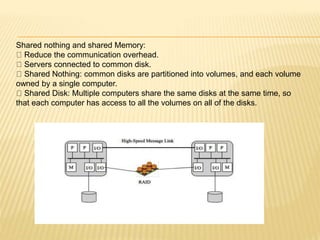
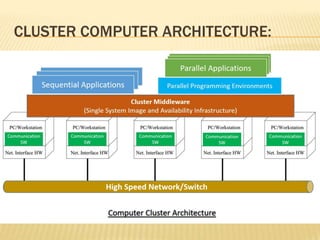
This document provides an overview of cluster computing. It defines a cluster as multiple independent computers combined through software and networking to work together as a unified system. Clusters are used for high availability and high performance computing. There are different types of clusters, including high availability clusters designed to provide uninterrupted services if a node fails, and load balancing clusters that distribute requests across nodes. The document discusses cluster configuration, methods like passive standby and shared disks, architecture involving middleware, and compares clusters to symmetric multiprocessing systems.