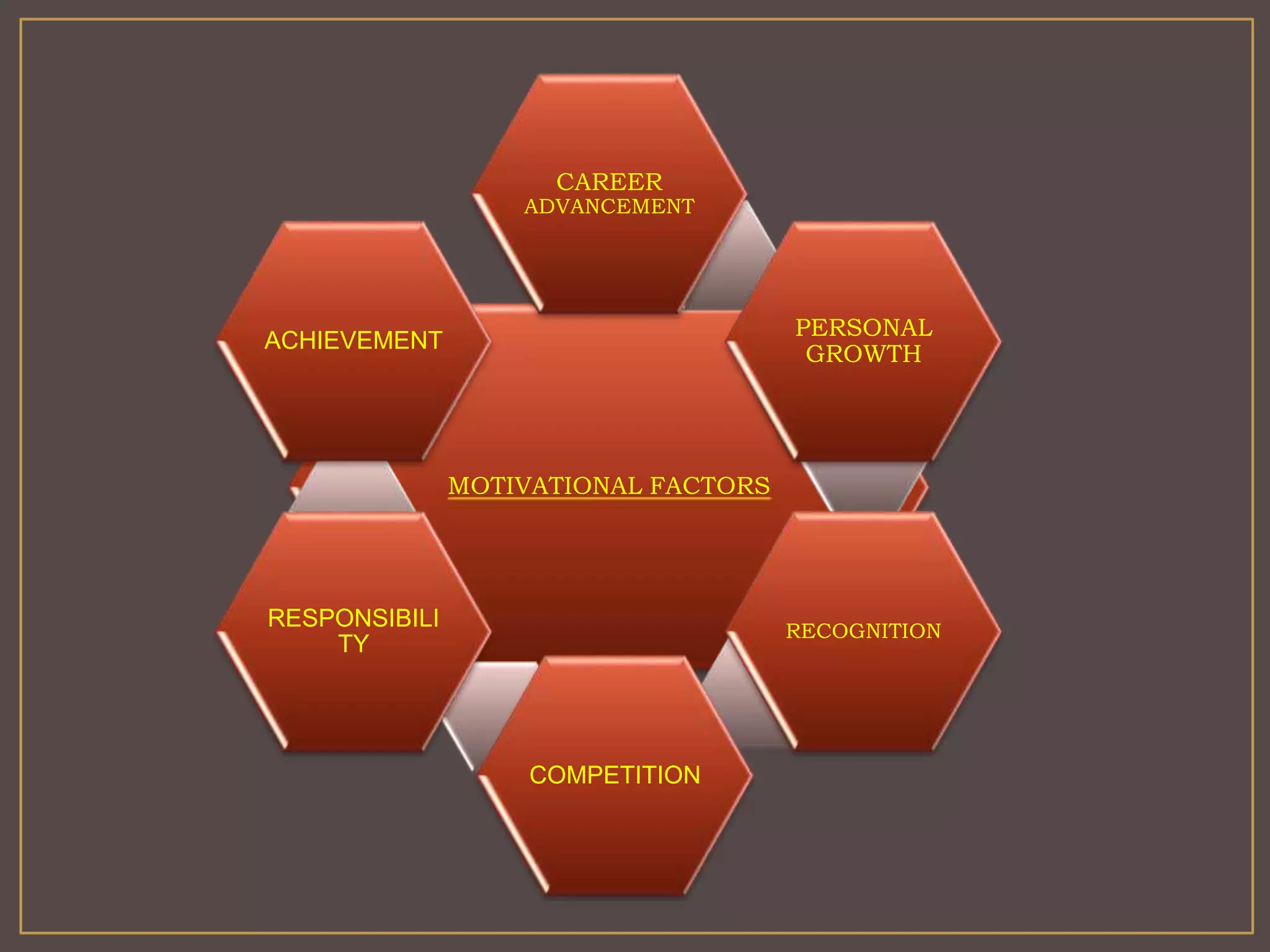
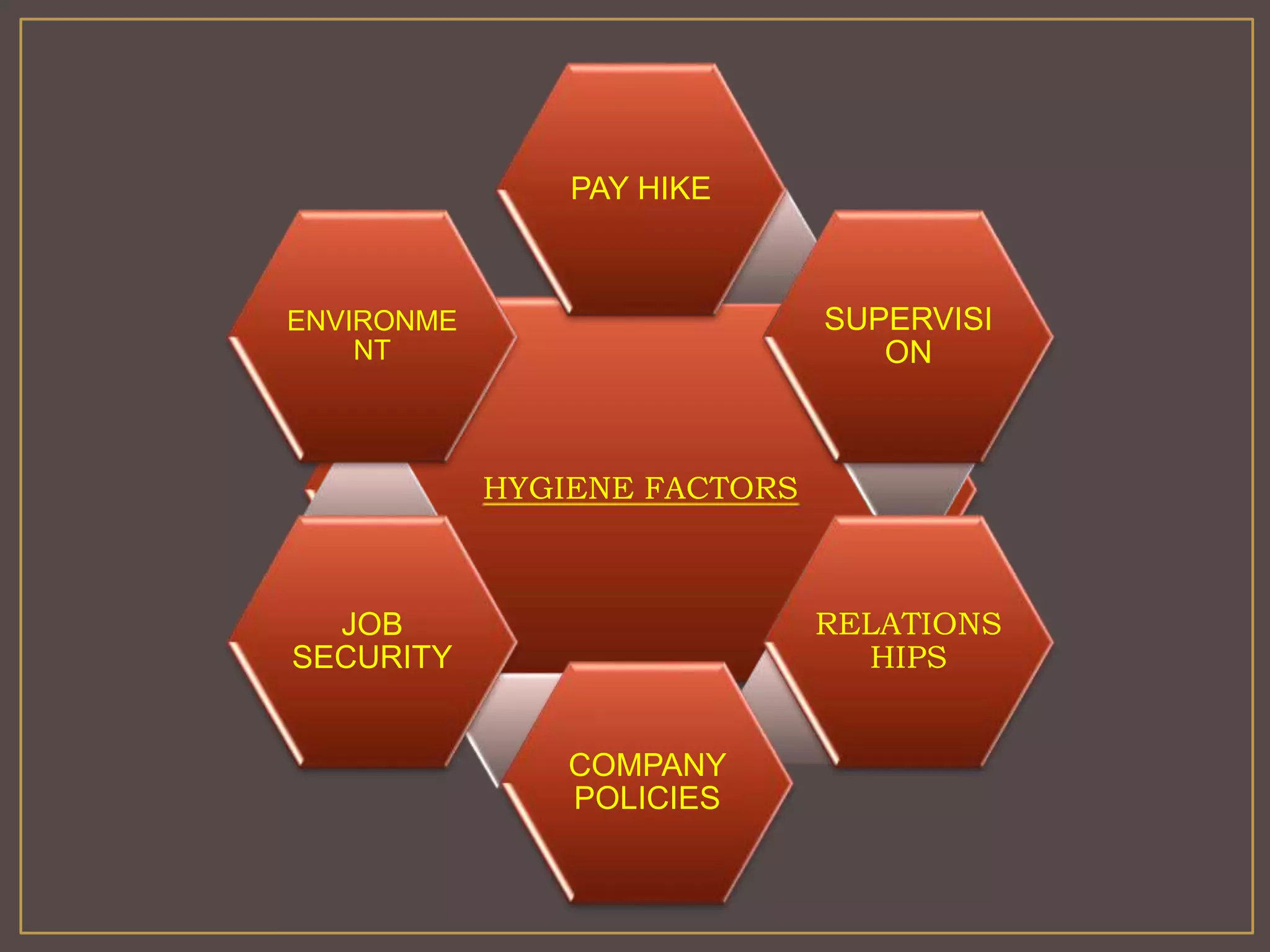
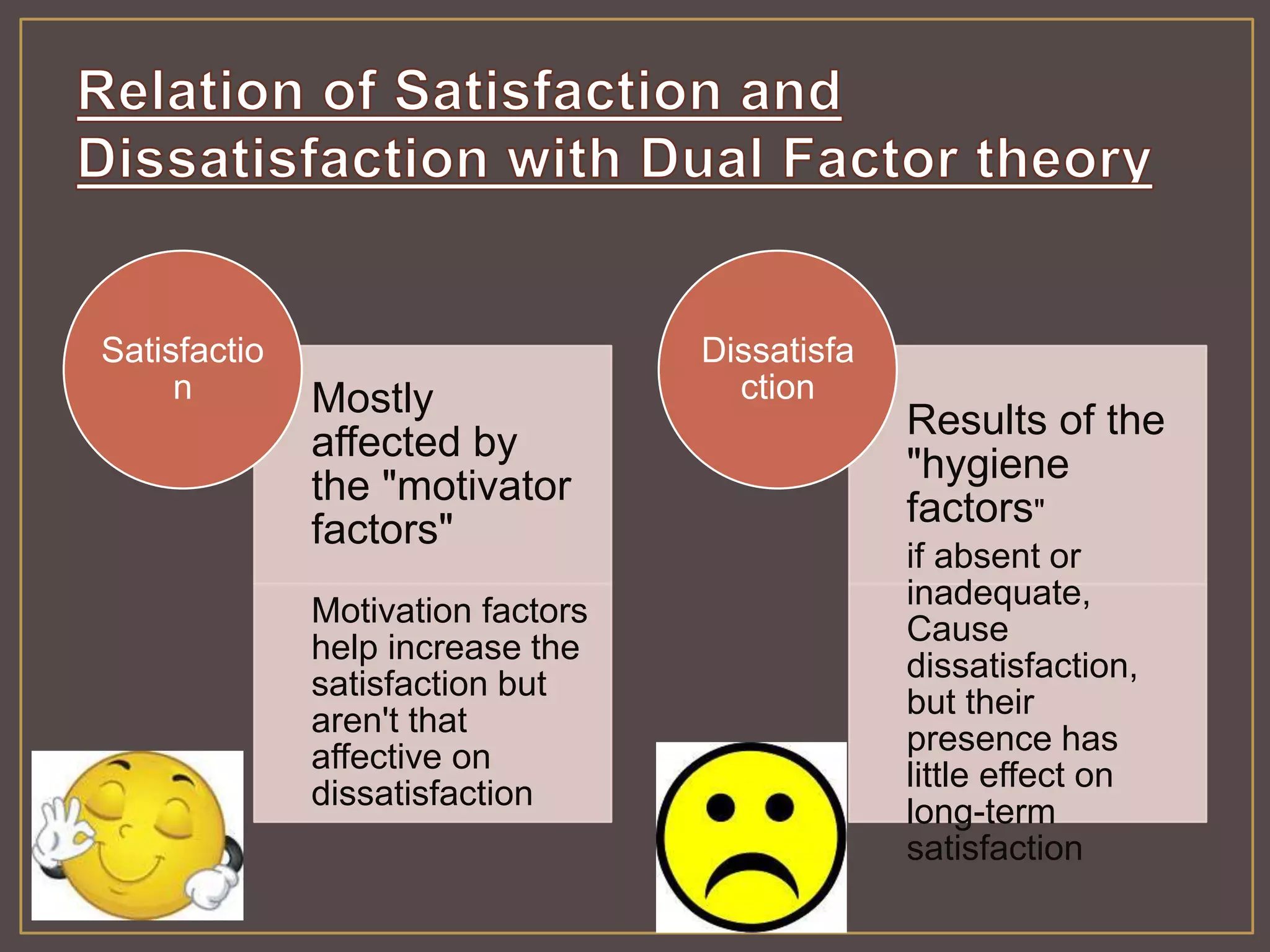
