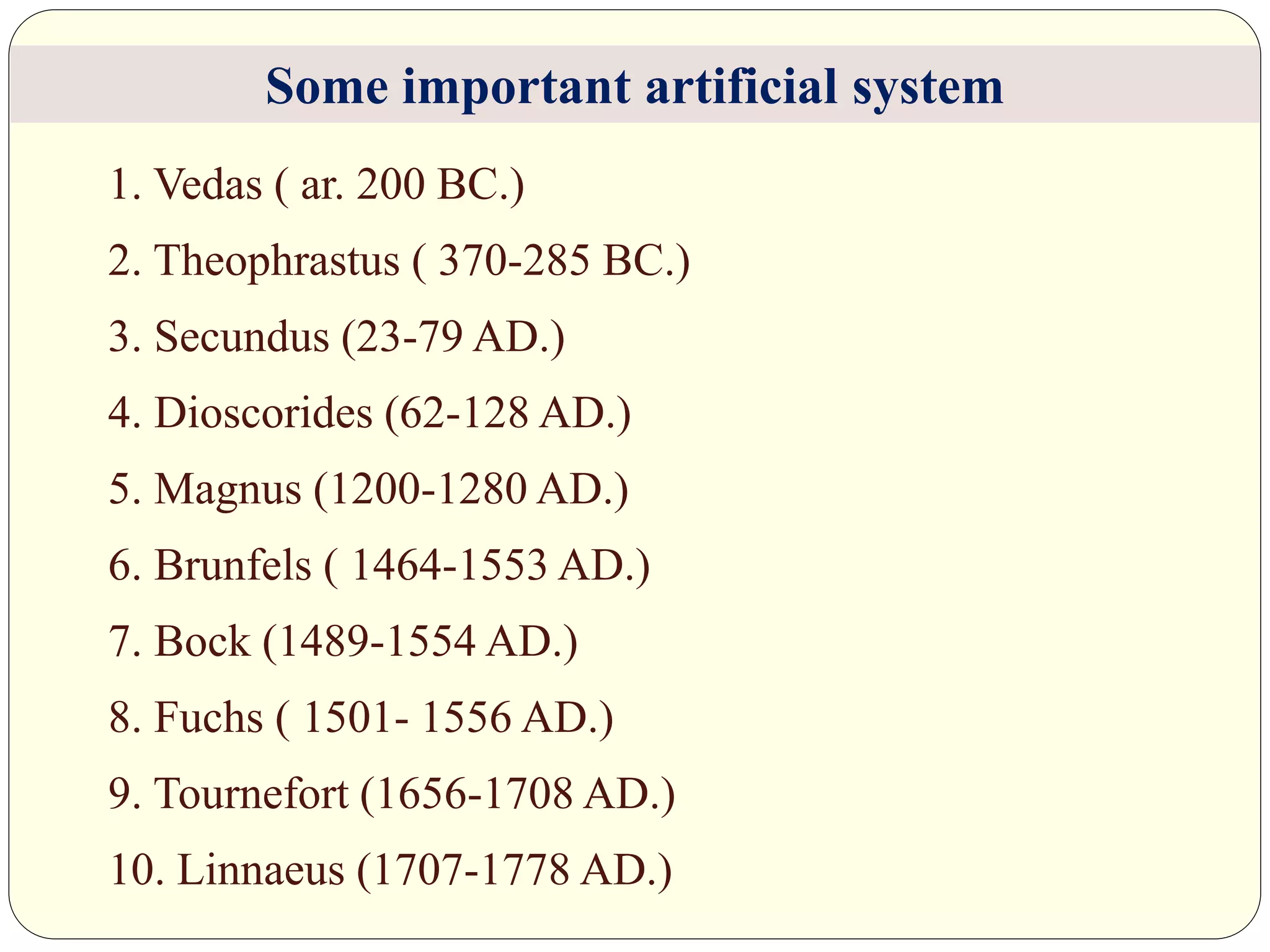
