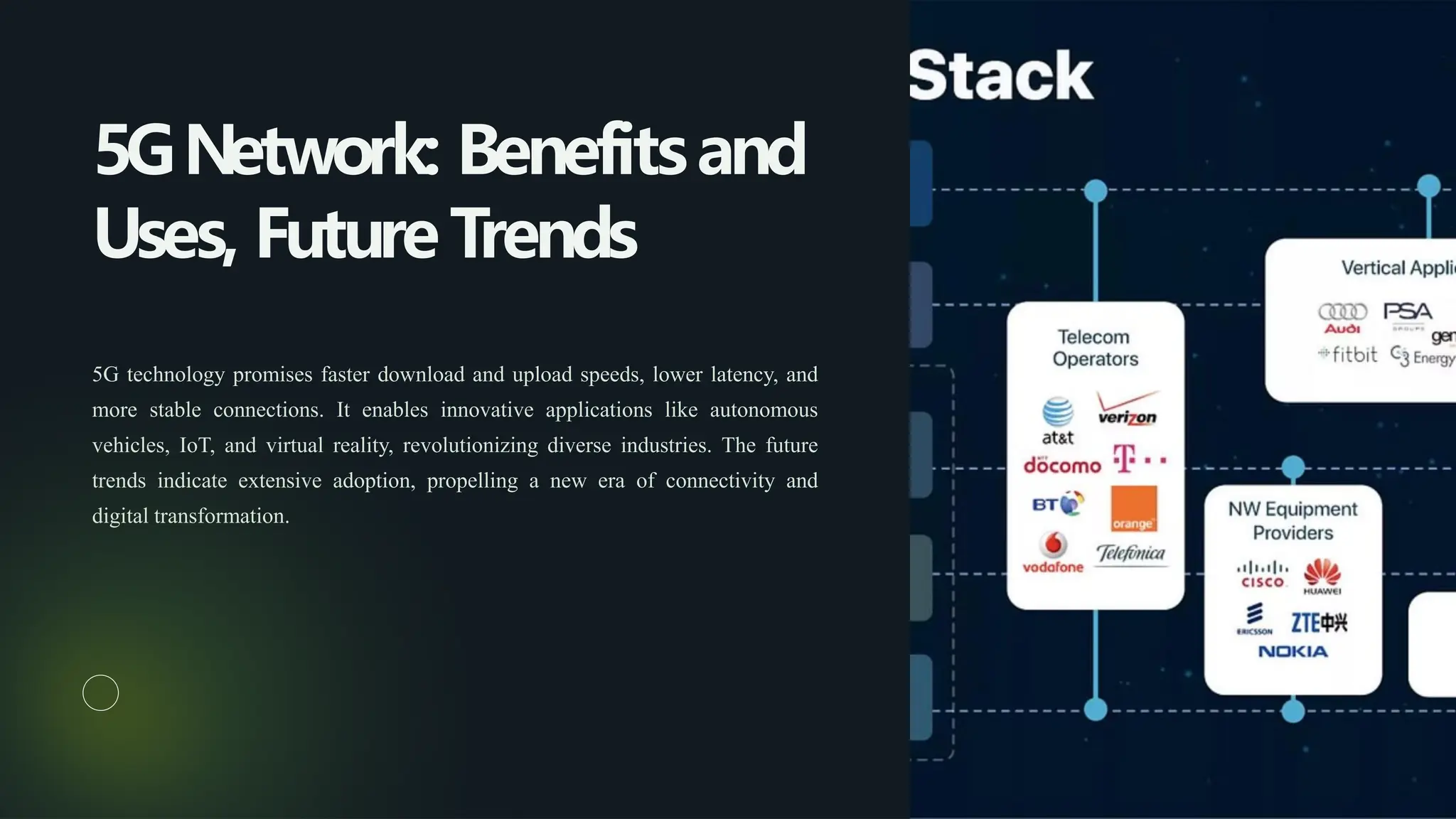
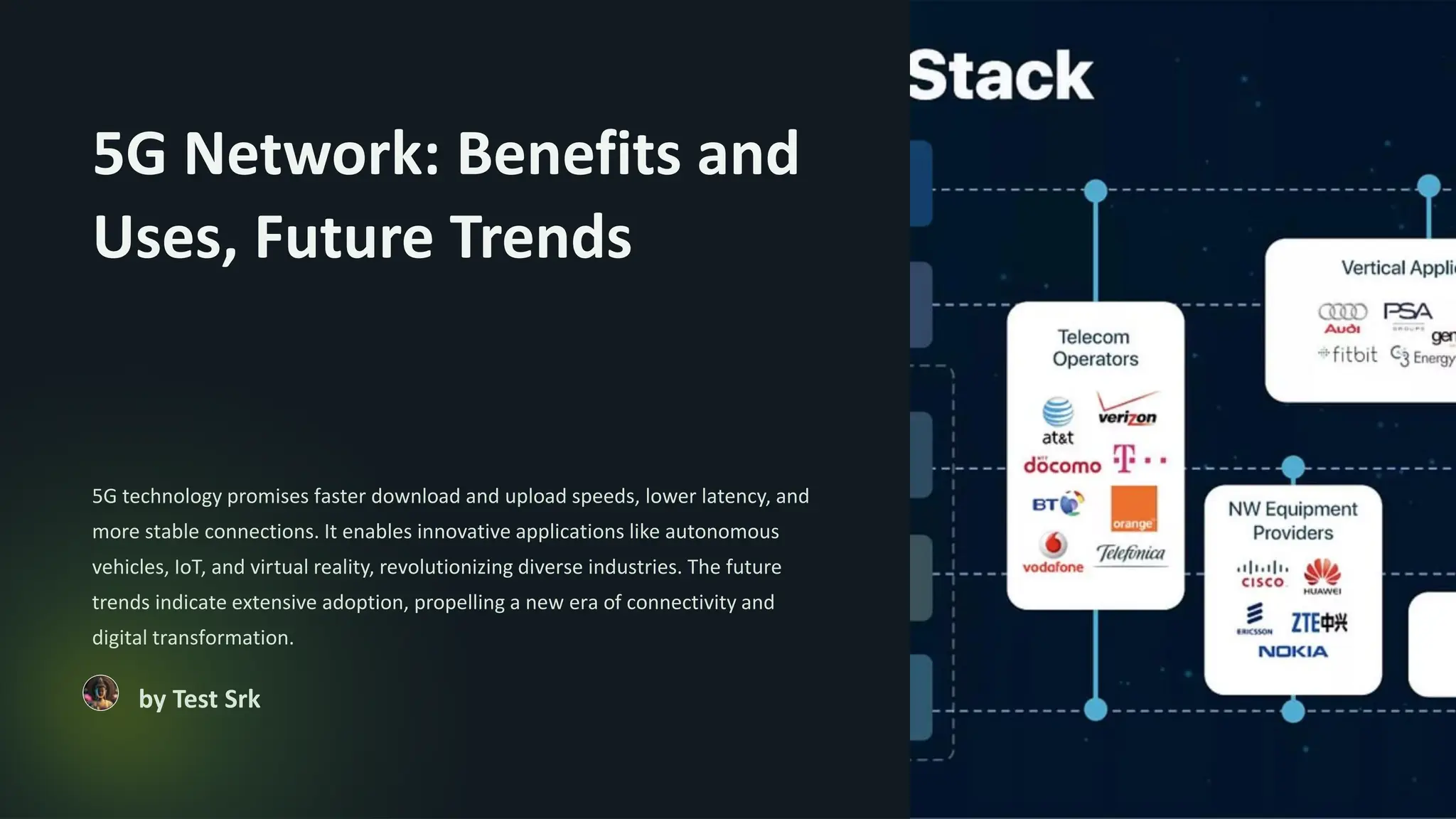
5G networks represent a significant advancement in mobile internet connectivity, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity, which can transform industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. The technology will support a vast array of applications, including IoT, autonomous vehicles, and enhanced cloud services while addressing challenges like infrastructure investment, regulatory hurdles, and cybersecurity threats. With a focus on global connectivity and environmental sustainability, 5G is set to usher in a new era of digital transformation.