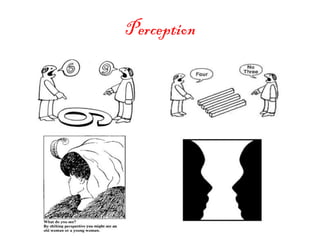
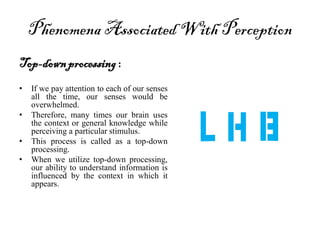
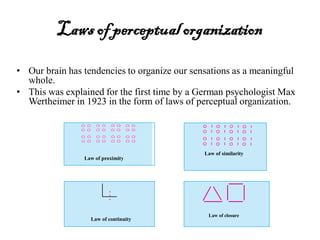
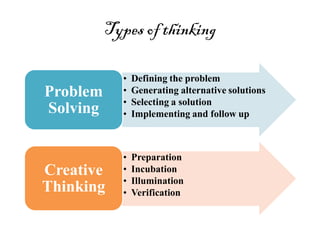
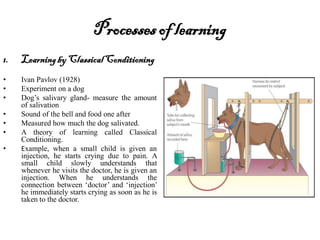
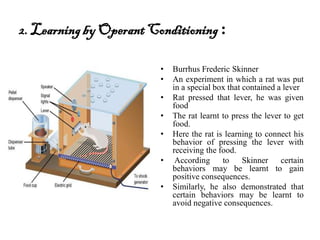
The document provides an overview of cognitive processes studied in cognitive psychology, including attention, perception, learning, and thinking. It details various aspects of attention, such as its span, distractions, division, and fluctuation, and explains concepts related to perception like top-down and bottom-up processing. Additionally, the text covers definitions and processes of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, cognitive learning, and observational learning.