactions like pain, swelling, fever, and irritability, while severe reactions like seizures and anaphylaxis are rare. It is important to monitor and report AEFIs to maintain public confidence in immunization programs and identify risks to improve safety. Programmatic errors during vaccine administration, the inherent properties of vaccines, coincidental events, injection reactions, and unknown causes can all potentially lead to AEFIs.