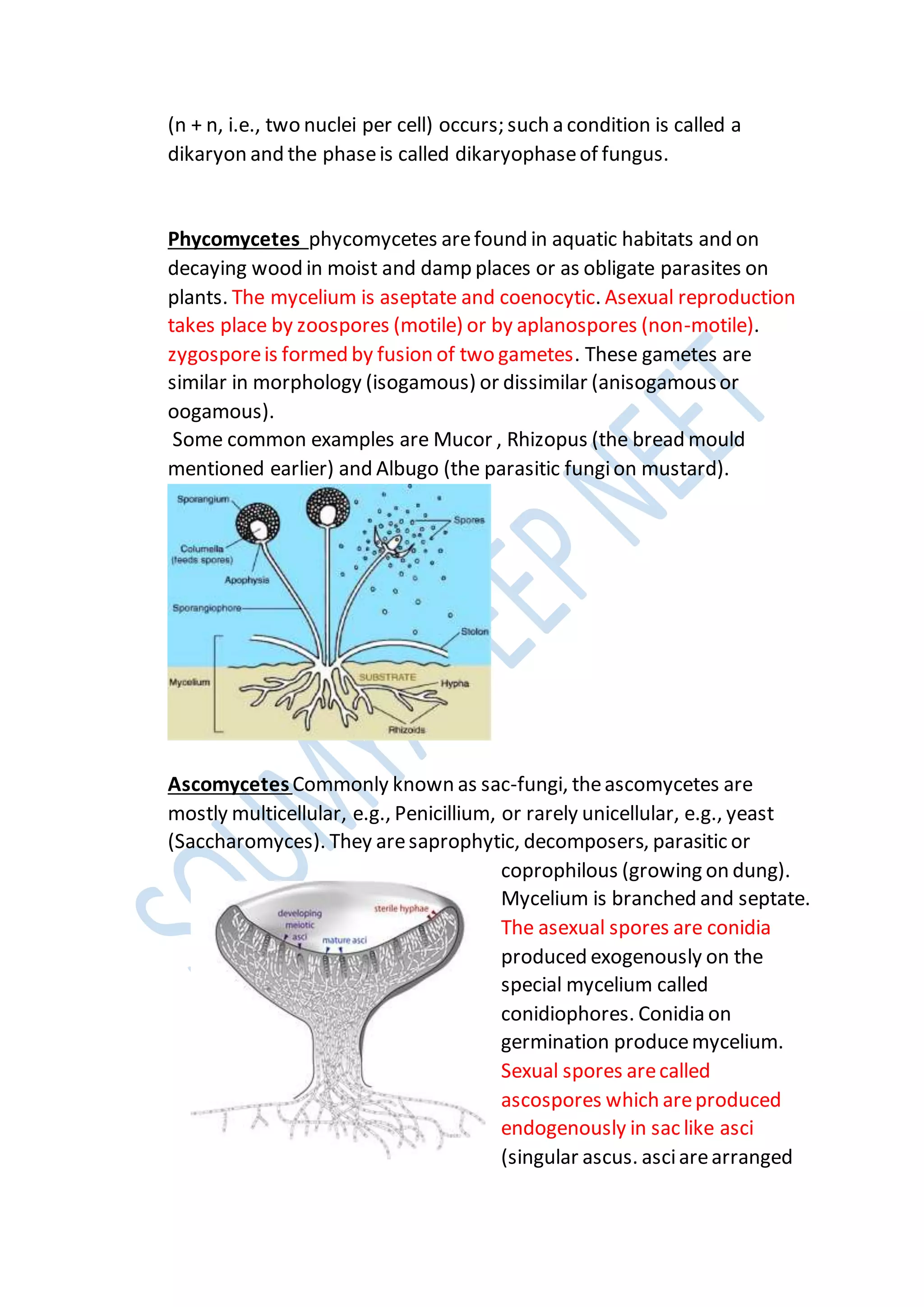
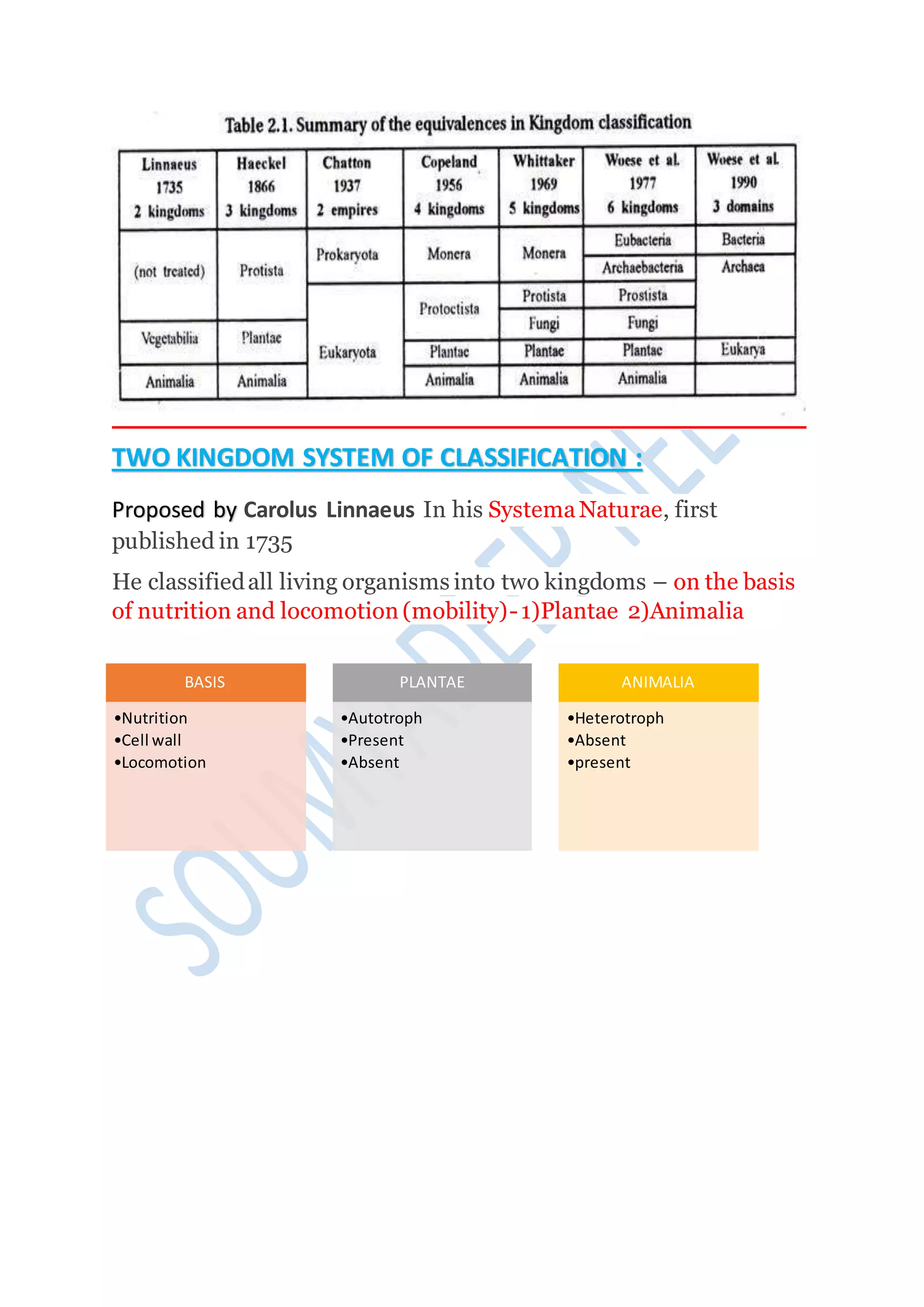
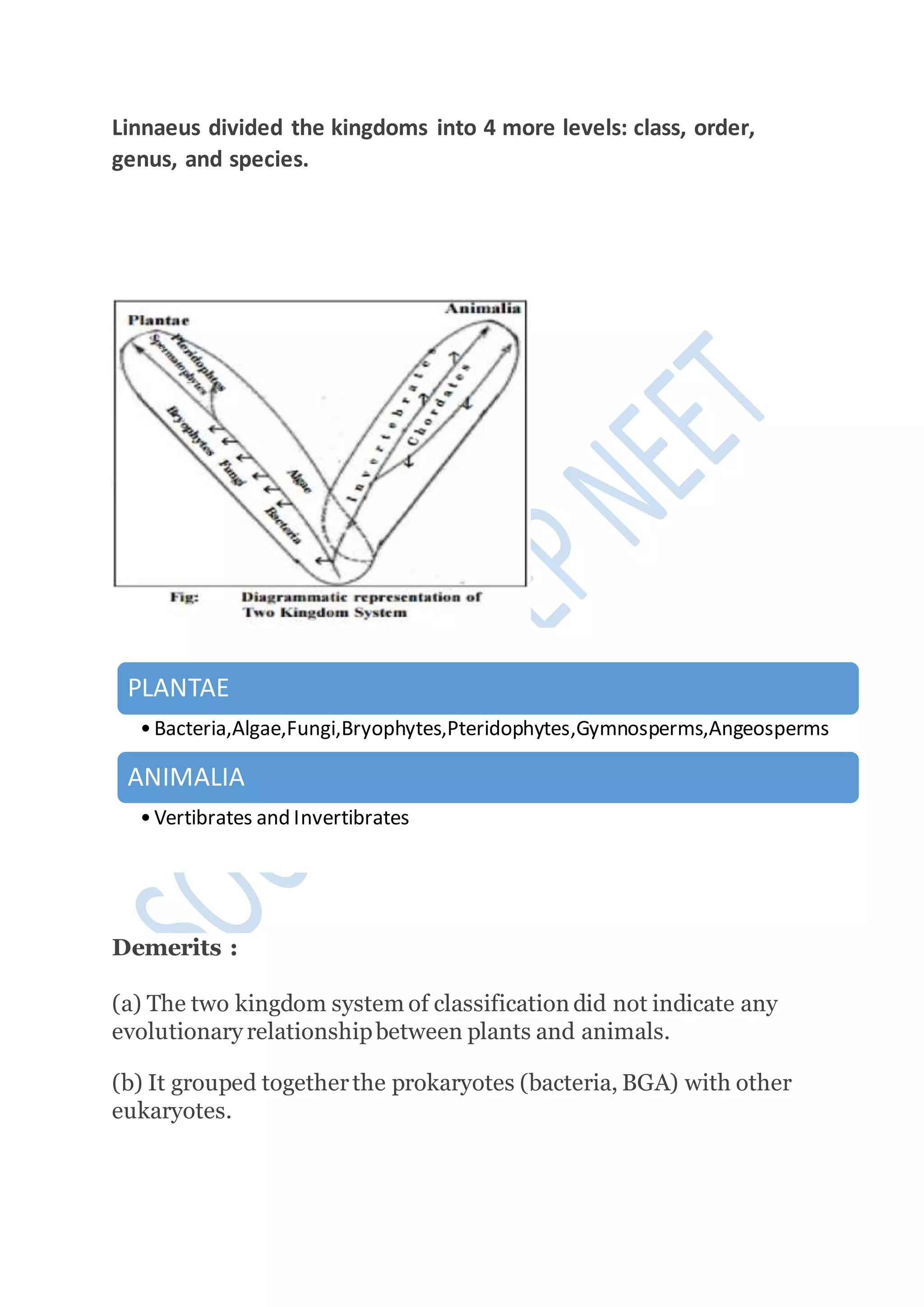
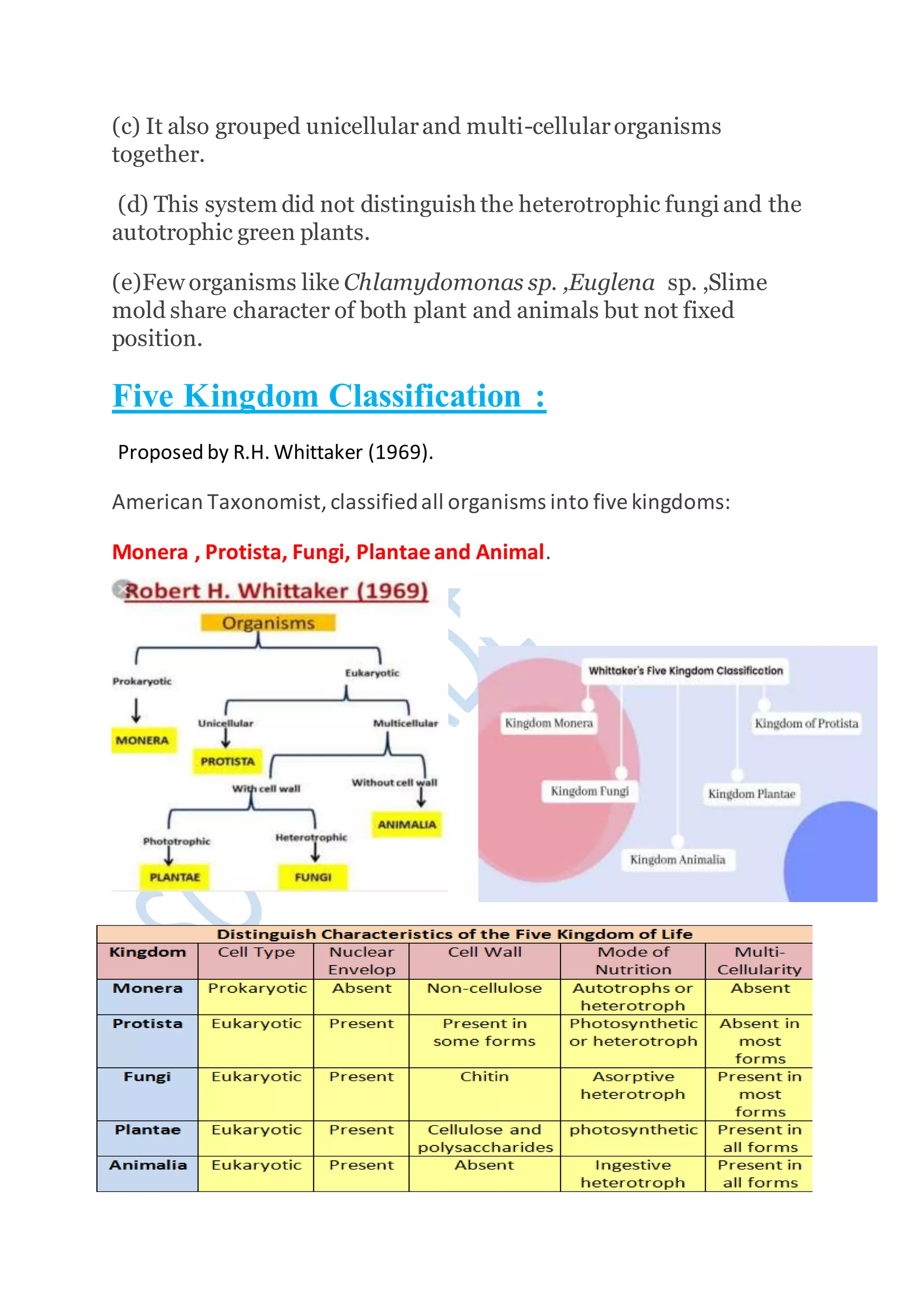