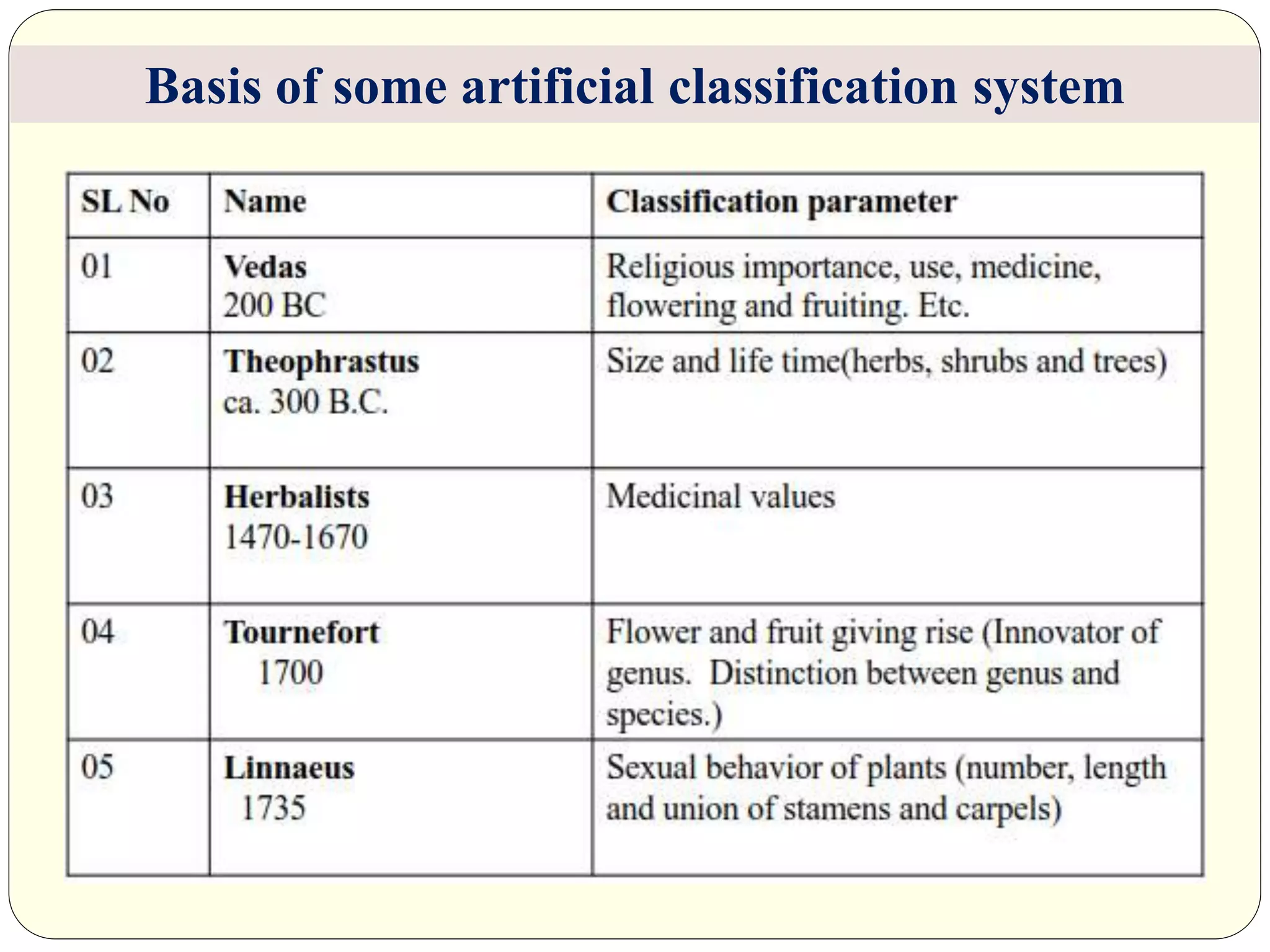
