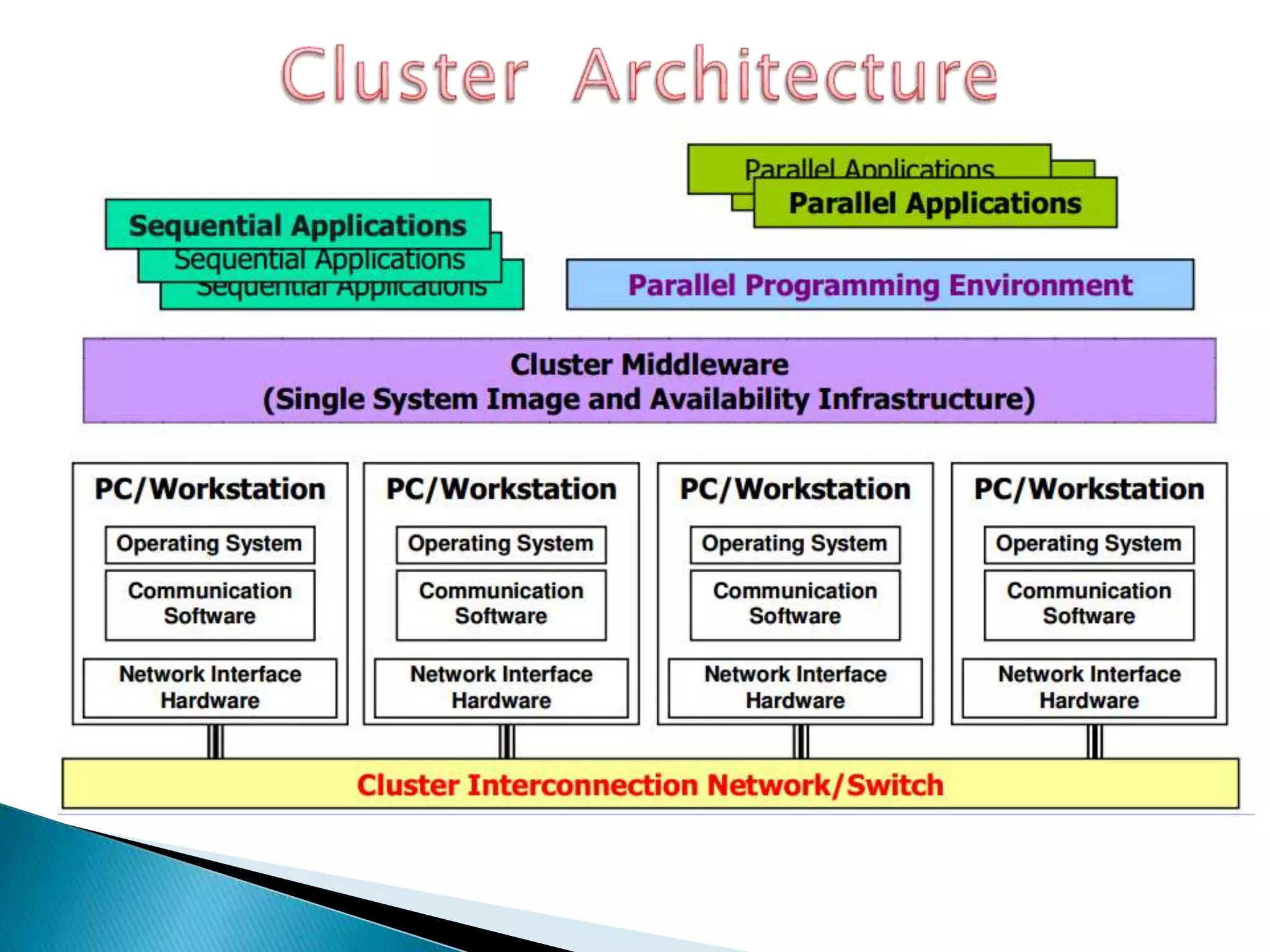
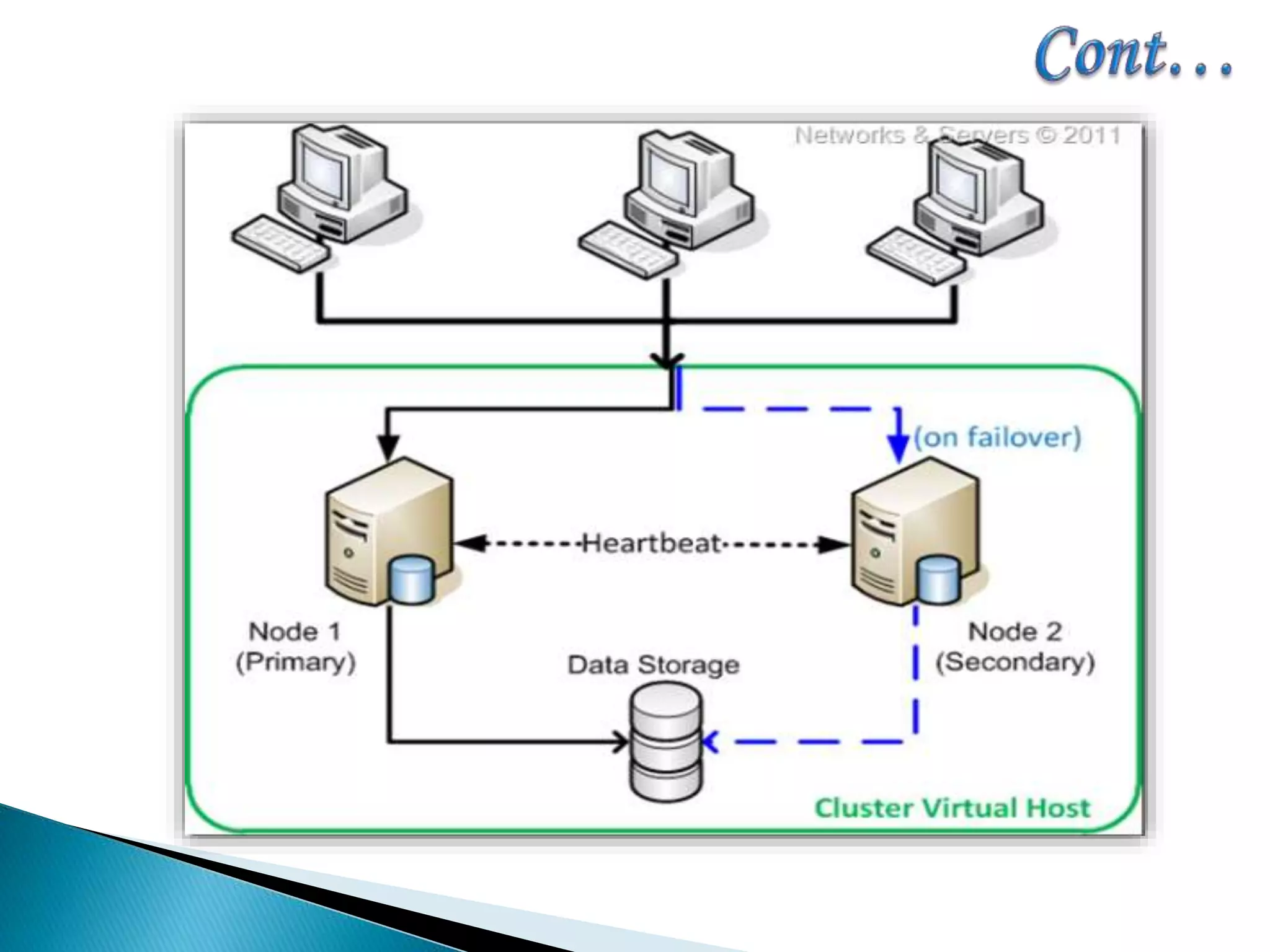
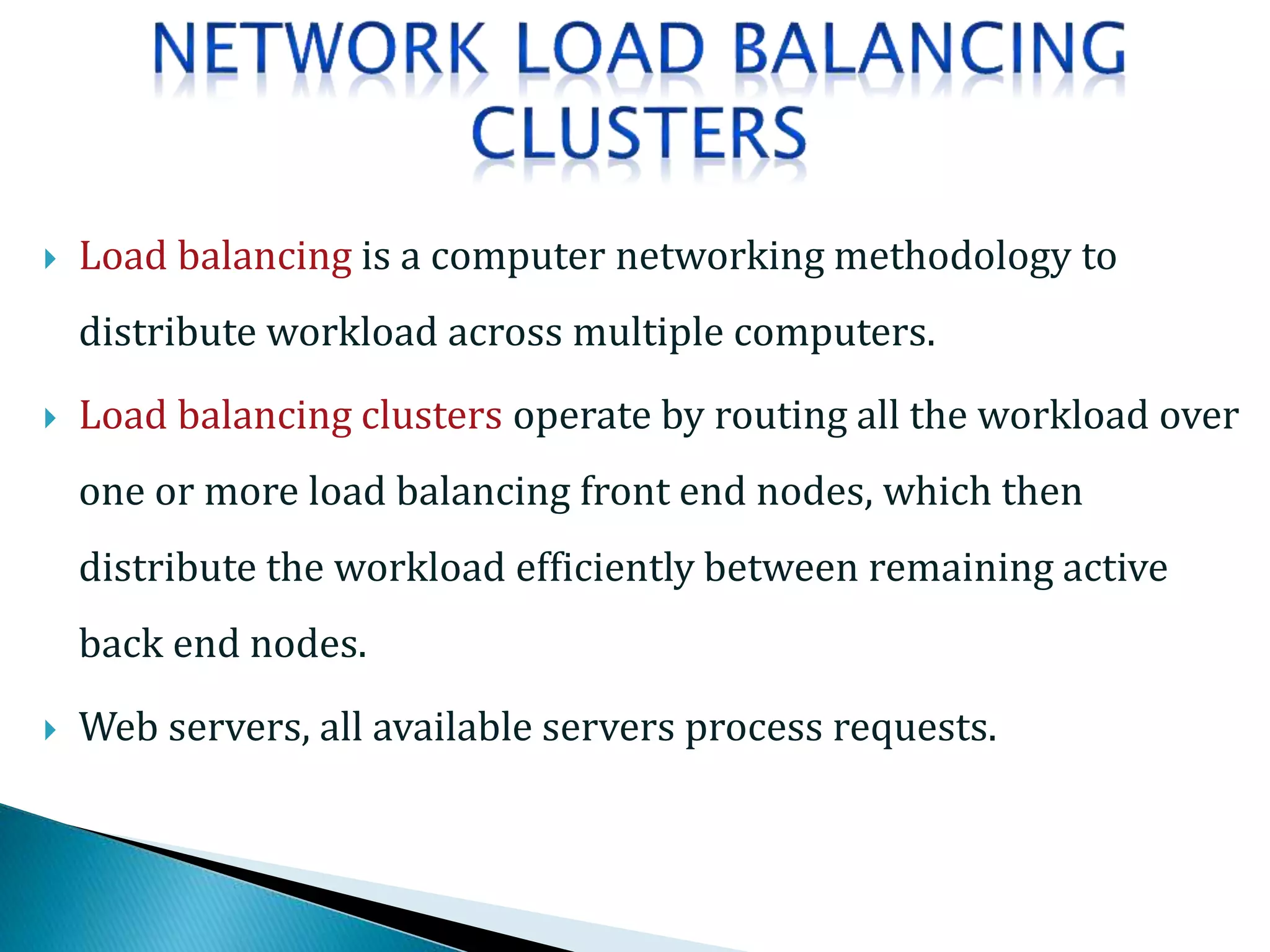