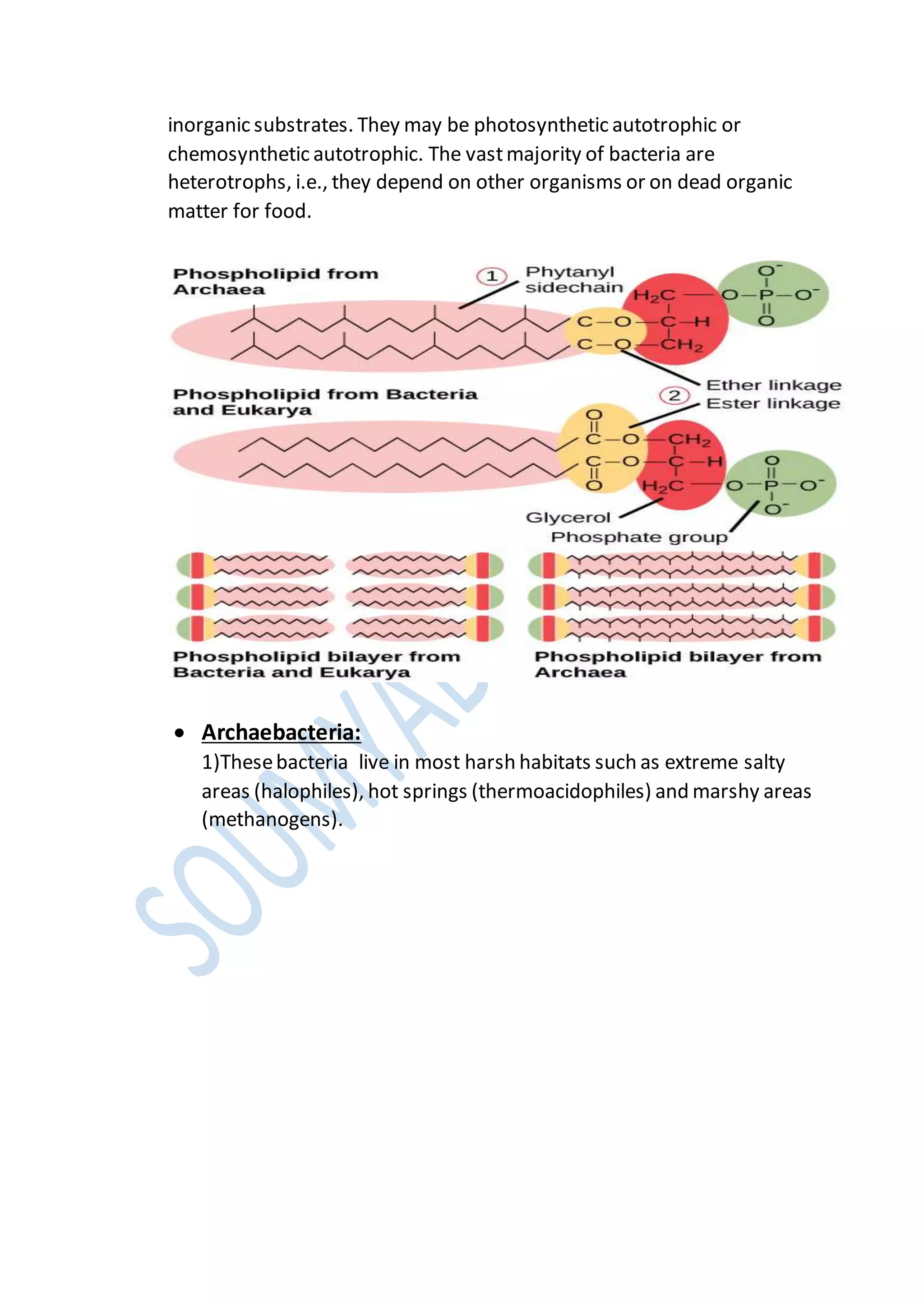
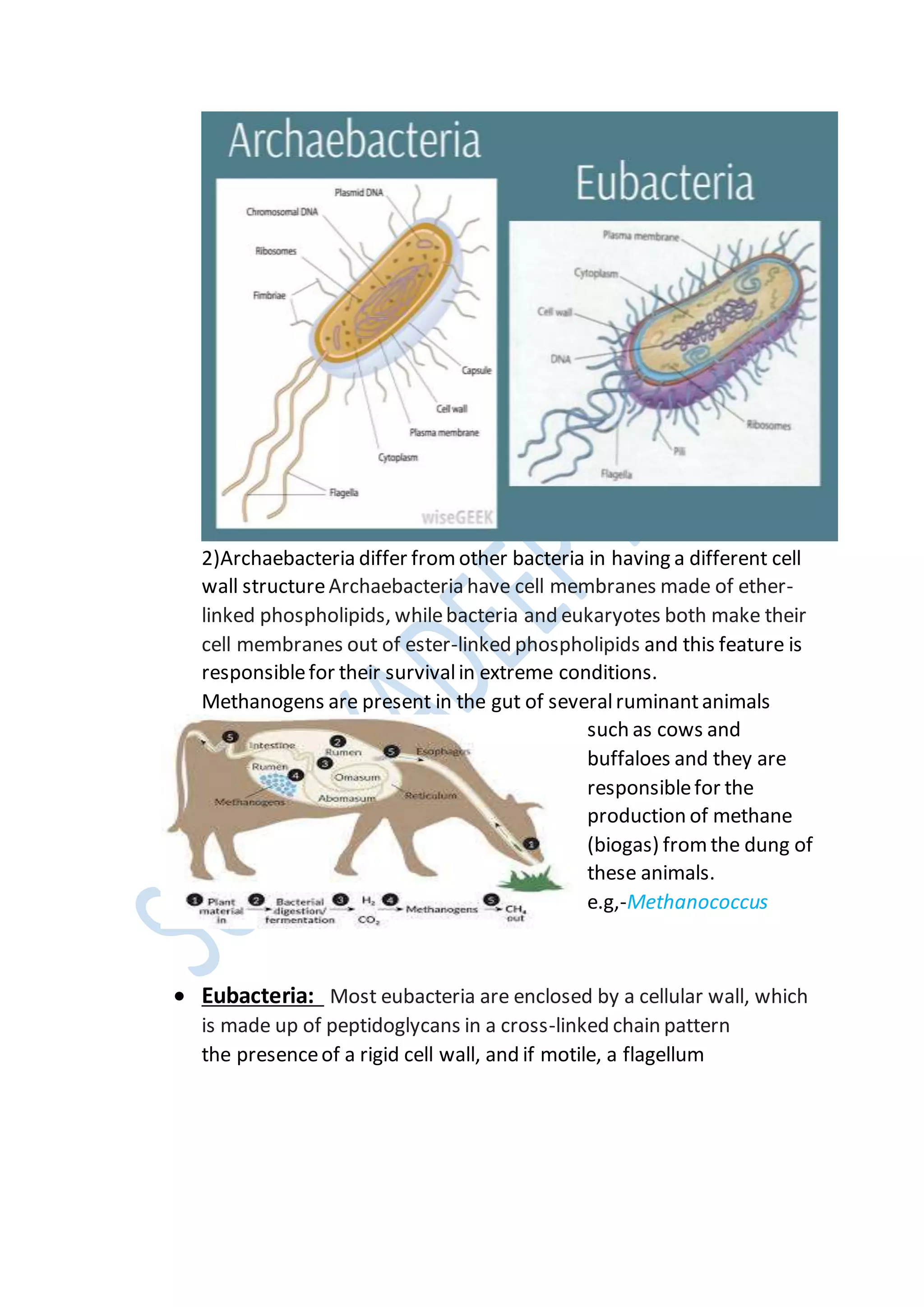
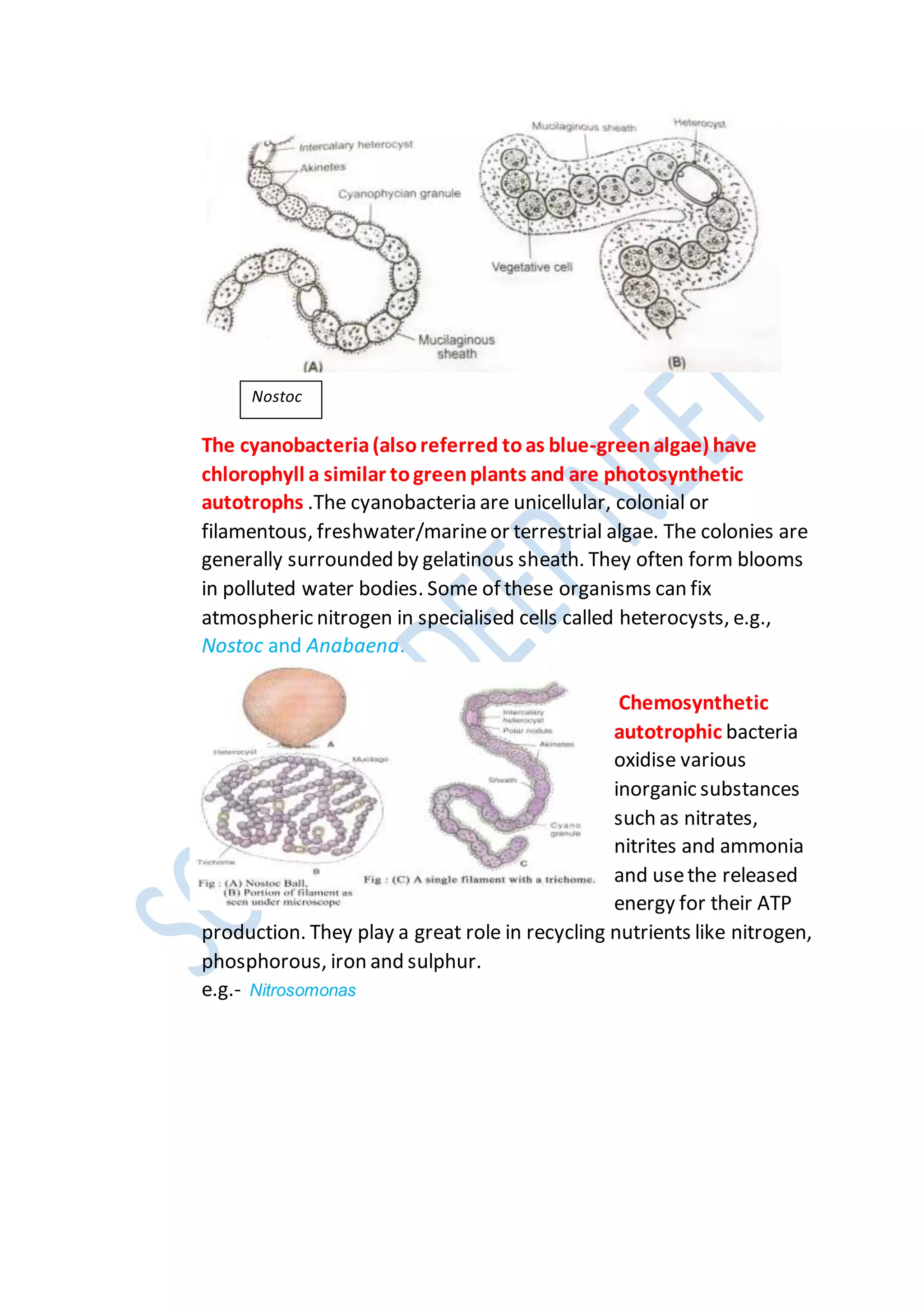
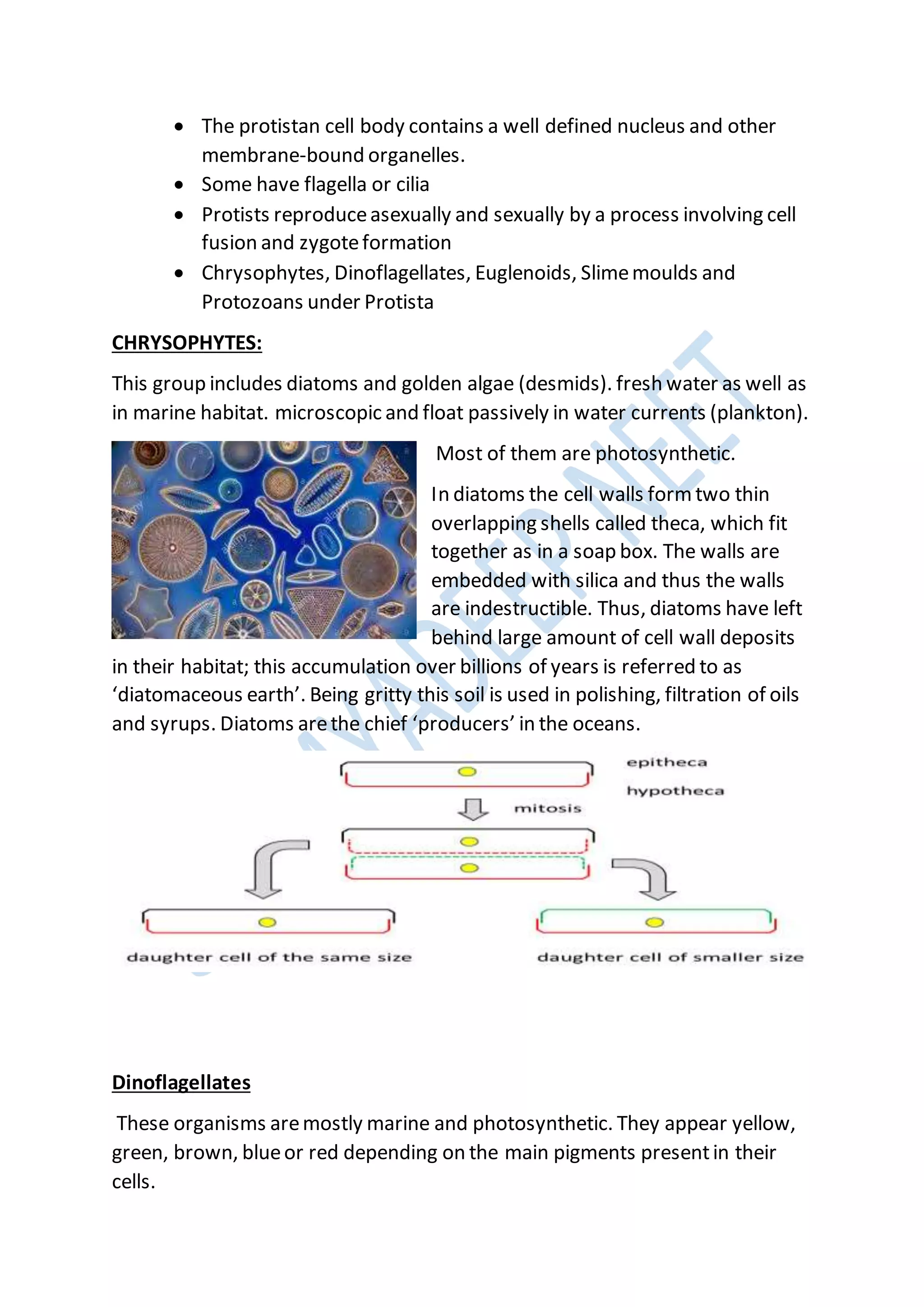
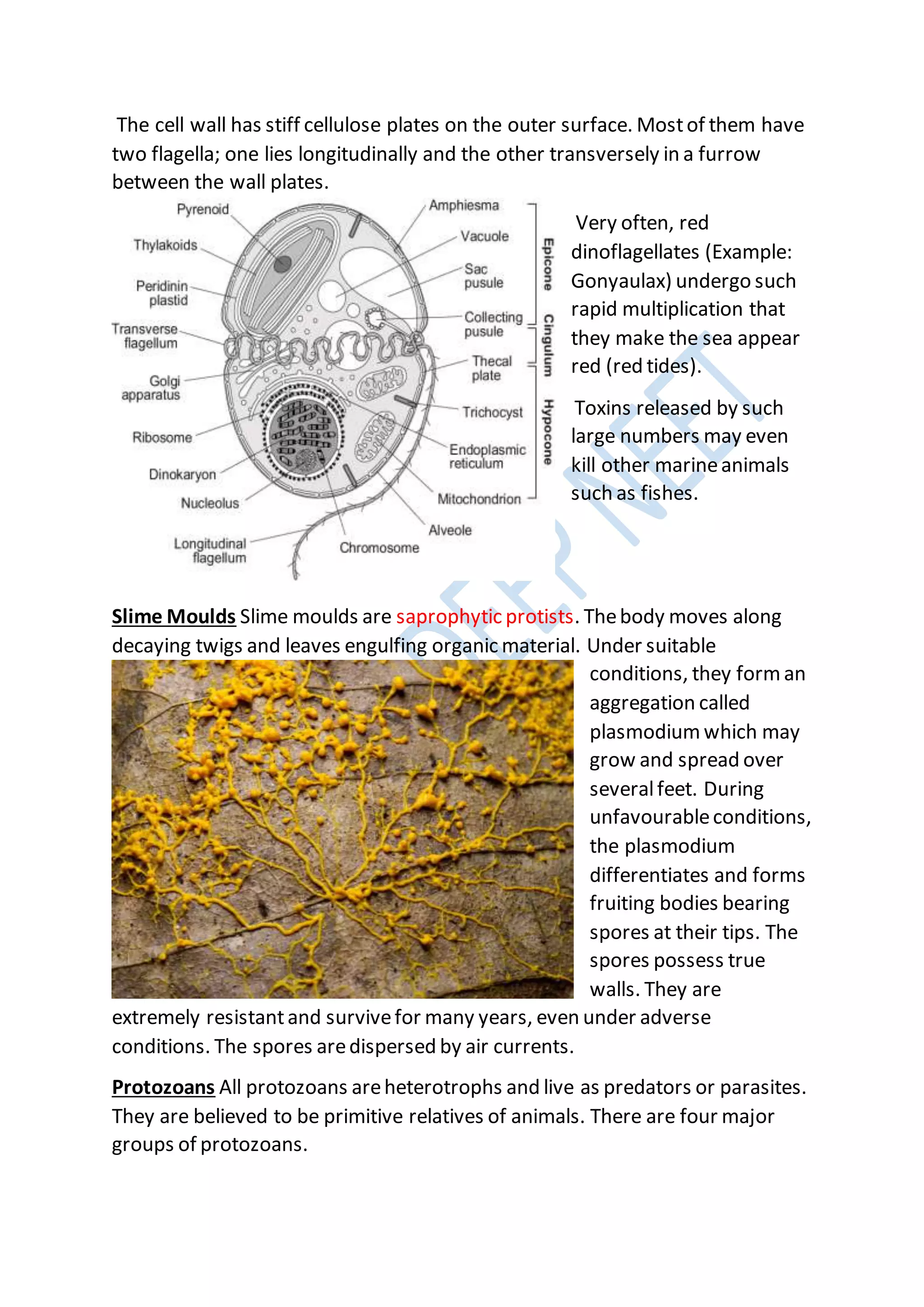
Kingdoms are the second highest rank in biological taxonomy. There are traditionally six kingdoms - Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaea/Archaebacteria, and Bacteria/Eubacteria. However, some systems use five kingdoms excluding Archaea/Archaebacteria. The document then discusses Aristotle's early two-kingdom system and Linnaeus' two-kingdom system. It introduces Whittaker's influential five kingdom system of Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia based on cell structure, nutrition, and other characteristics. Each kingdom is then described in more detail covering key defining features.




![Sporozoans: This includes diverseorganisms thathave an infectious spore-like
stage in their life cycle. The most notorious is Plasmodium (malarial parasite)
which causes malaria, a disease which has a staggering effect on human
population.
