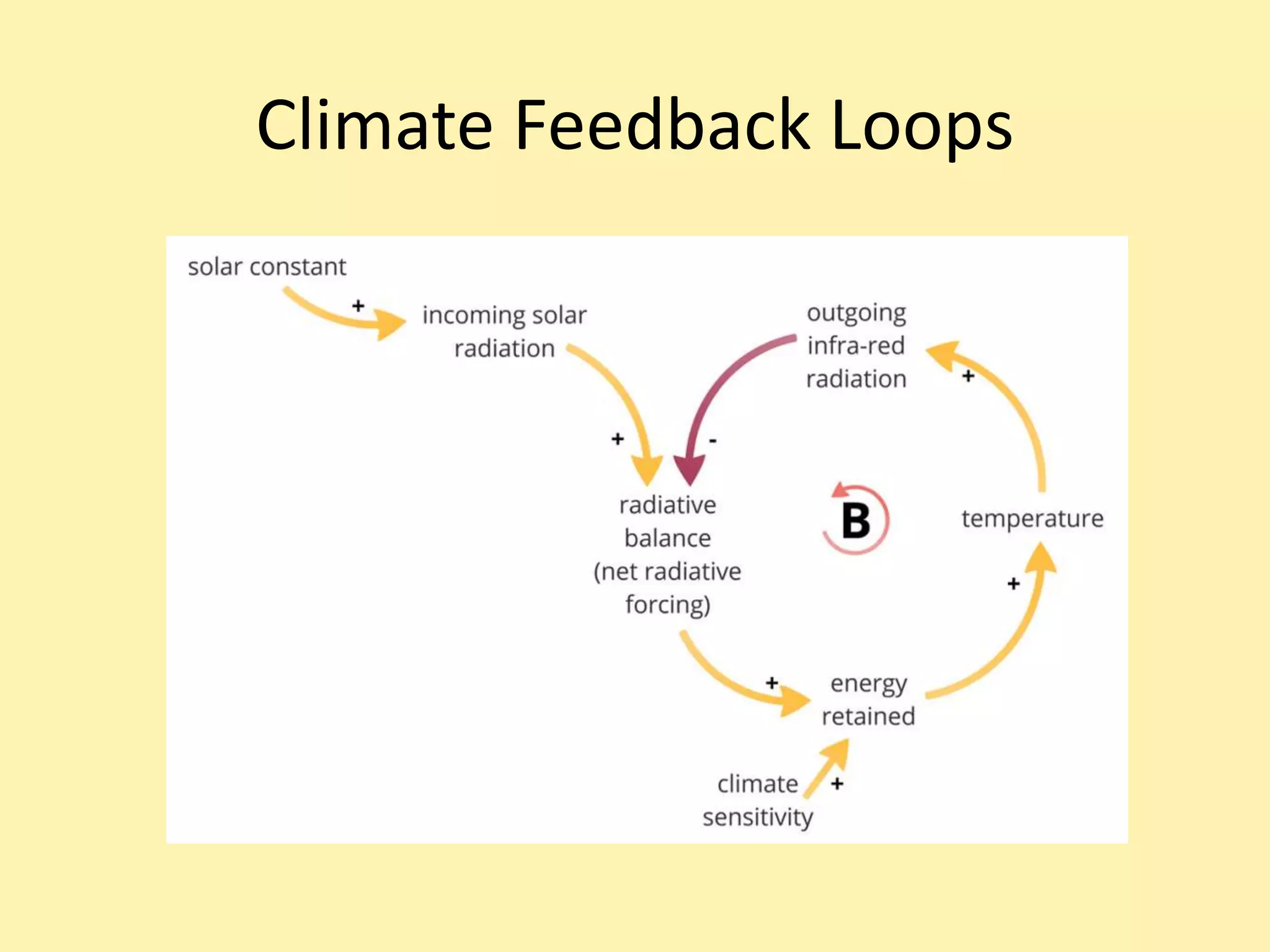
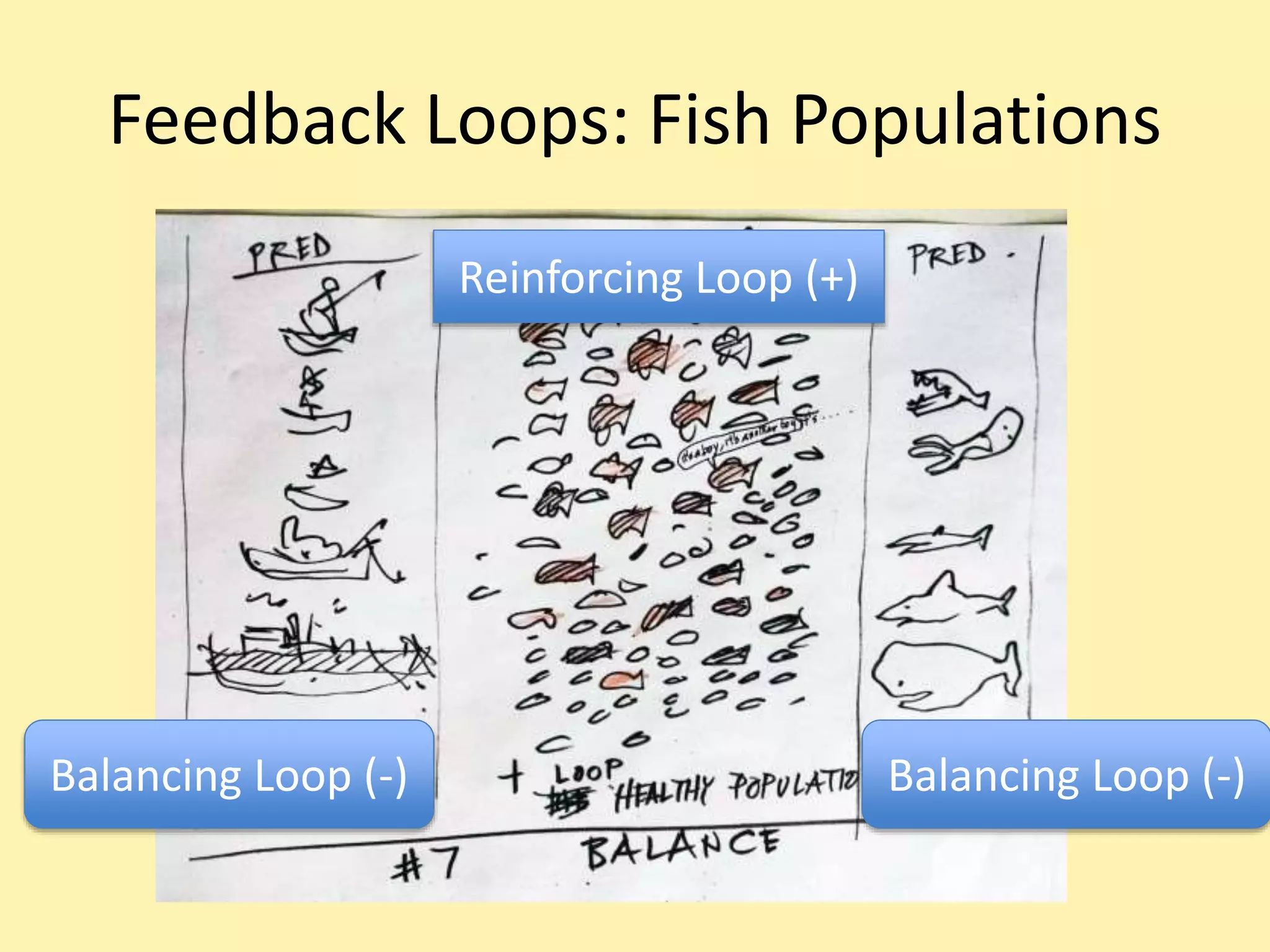
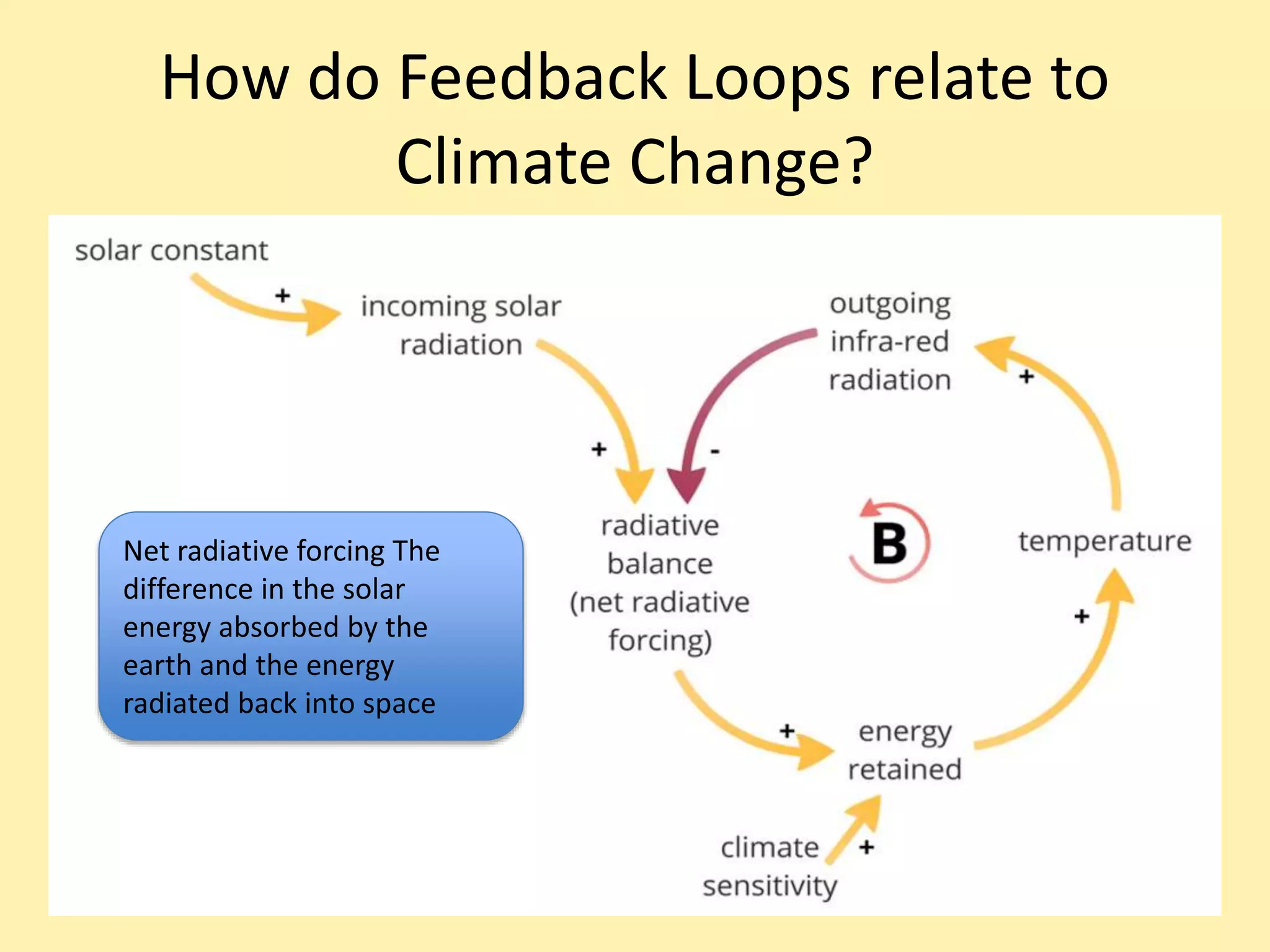
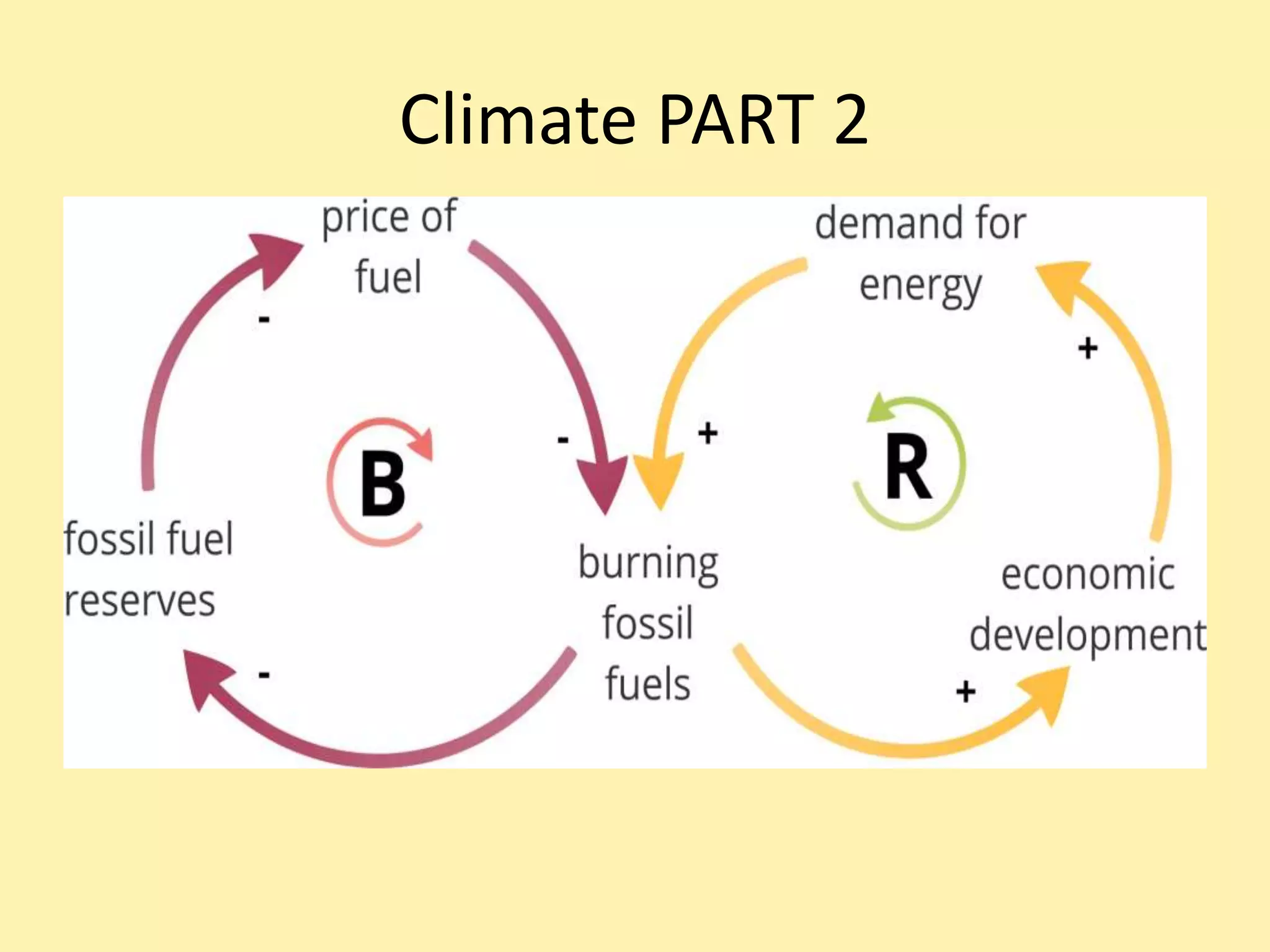
Climate systems form feedback loops that can either be reinforcing or balancing. Reinforcing loops amplify changes and move a system away from equilibrium, while balancing loops dampen changes and maintain stability. When net radiative forcing is increased through activities like burning fossil fuels, balancing loops act to restore equilibrium over decades by warming the oceans. However, if radiative forcing continues to change due to factors like increasing greenhouse gases, temperature will also continue to change rather than reaching a new stable point. While aerosols from burning fossil fuels cause some cooling by blocking sunlight, greenhouse gases are the dominant factor currently increasing radiative forcing and global temperatures.