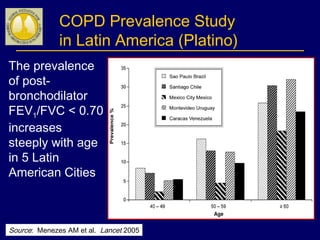
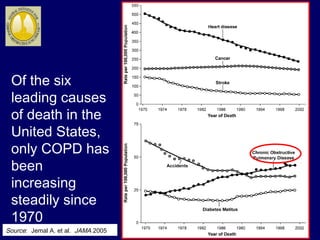
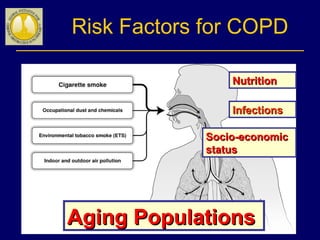
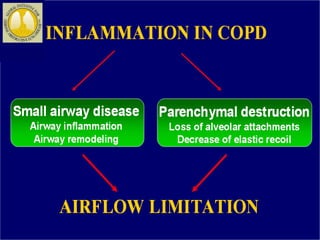
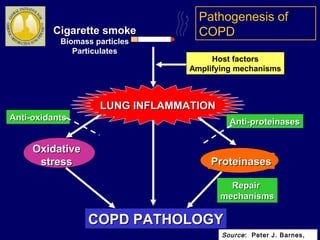
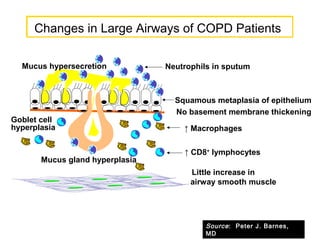
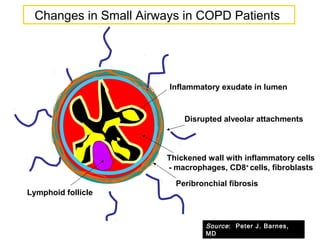
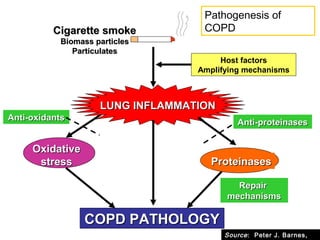
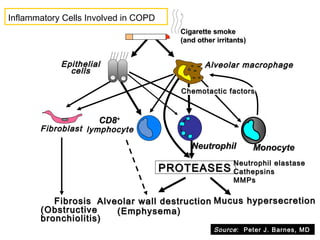
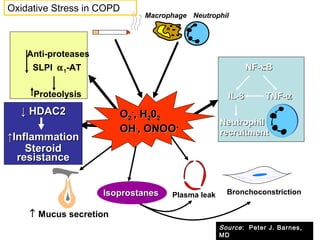
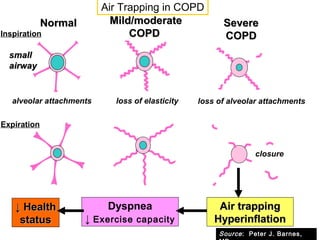
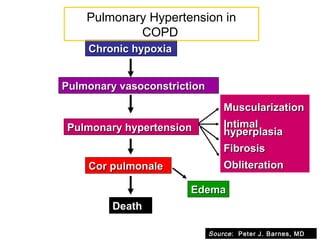
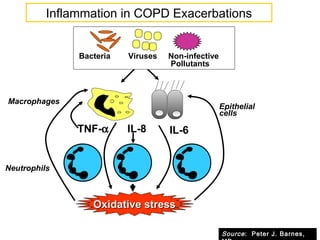
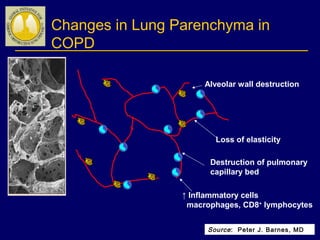
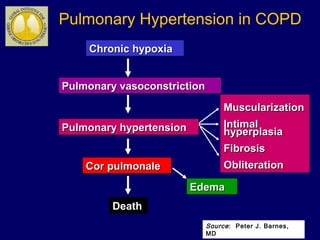
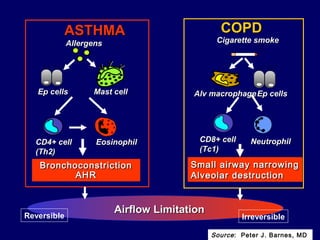
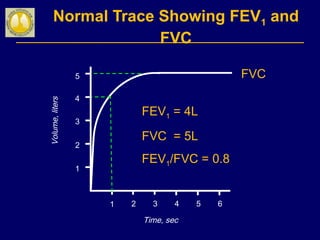
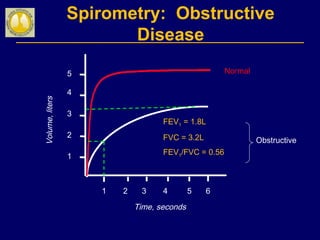
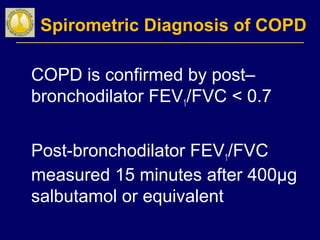
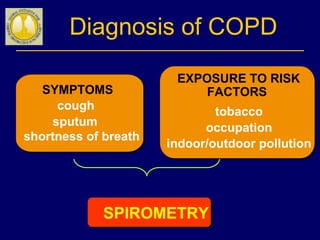
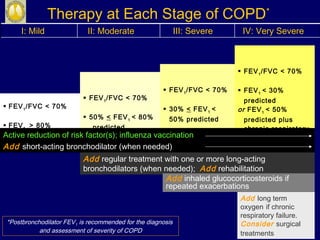
COPD is characterized by airflow limitation caused by chronic inflammation in the lungs in response to noxious particles. The document discusses the pathogenesis and pathology of COPD, including oxidative stress and protease-antiprotease imbalance leading to lung destruction and inflammation. Cigarette smoke and other irritants are major risk factors that induce inflammation through recruitment of cells like macrophages and neutrophils. This causes emphysema of the lung parenchyma and obstruction of small airways.