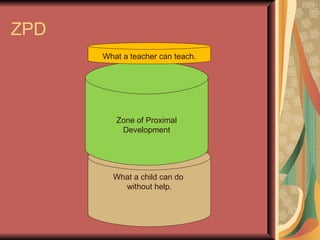
Cognitivism views learning as involving mental processes and symbolic mental constructs. Key figures who contributed to cognitivism include Piaget, who studied child development in stages, and Vygotsky, who believed concepts are formed socially then individually and that culture determines development. Cognitivism holds that learning is measured by what learners know rather than what they do, and that memory plays a key role in organizing and retrieving information for learning to occur.