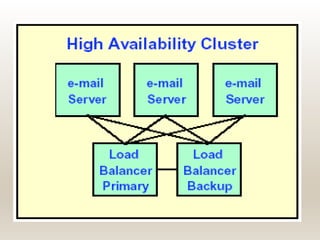
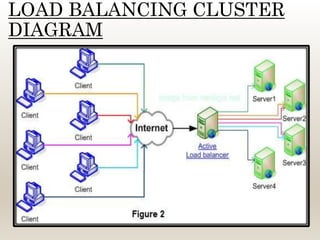
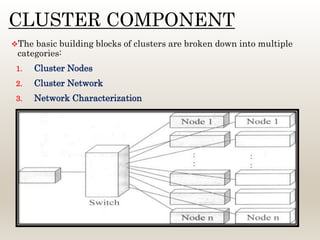
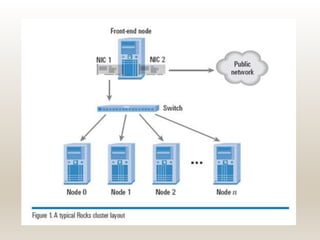
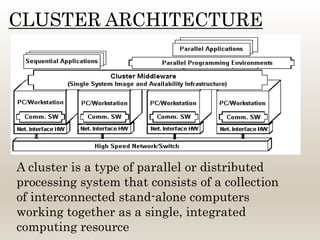
This document summarizes a technical seminar on cluster computing. It defines a cluster as a group of interconnected computers that work together as a single system. It describes three main types of clusters: high-availability clusters for reliability, load balancing clusters for distributing messages, and high-performance clusters for parallel processing. The key components of a cluster are nodes, a network, and network characterization. Clusters provide benefits like high availability, performance, and scalability through features such as various network technologies, communication protocols, and a single system image. Common cluster applications include compute-intensive, data-intensive, and transaction-intensive workloads.