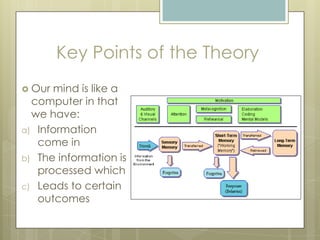
The cognitive learning theory views learners as information processors similar to computers. It argues that thinking, memory, and problem-solving should be explored by opening the "black box" of the mind. Key people who developed cognitive learning theory include Gagne, Bloom, Paivio, and Gardner. Under this theory, teachers highlight important ideas and help students connect new information to prior knowledge. Students learn by actively participating and relating new ideas to existing schemas or mental frameworks.