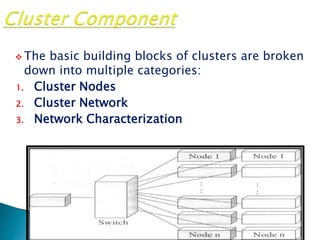
This document provides an overview of cluster computing. It defines a cluster as multiple interconnected computers that function as a single system through software and networking. Clusters are used for high availability and high performance computing applications. The key components of a cluster are the nodes, network, and job scheduler. The document discusses different types of clusters and their applications, benefits like availability and scalability, and some limitations.