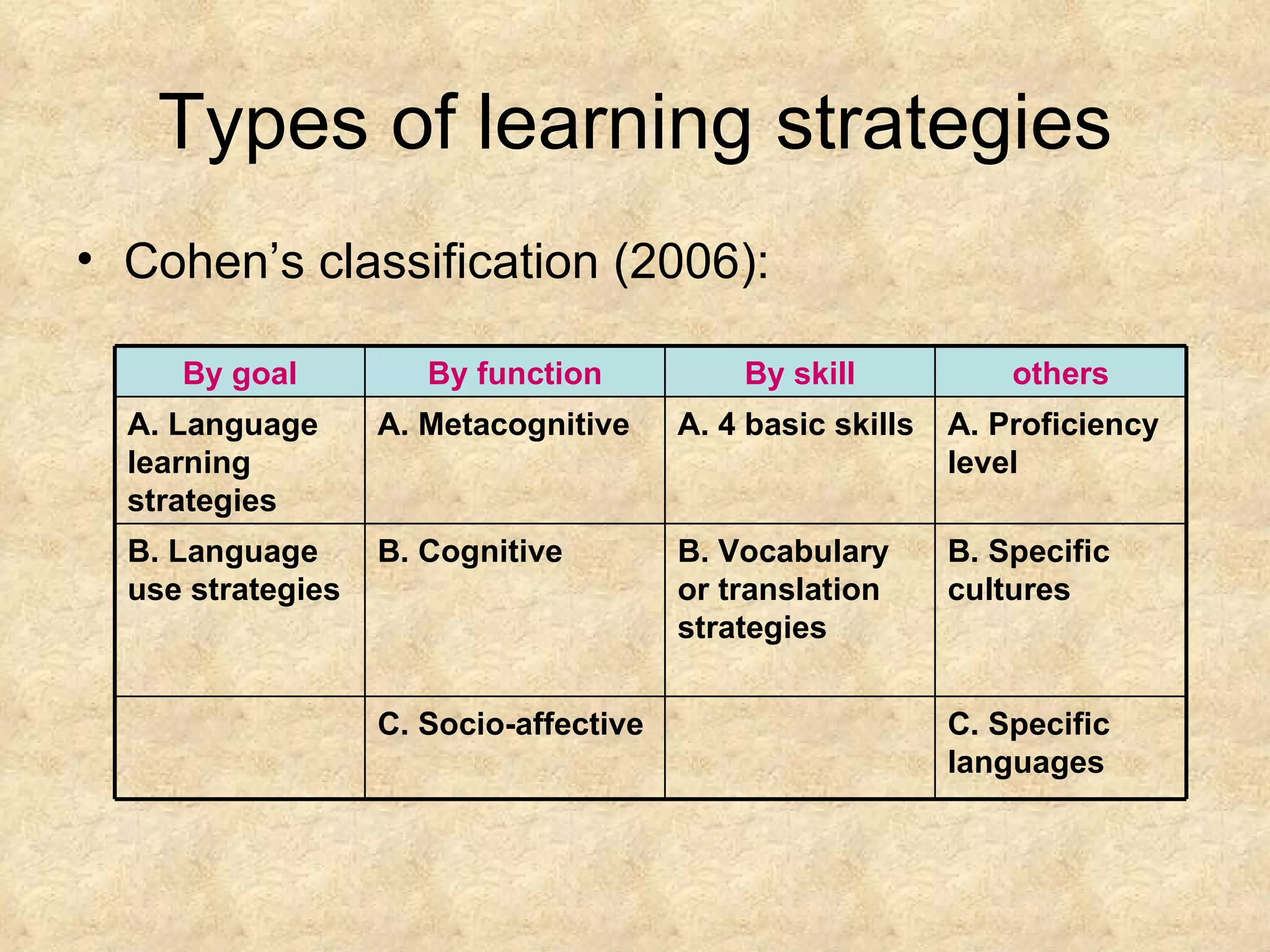
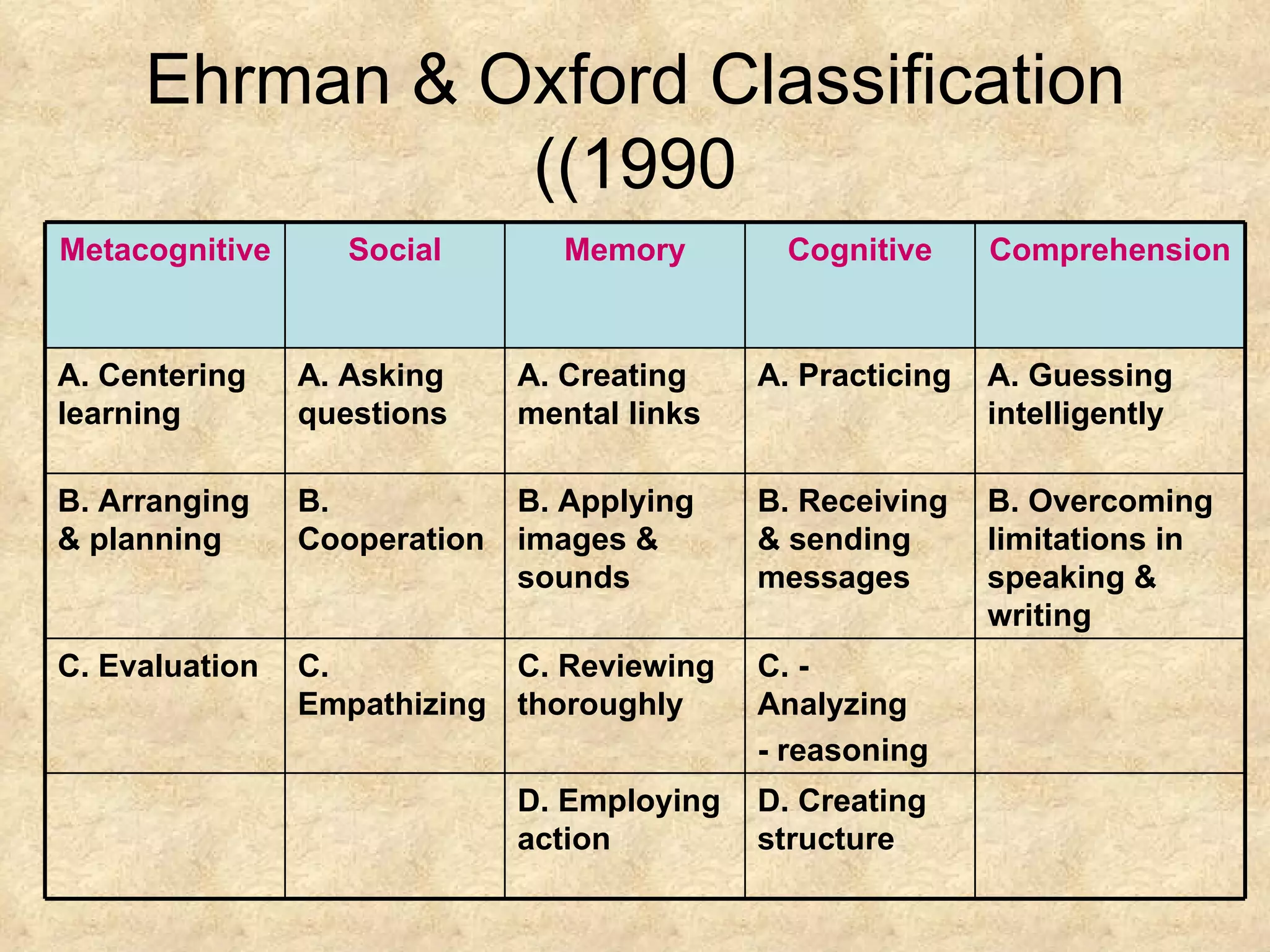
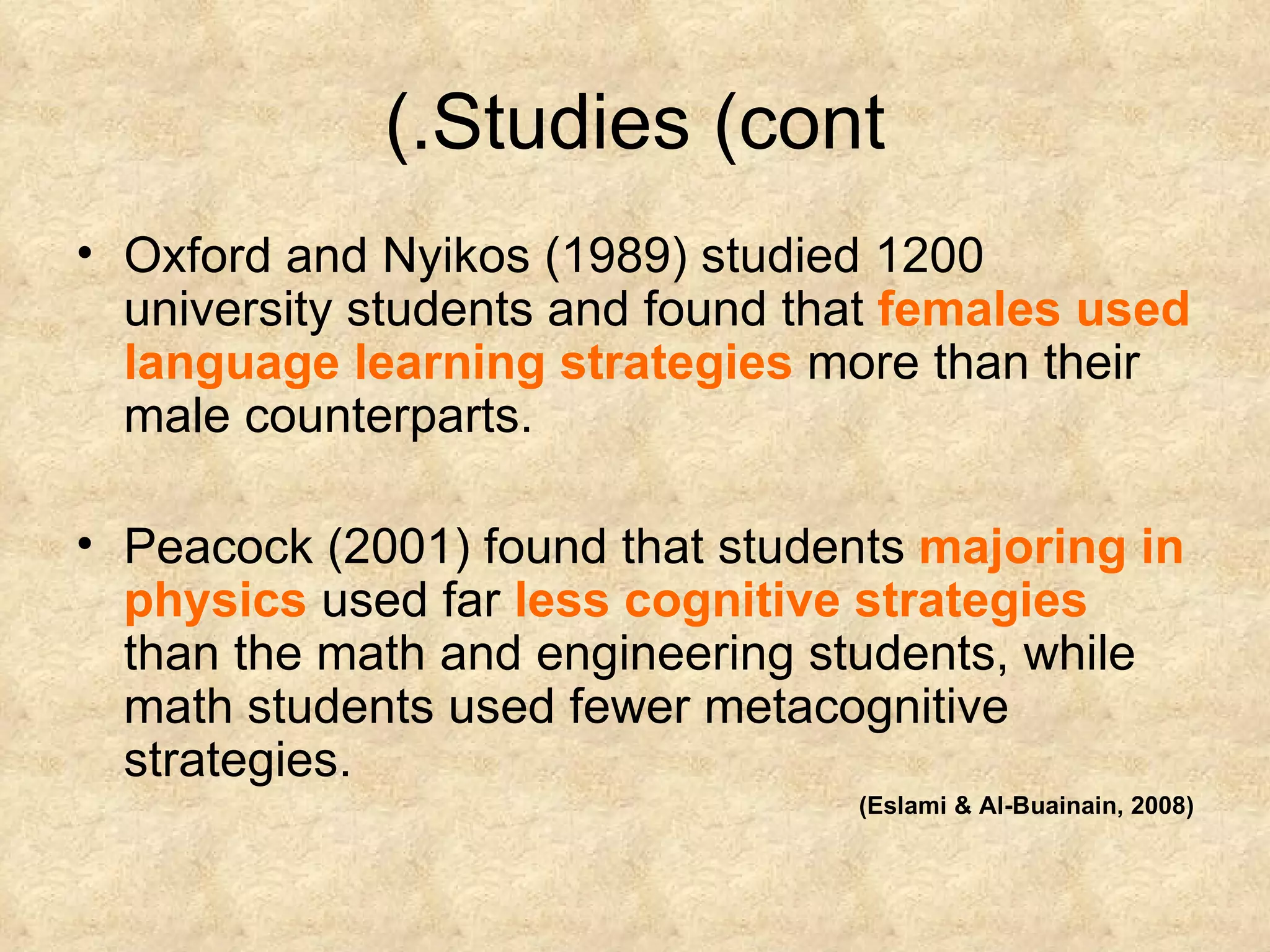
The document discusses learning strategies and their importance for language learning. It defines learning strategies as specific actions taken by learners to make learning easier, faster and more effective. Some key learning strategy types include cognitive, metacognitive, memory and social strategies. Successful language learners actively involve themselves in the learning process, develop awareness of language as a system and means of communication, and accept the emotional challenges of learning. While some strategies are more stable, others can be changed based on the learning task. Studies show strategies can improve language skills if used appropriately for the person, task and context.