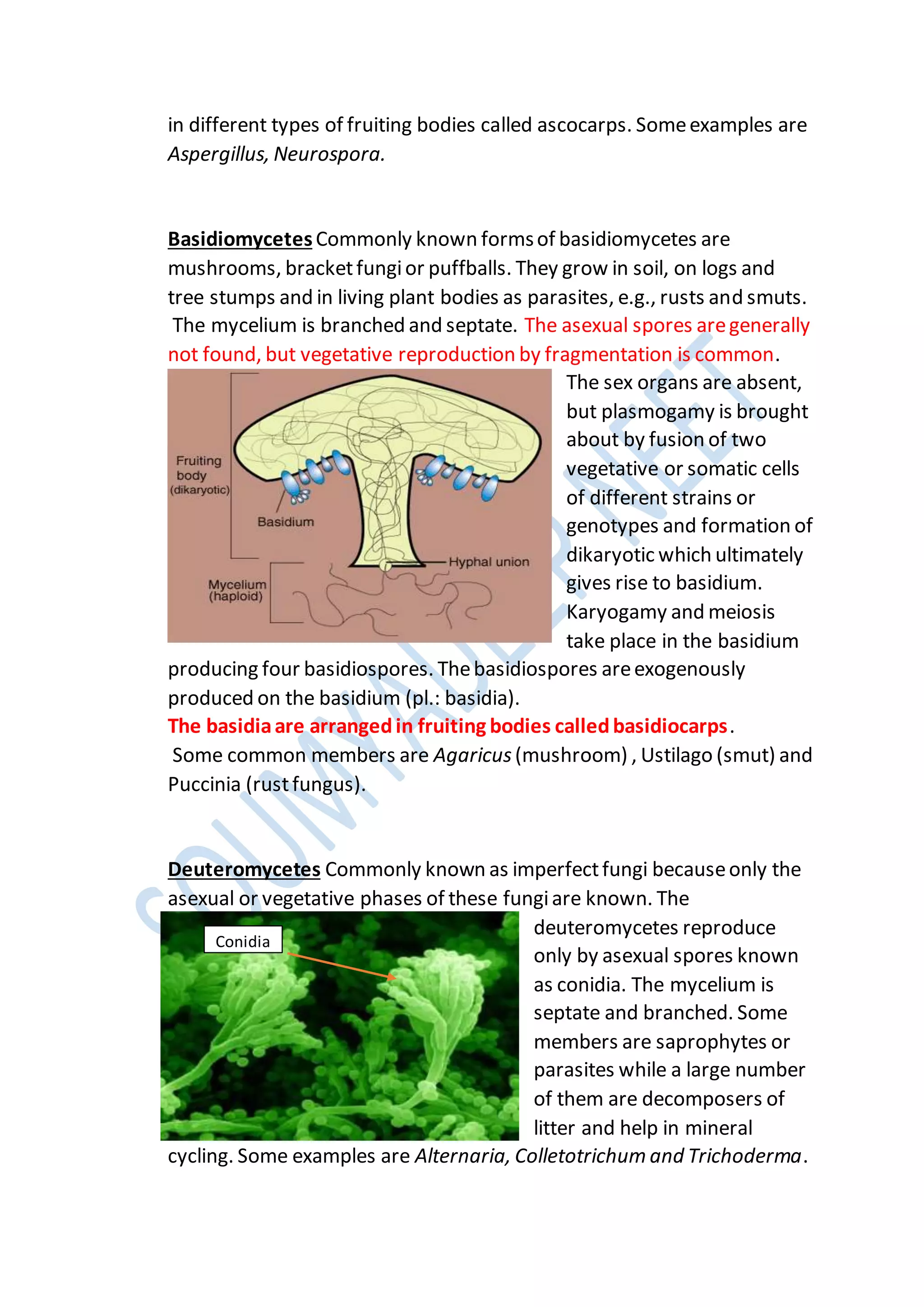
KINGDOM FUNGI
heterotrophic organisms
Exception of yeasts (unicellular), fungiare filamentous.
Their bodies consistof long slender thread-like structures called hyphae
The network of hyphaeis known as mycelium. Some hyphaeare
continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm with out septa–
these are called coenocytic hyphae. Some haveseptae or cross walls in
their hyphae
The cell walls of fungiare composed of chitin and polysaccharides
Most fungiare heterotrophic and absorb solubleorganic matter from
dead substrates and hence are called saprophytes.
Those that depend on living plants and animals are called parasites.
They can also live as symbionts – in association with algae as lichens and
with roots of higher plants as mycorrhiza
Puccinia causewheat rust. penicillium is sourceof antibiotics
Reproduction in fungican take place by
1)vegetative means – [fragmentation, fission and budding. ]
2)Asexualreproduction [ by spores called conidia or sporangiospores or
zoospores]
3)sexualreproduction [is by oospores, ascospores and basidiospores.]
The sexual cycle involves the following three steps:
(i) Fusion of protoplasms between two motile or non-motile gametes
called plasmogamy. (ii) Fusion of two nuclei called karyogamy.
(iii) Meiosis in zygoteresulting in haploid spores.
When a fungus reproduces sexually, two haploid hyphaeof compatible
mating types come together and fuse. In somefungi the fusion of two
haploid cells immediately results in diploid cells (2n). However, in other
fungi (ascomycetes and basidiomycetes), an intervening dikaryotic stage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicalclassification-201231045613-210622063727/75/Chapter-2-Biological-classification-notes-13-2048.jpg)