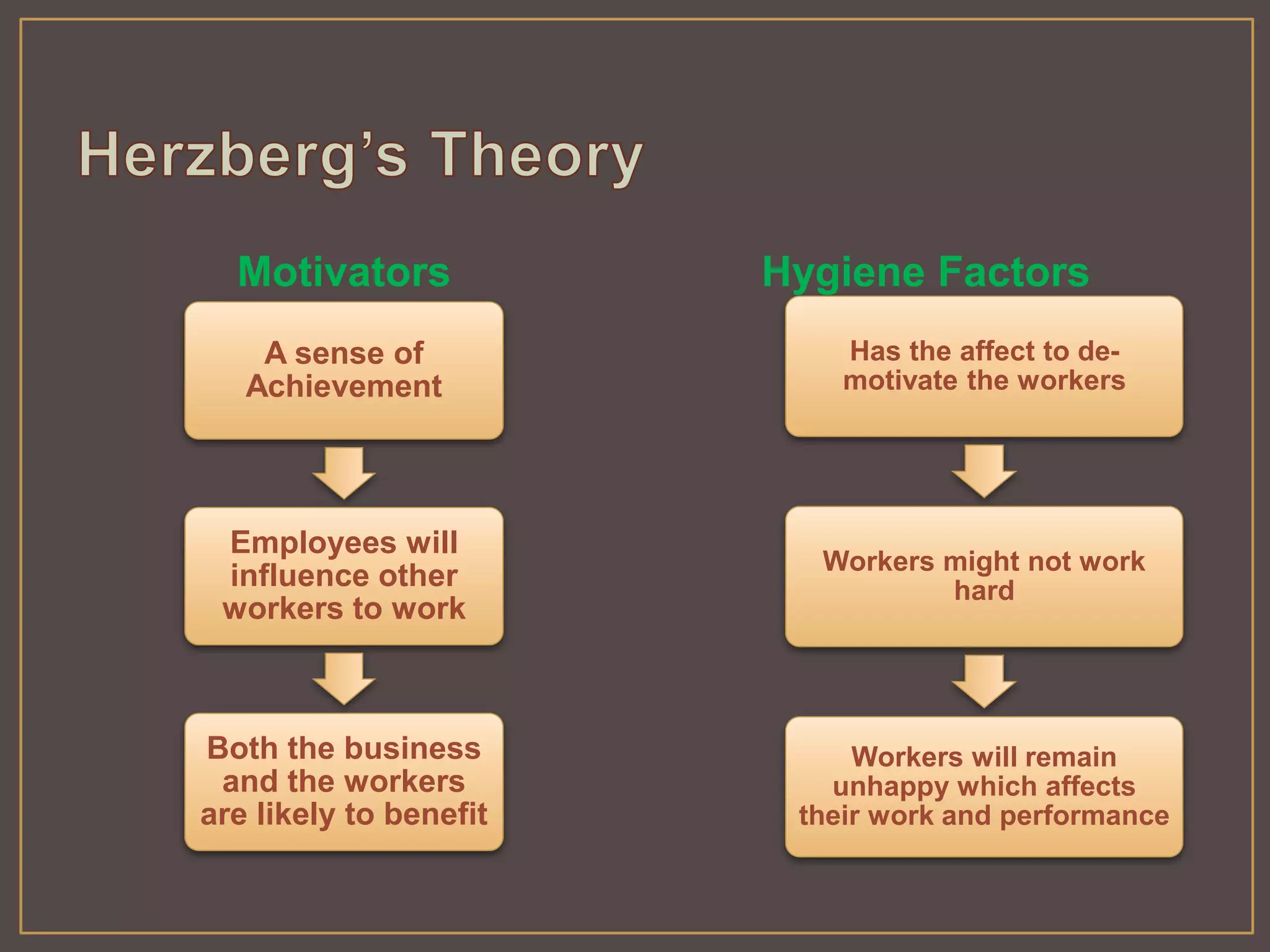
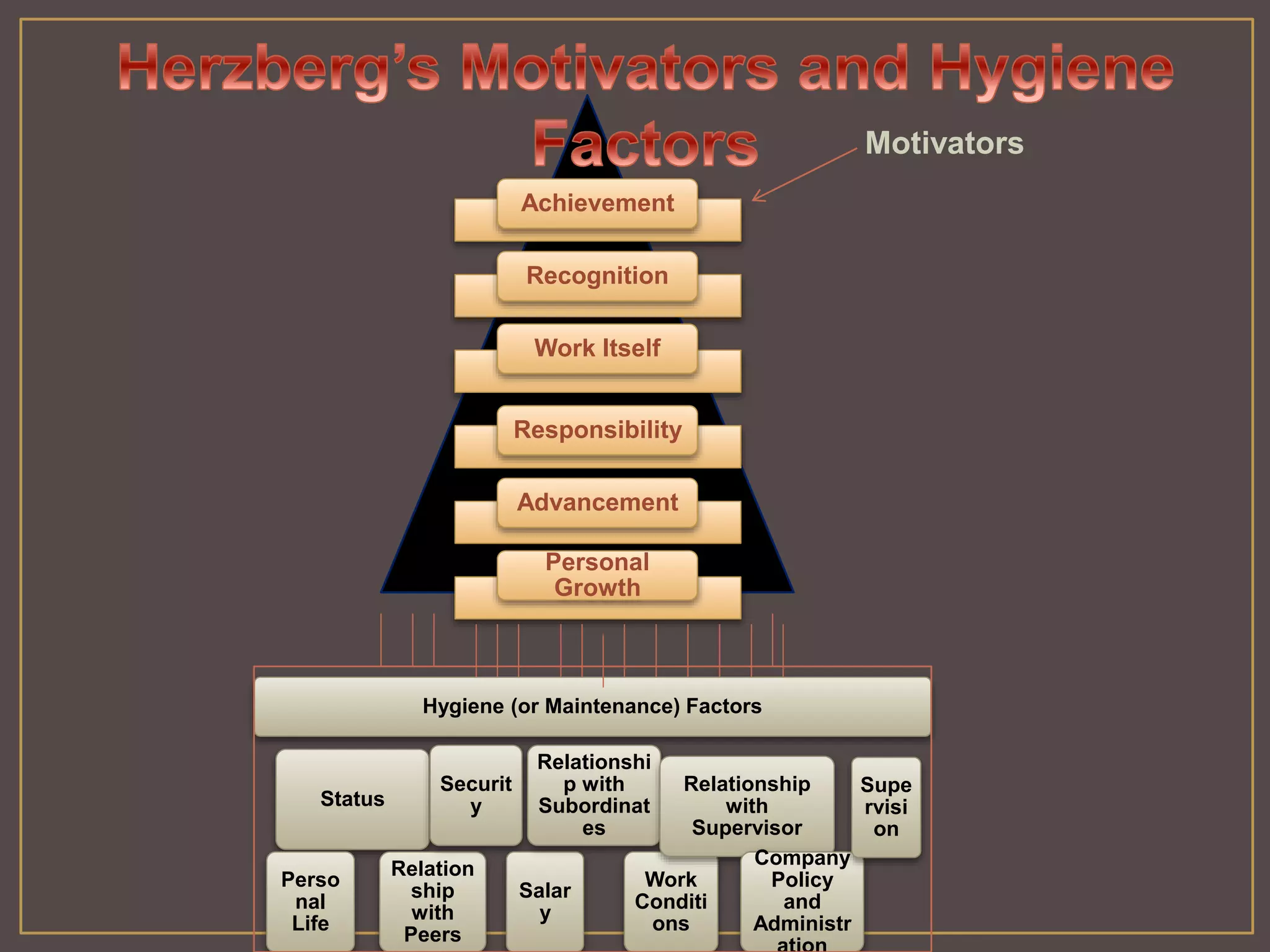
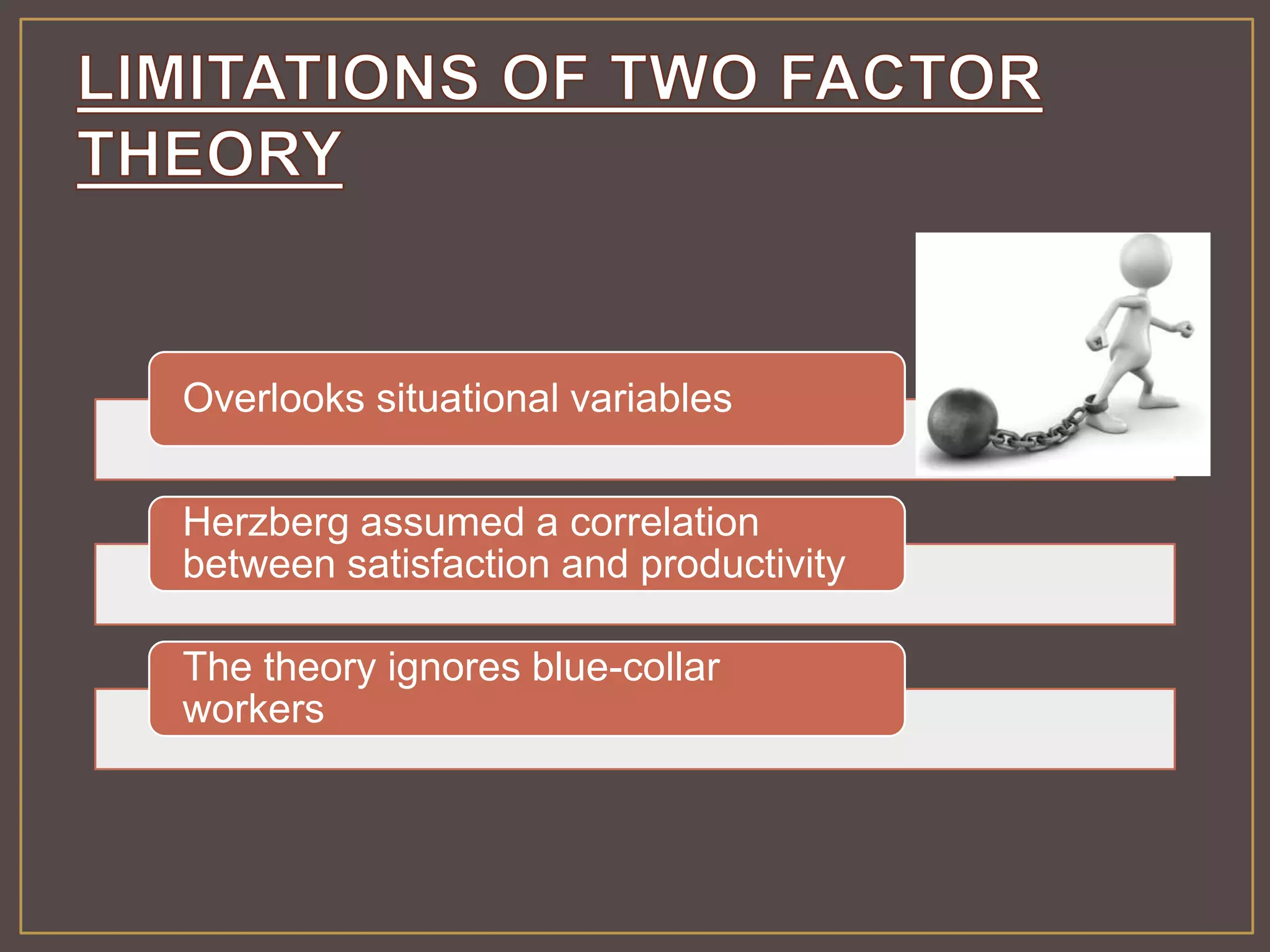
