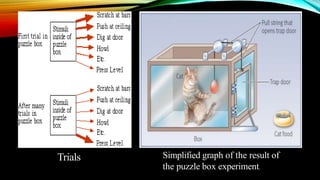
Edward Thorndike was an American psychologist known for pioneering the field of comparative psychology and establishing the law of effect, exercise, and readiness. Through experiments with animals, such as putting cats in puzzle boxes, he determined that learning is the result of forming associations between stimuli and responses through a process of trial and error. Thorndike proposed three laws of learning: readiness, exercise, and effect - where behaviors are strengthened by satisfaction or weakened by annoyance through repeated practice over time. His work significantly influenced the study of educational psychology and emphasized the role of motivation and feedback in the learning process.