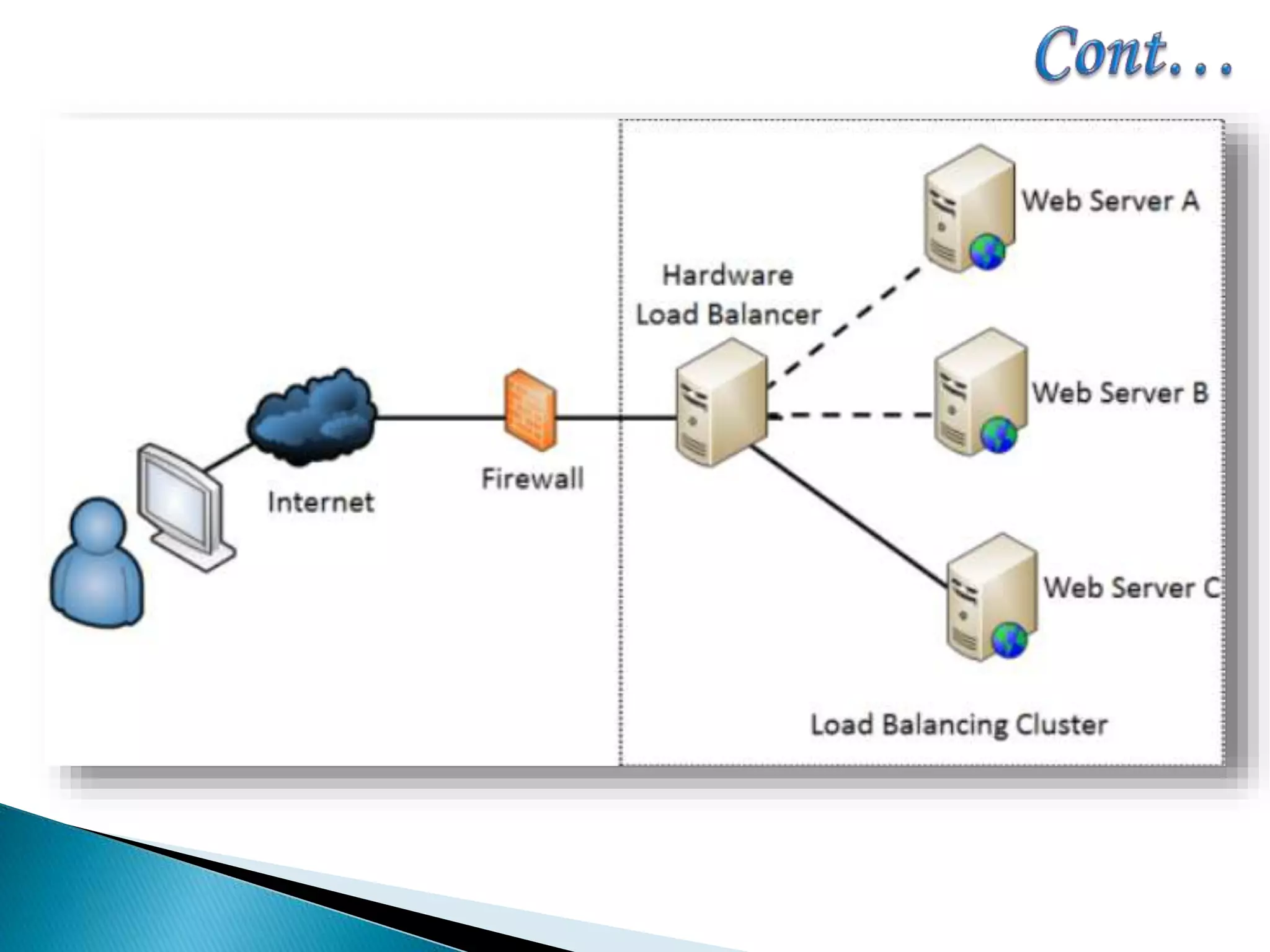
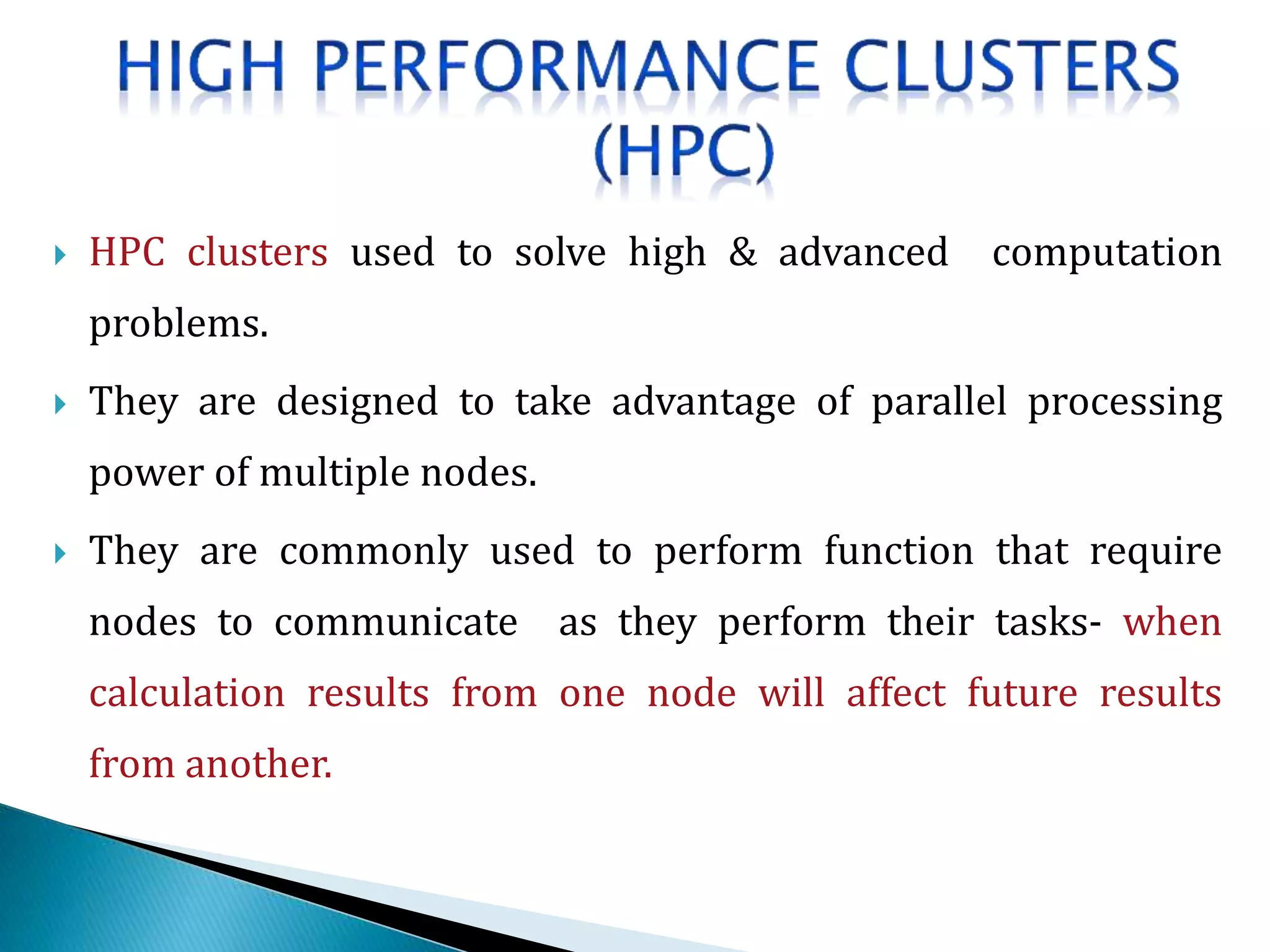
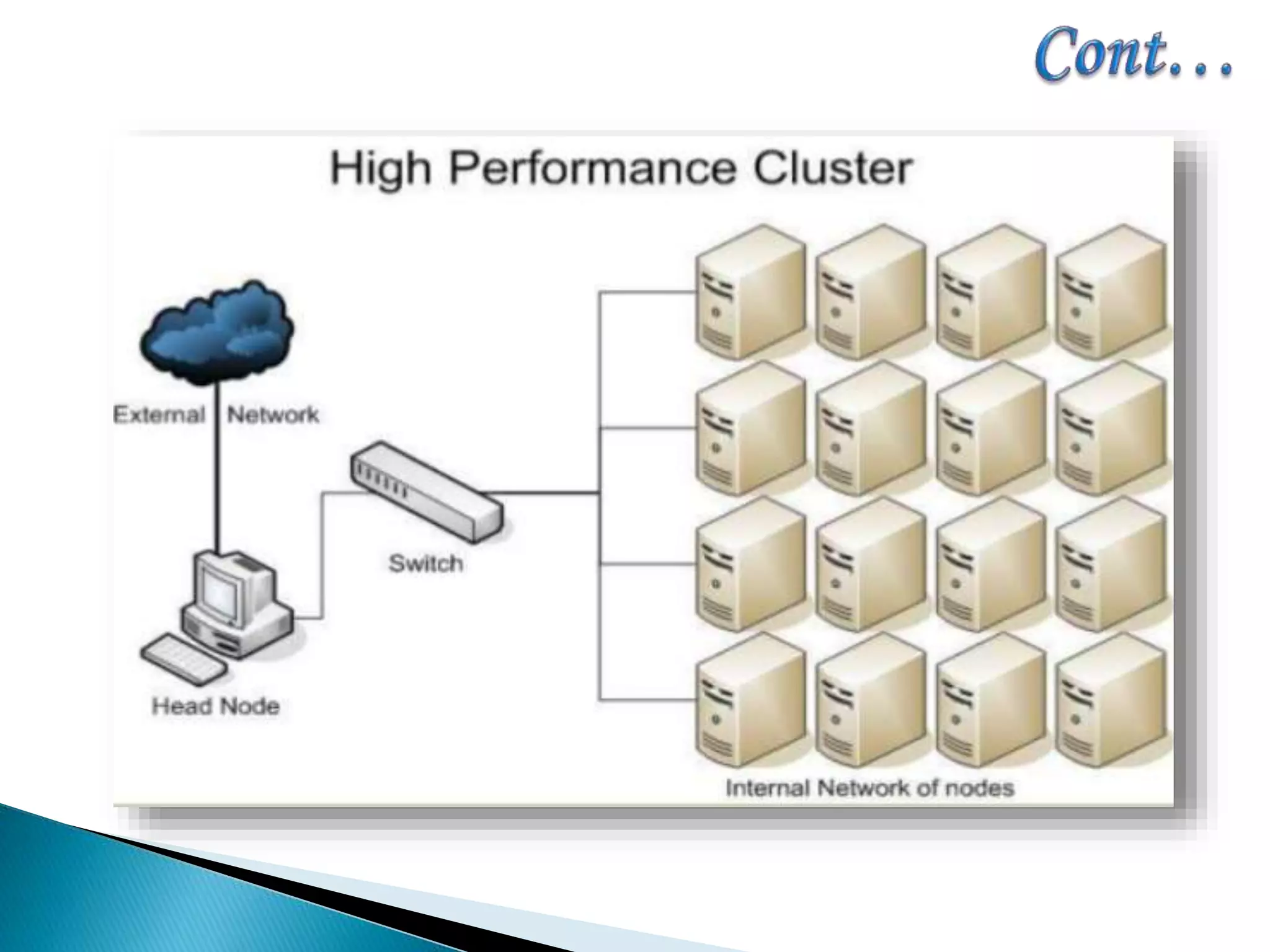