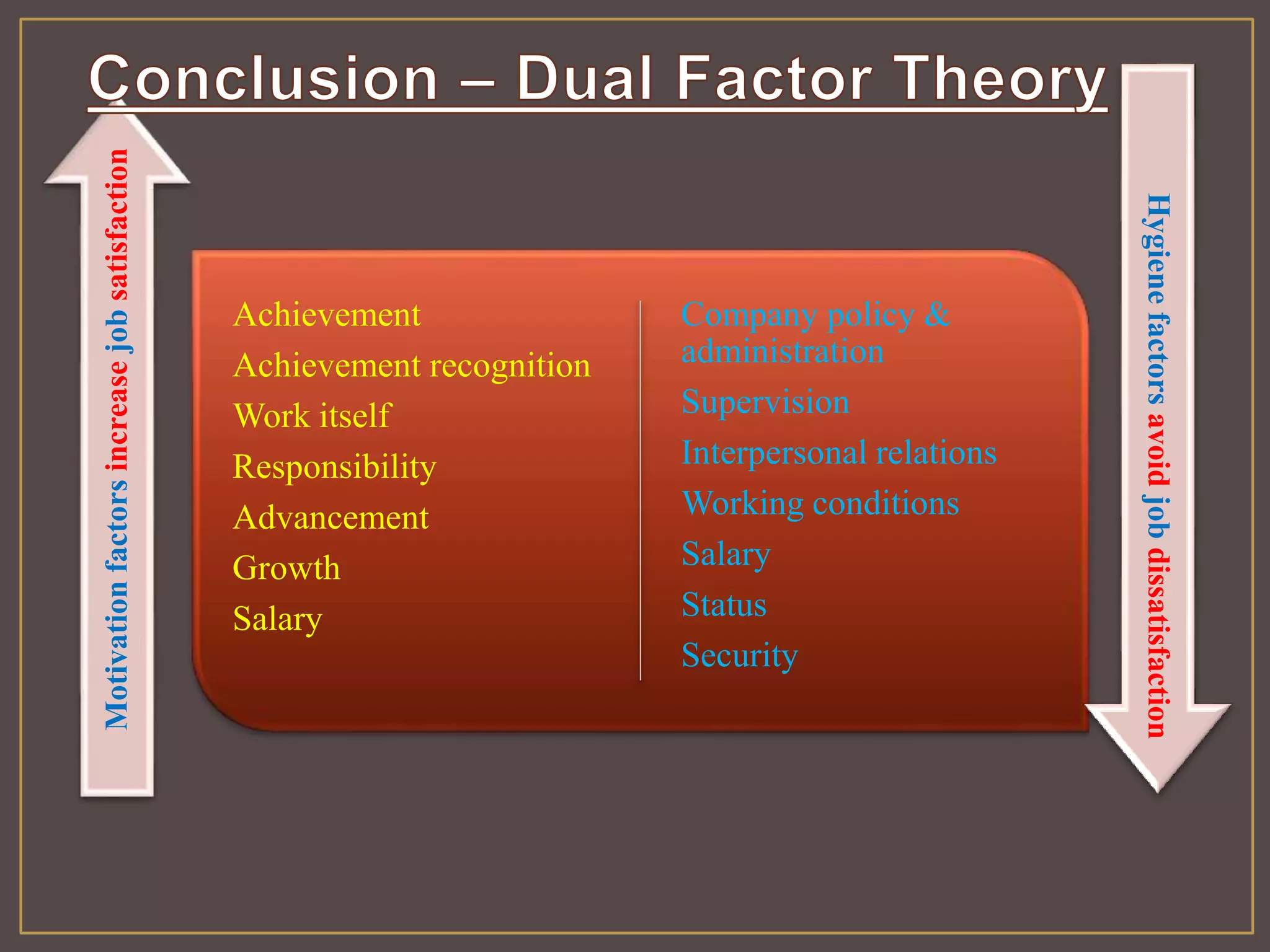
The document outlines Herzberg's two-factor theory of motivation, which distinguishes between motivational factors and hygiene factors. Motivational factors like achievement, recognition, responsibility, and advancement can increase job satisfaction, while hygiene factors like company policies, supervision, and salary must be adequate to prevent dissatisfaction. The theory implies managers should focus on both guaranteeing strong hygiene factors and stimulating employees through motivational factors in the work itself.