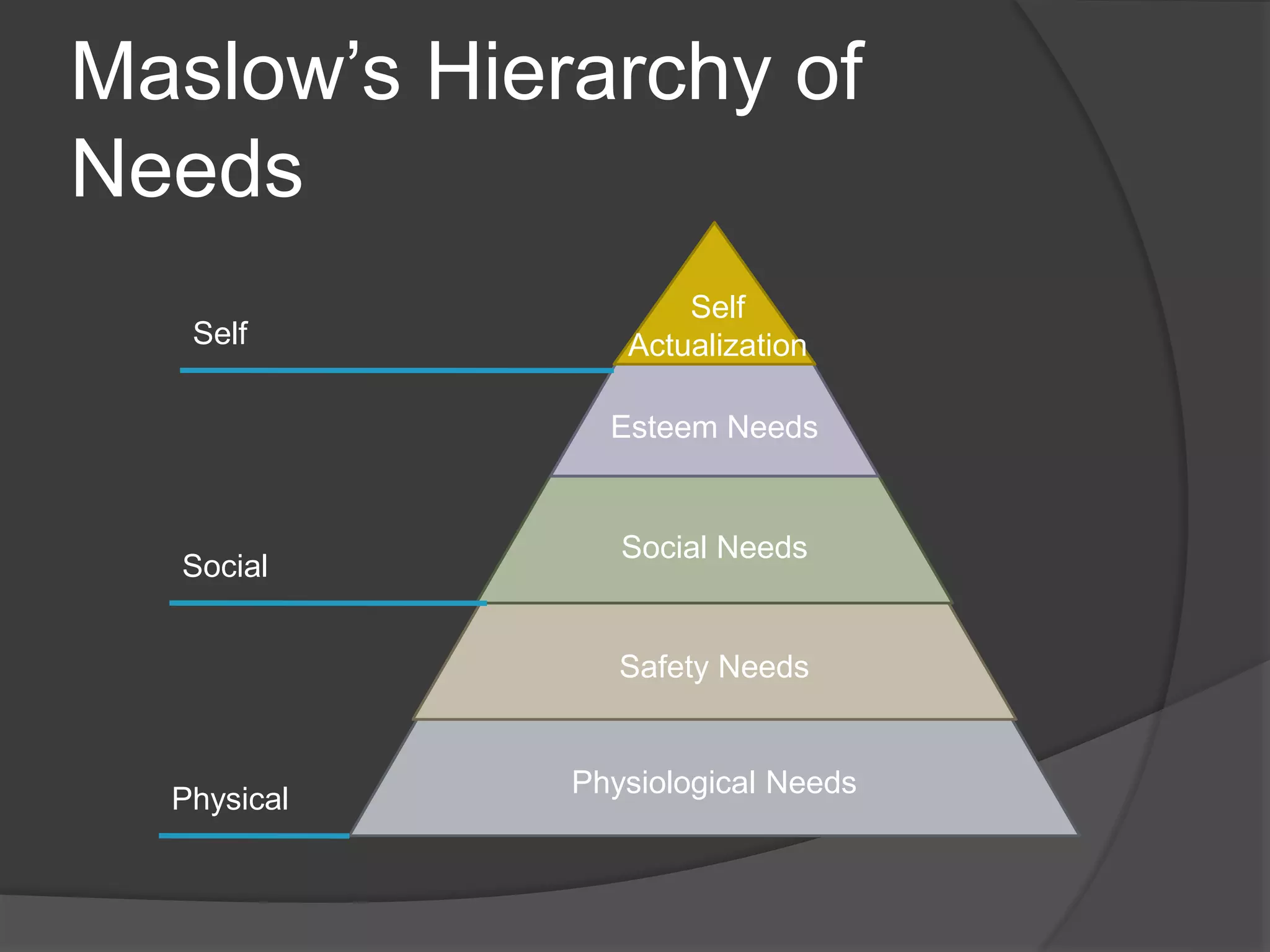
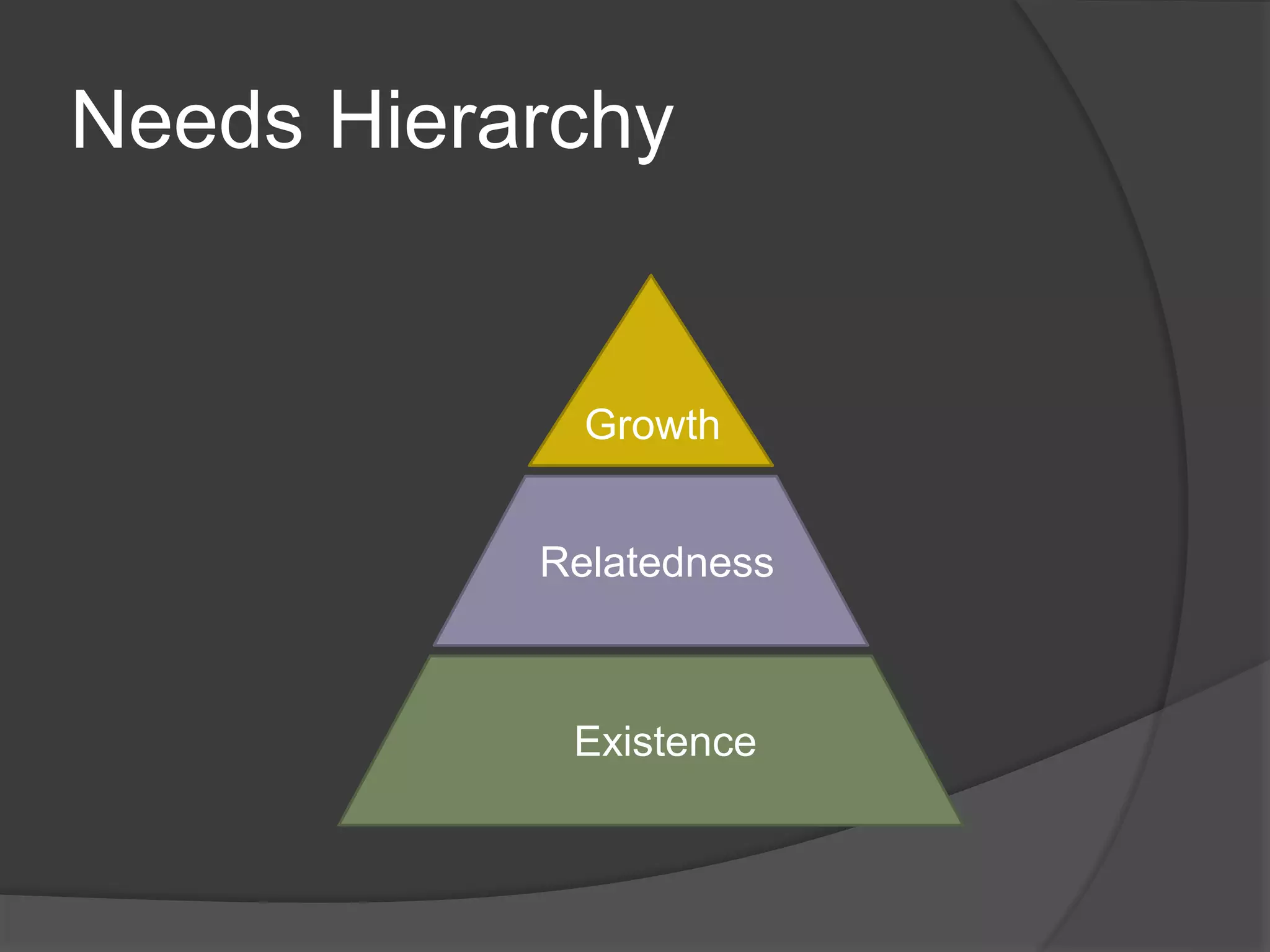
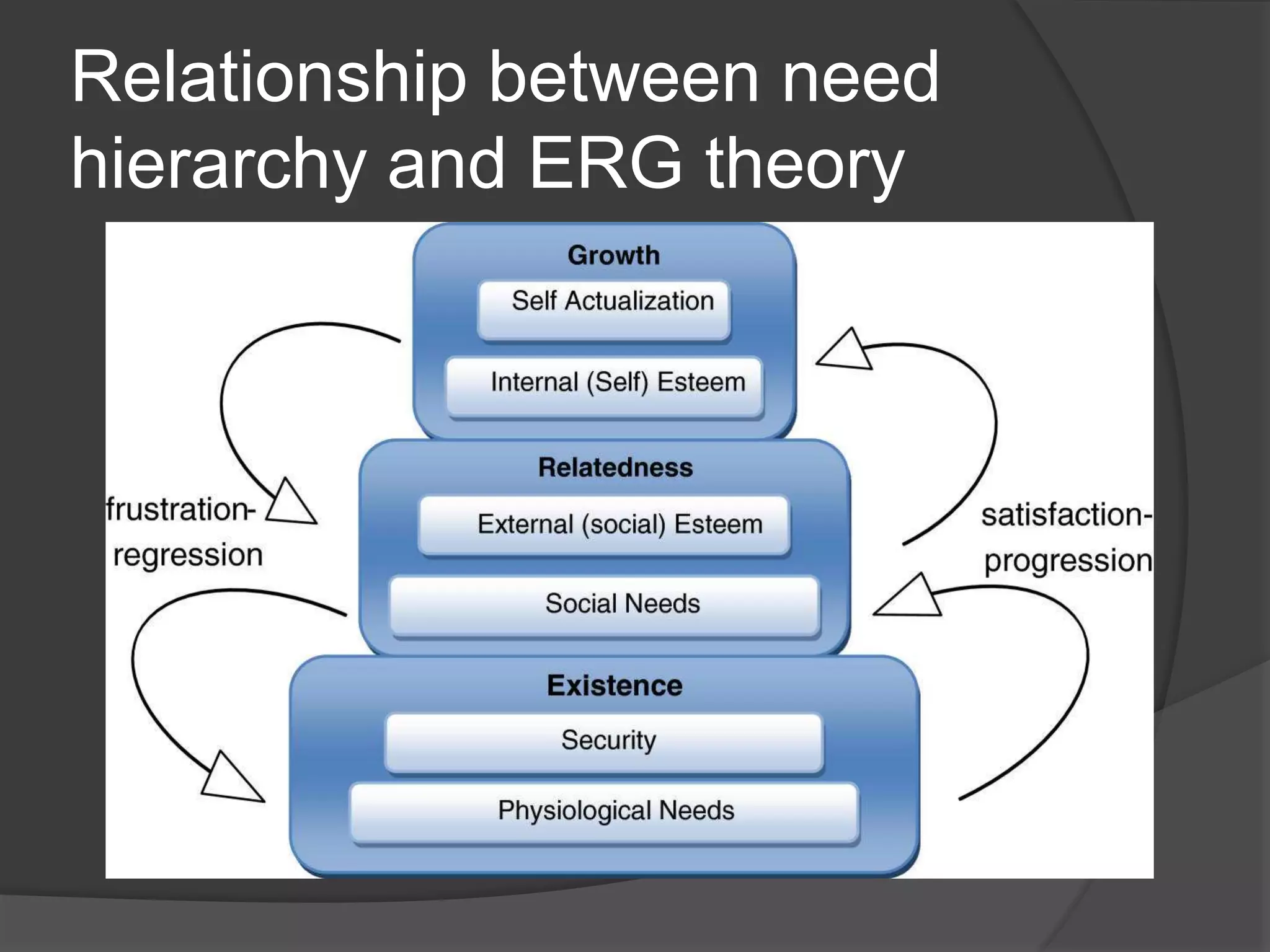
Clayton Paul Alderfer developed the ERG theory as an extension of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs. The ERG theory categorizes human motivation into three core needs - Existence, Relatedness, and Growth. These needs do not necessarily follow a strict hierarchy but their importance can change based on circumstances. Alderfer grouped physiological, safety, and security needs into "Existence needs," social and external esteem needs into "Relatedness needs," and internal esteem and self-actualization needs into "Growth needs."