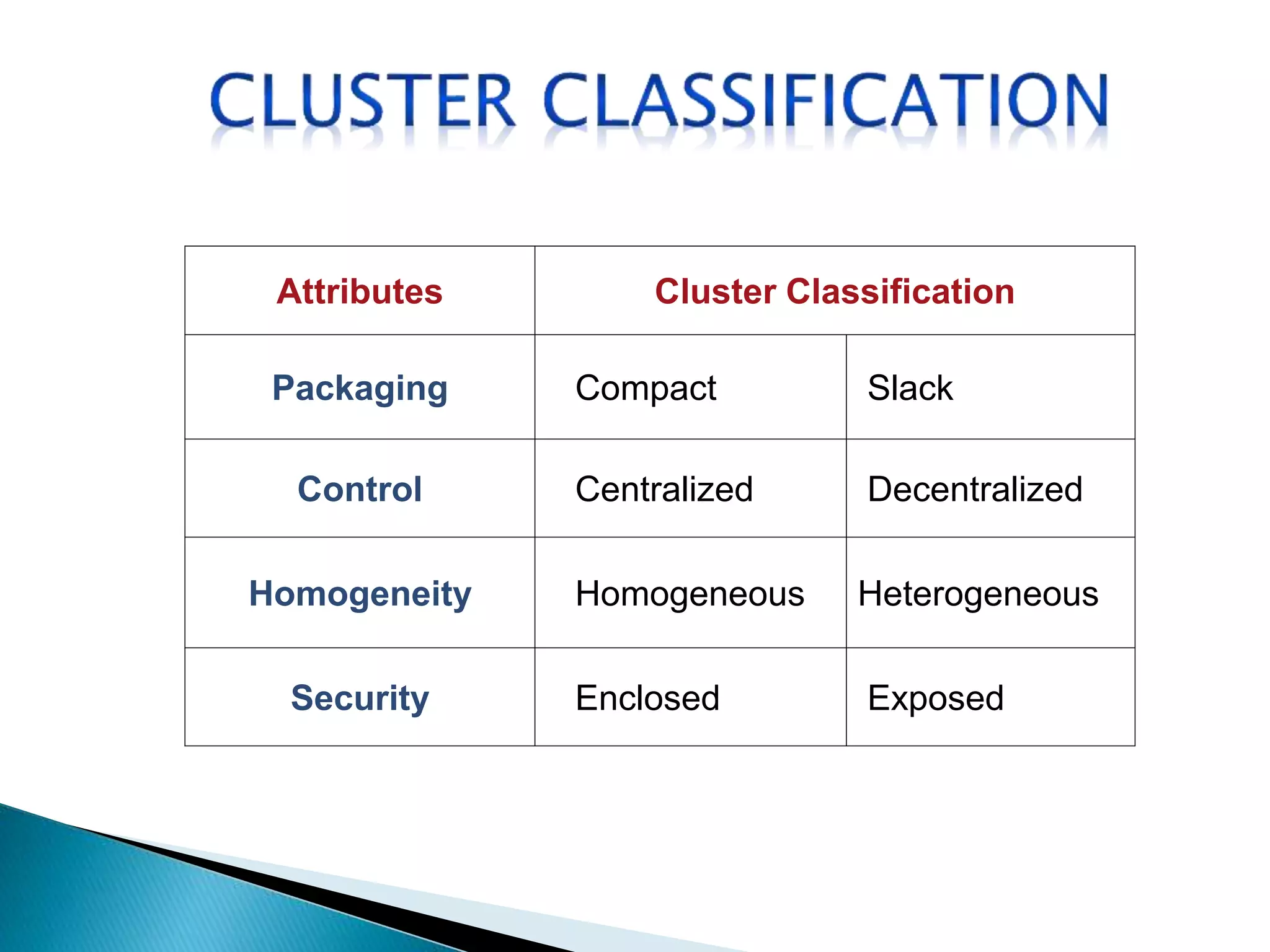
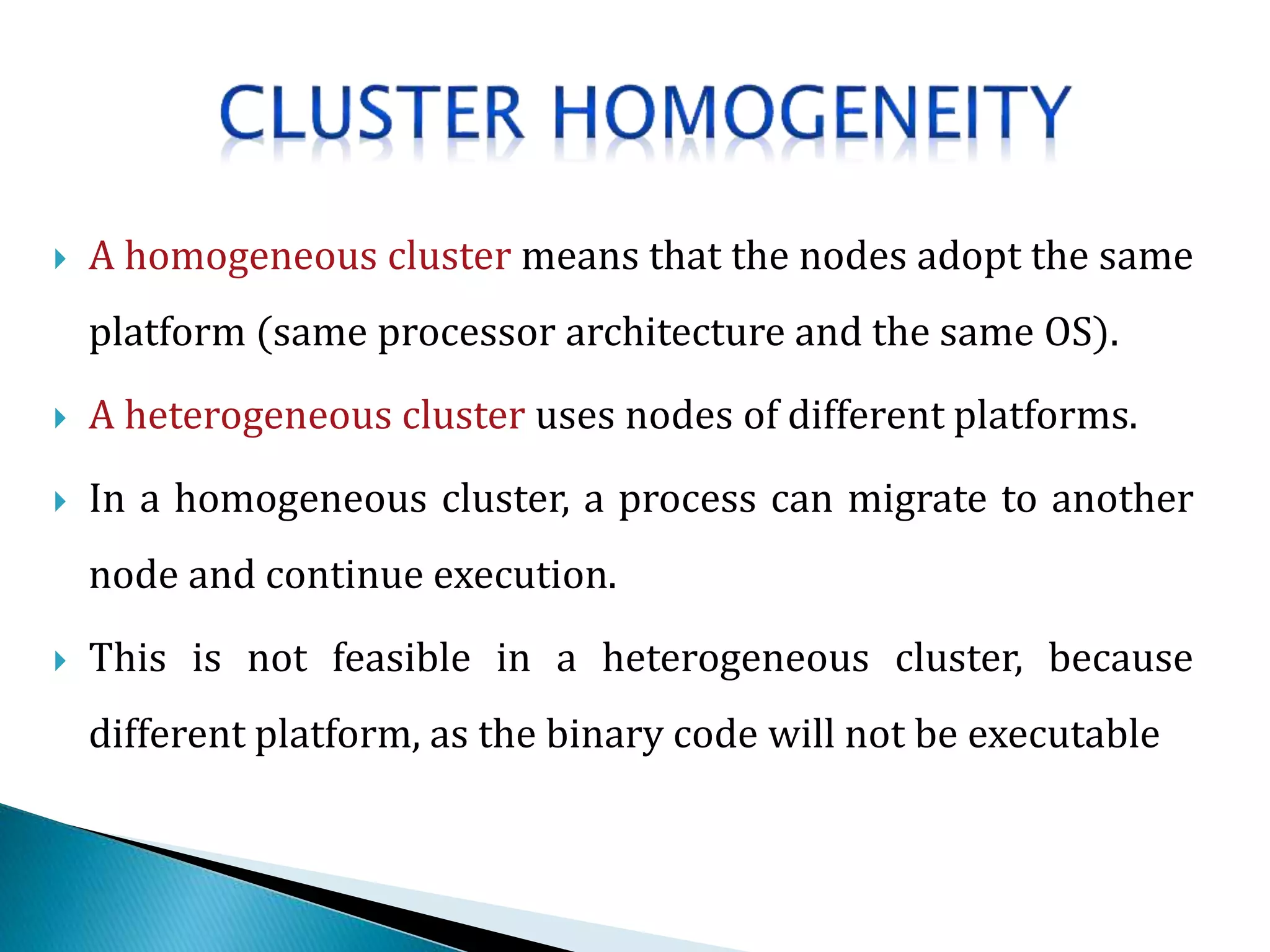
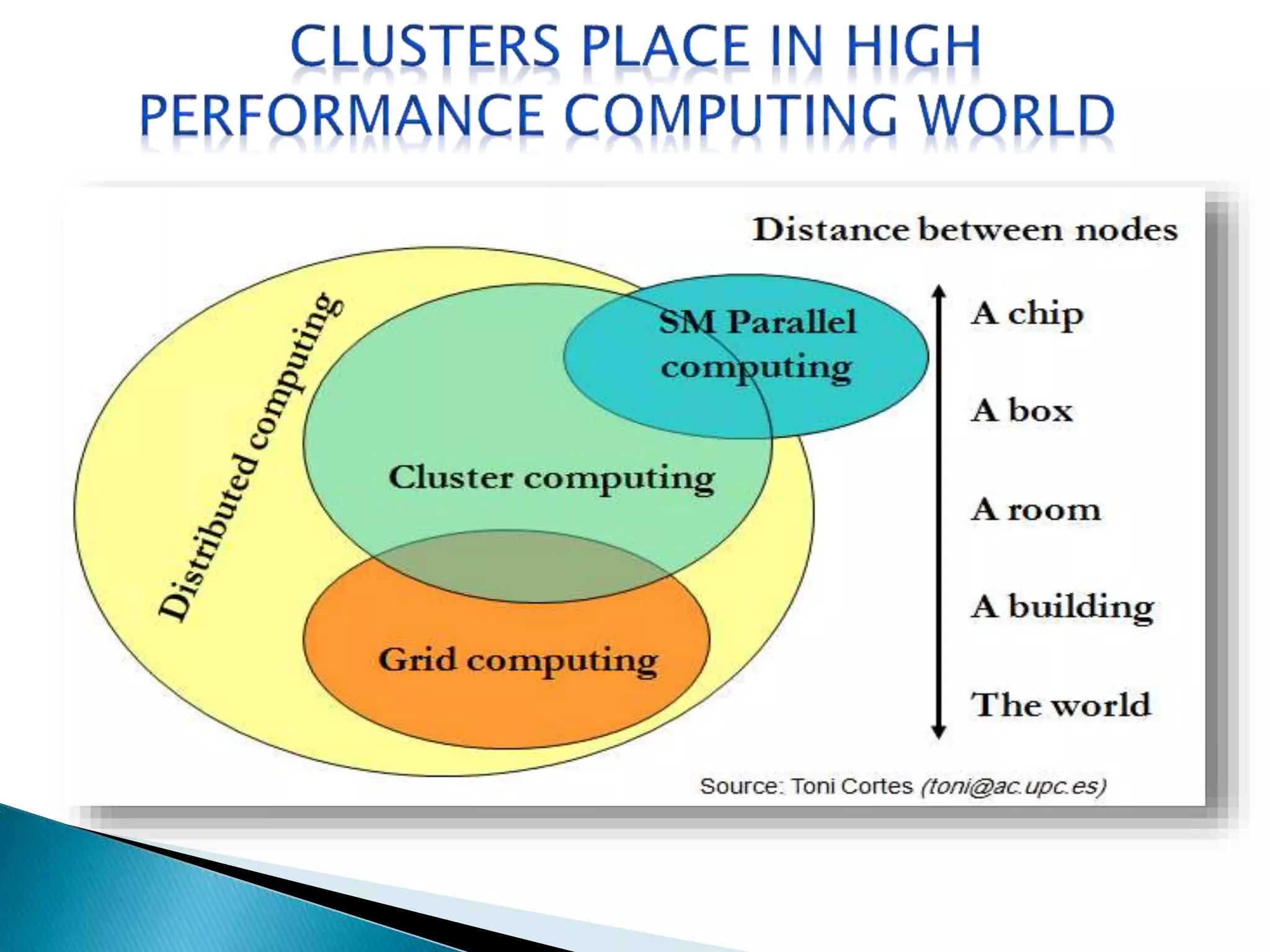
The document provides an overview of cluster computing, discussing its purpose, benefits, and components, including the importance of performance optimization through faster hardware and parallel processing. It highlights the advantages of clusters such as high availability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, while also addressing challenges such as manageability and fault tolerance. The text also covers various cluster types and architectures, including high-performance and load balancing clusters, as well as the technologies required for effective interconnection.