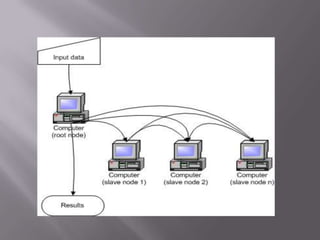
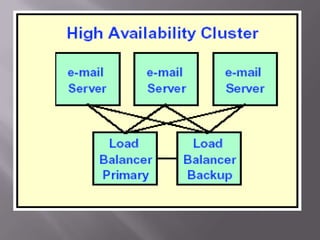
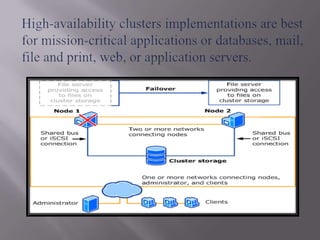
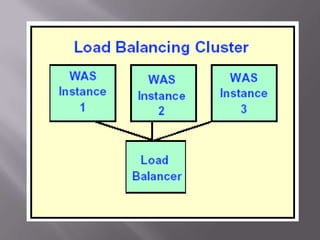
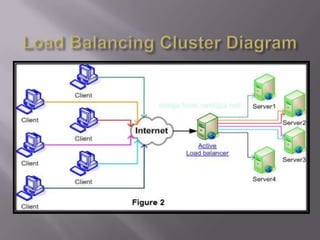
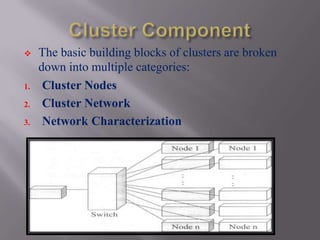
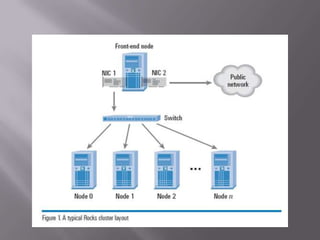
A computer cluster is a group of loosely coupled computers that work together as a single system. Clusters provide improved speed, reliability, and cost effectiveness over single computers. There are three main types of clusters: high availability clusters which provide uninterrupted services if a node fails; load balancing clusters which distribute work across nodes; and parallel processing clusters which solve problems faster through distributed processing. The basic components of clusters are nodes, networks, and applications. Clusters provide benefits like high availability, improved performance, and scalability.