The document summarizes the design of the Himurja Office Building in Shimla, India. Some key points:
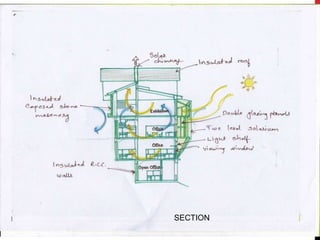
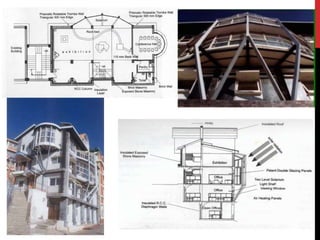
1) The building was designed by architect Arvind Krishan to be energy efficient using passive solar techniques suitable for Shimla's cold climate, including air heating panels, insulation, and a connective loop staircase to distribute heat.
2) Sustainability was a focus, utilizing materials like recycled steel, solar panels, and maximizing natural light through oversized windows.
3) The design achieved energy efficiency through features like double glazing, minimal northern fenestration, insulation, and a solar water heating system.
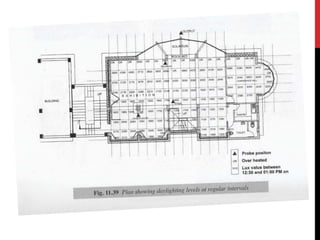
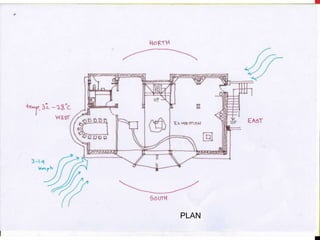
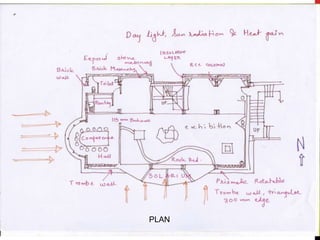
4) Plans and sections show the layout including solariums