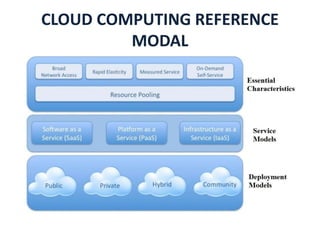
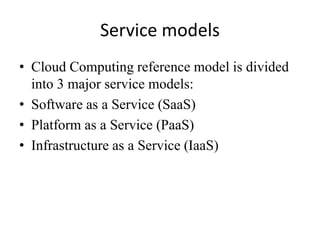
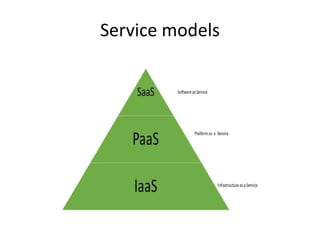
The document outlines the cloud computing reference model, which is divided into five logical layers and three service models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). It also describes four deployment models (public, private, community, and hybrid) and essential characteristics of cloud computing including on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. These concepts aim to standardize and clarify the functions and operations within a cloud environment.