Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times


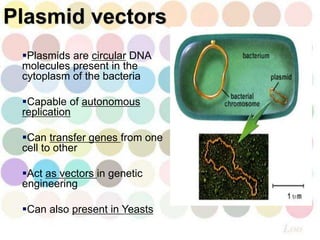


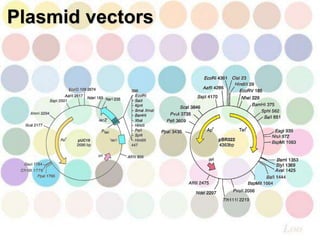

Plasmid vectors are circular, self-replicating DNA molecules found in bacteria cytoplasm that can transfer genes between cells. They are useful for cloning small DNA fragments under 10kb due to their small size and selection strategies. However, plasmids are less useful for cloning large fragments over 10kb. Plasmid vectors for cloning contain an origin of replication for independent replication, selective markers for identifying cells containing the plasmid, and a multiple cloning site to insert DNA fragments.






