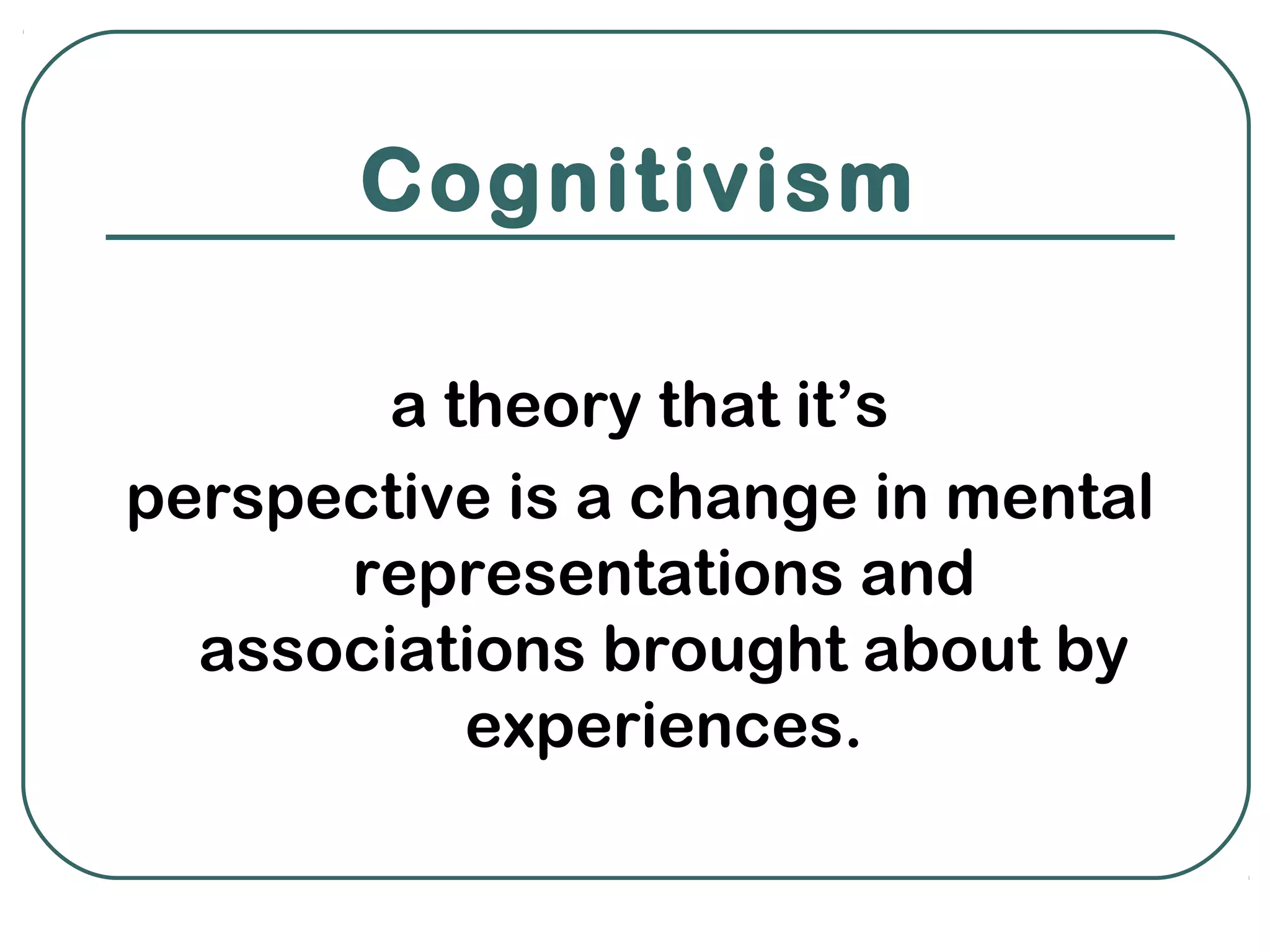
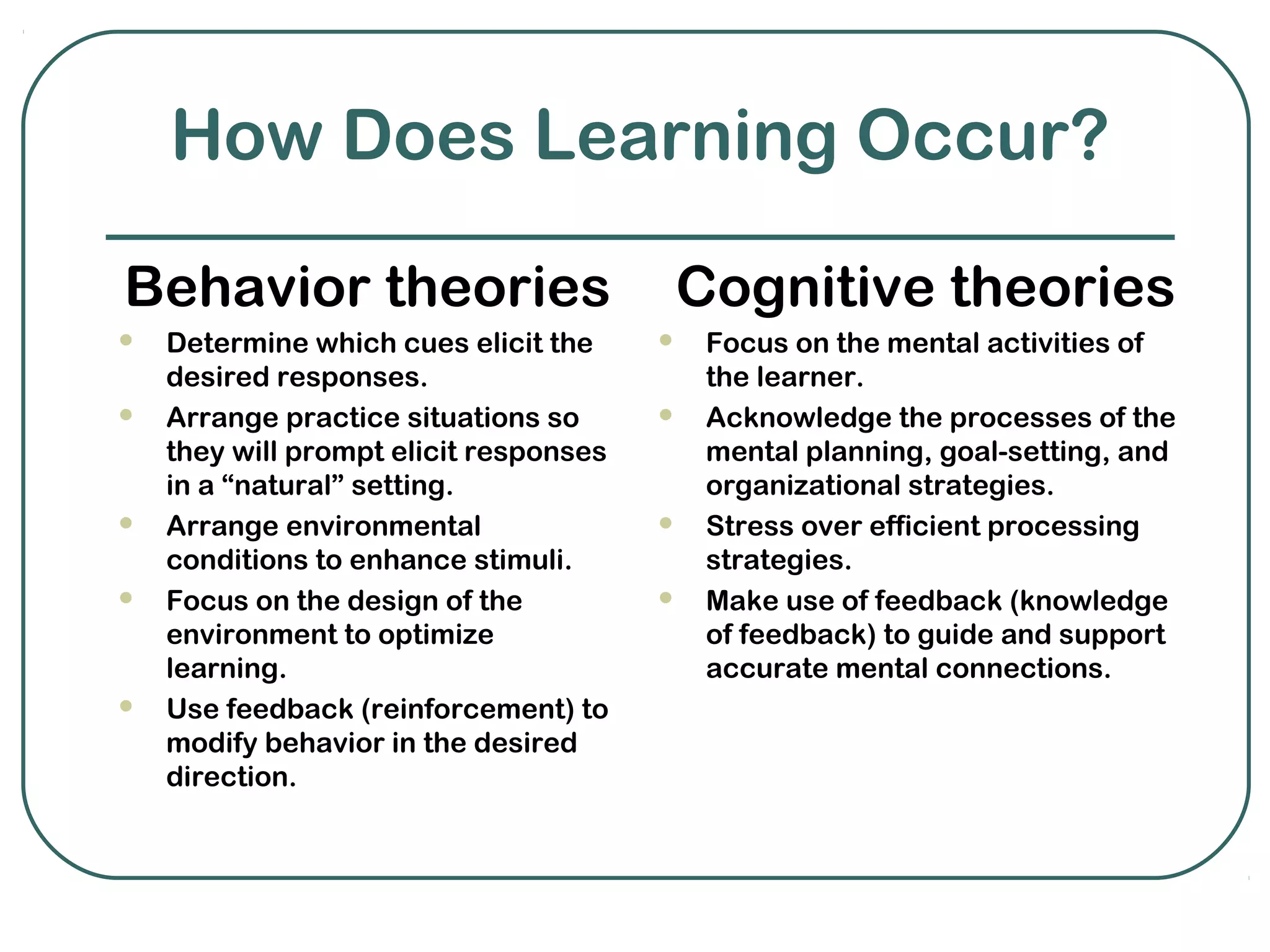
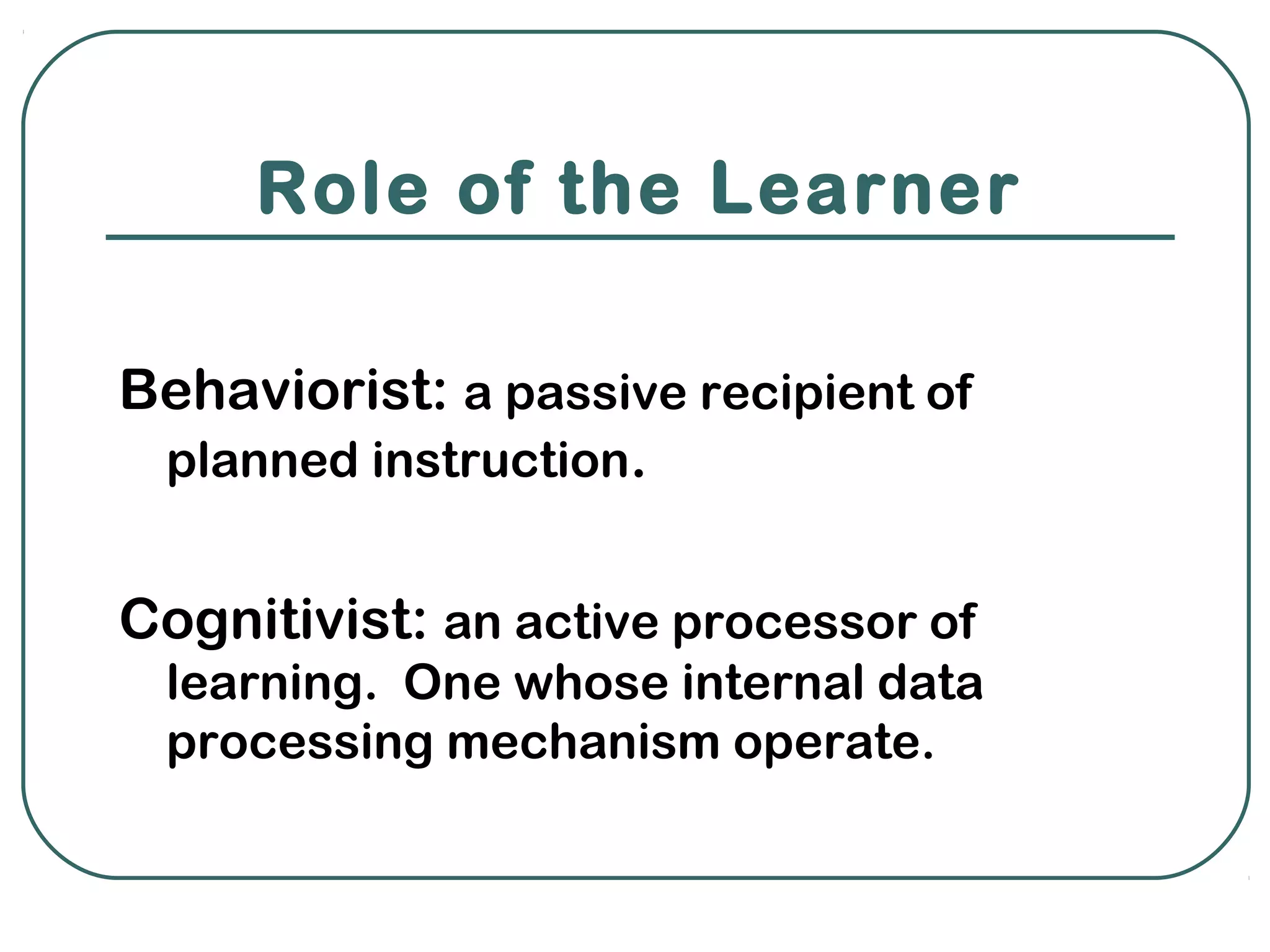
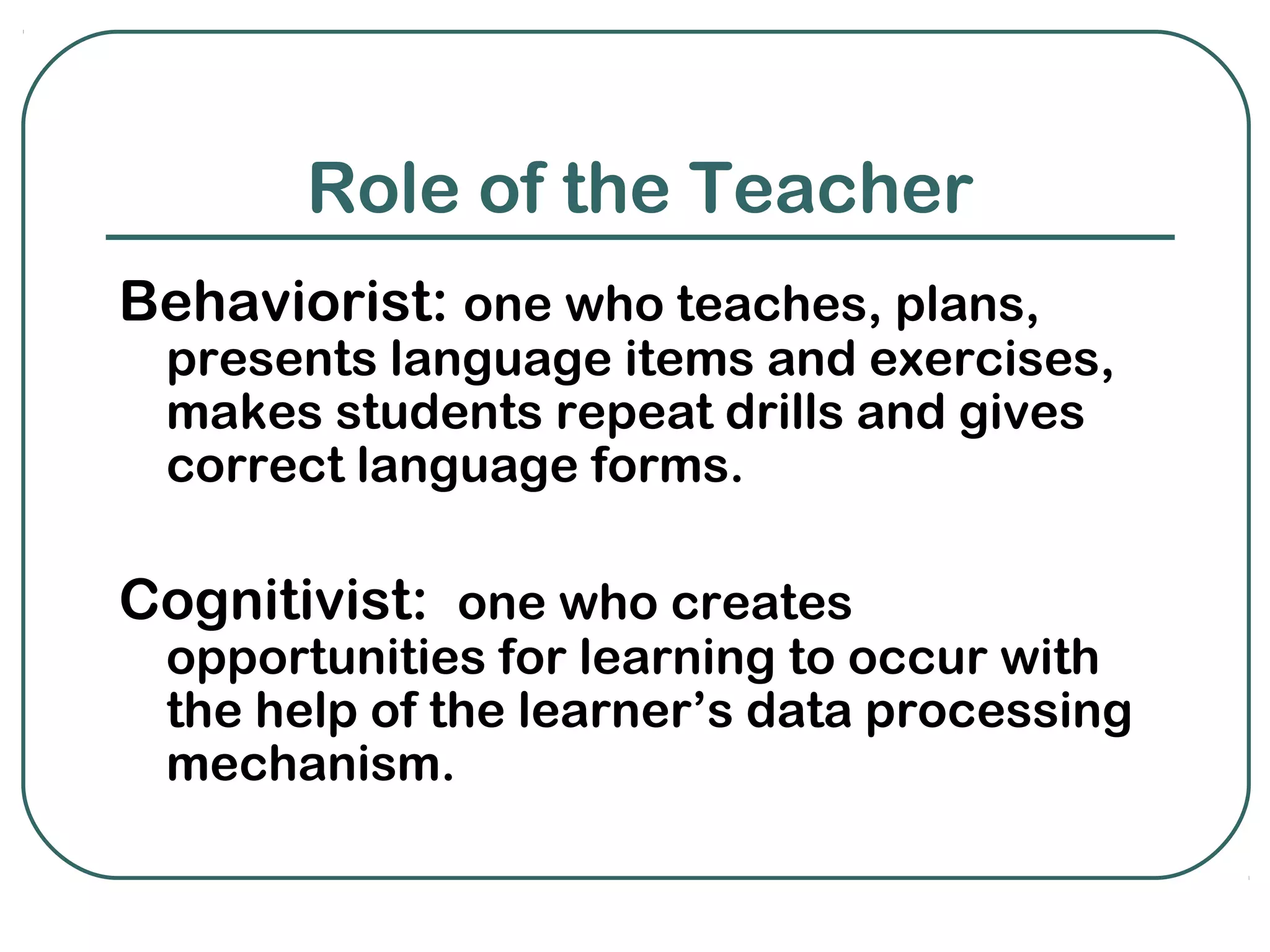
Behaviorism and cognitivism are two theories of learning that differ in their perspectives. Behaviorism views learning as changes in observable behavior due to environmental experiences, while cognitivism sees it as changes in mental representations and associations from experiences. Both theories emphasize the role of environmental conditions and practice with feedback in facilitating learning, though they differ in areas like the role of errors, exposure, and the learner's level of activity.