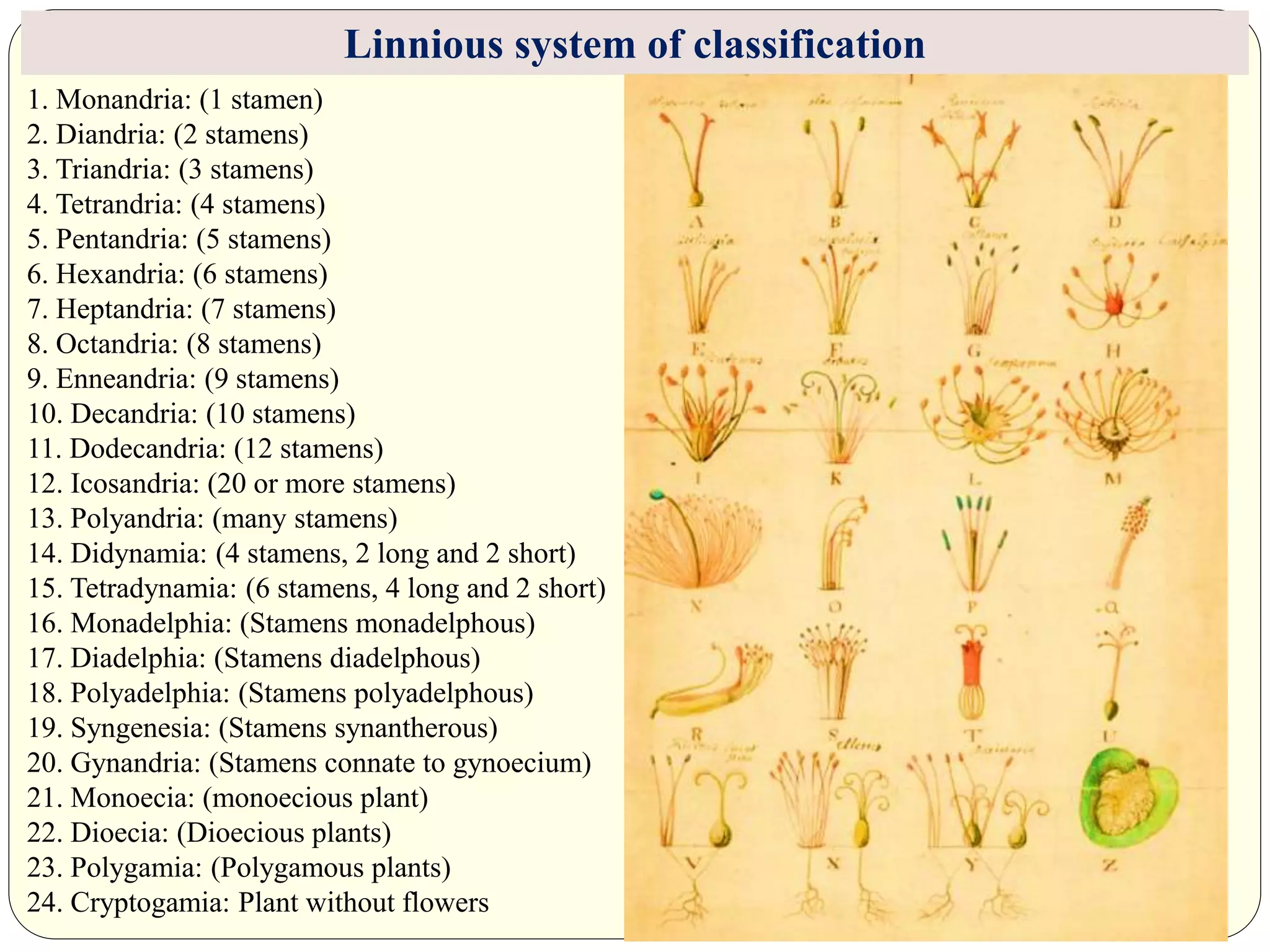
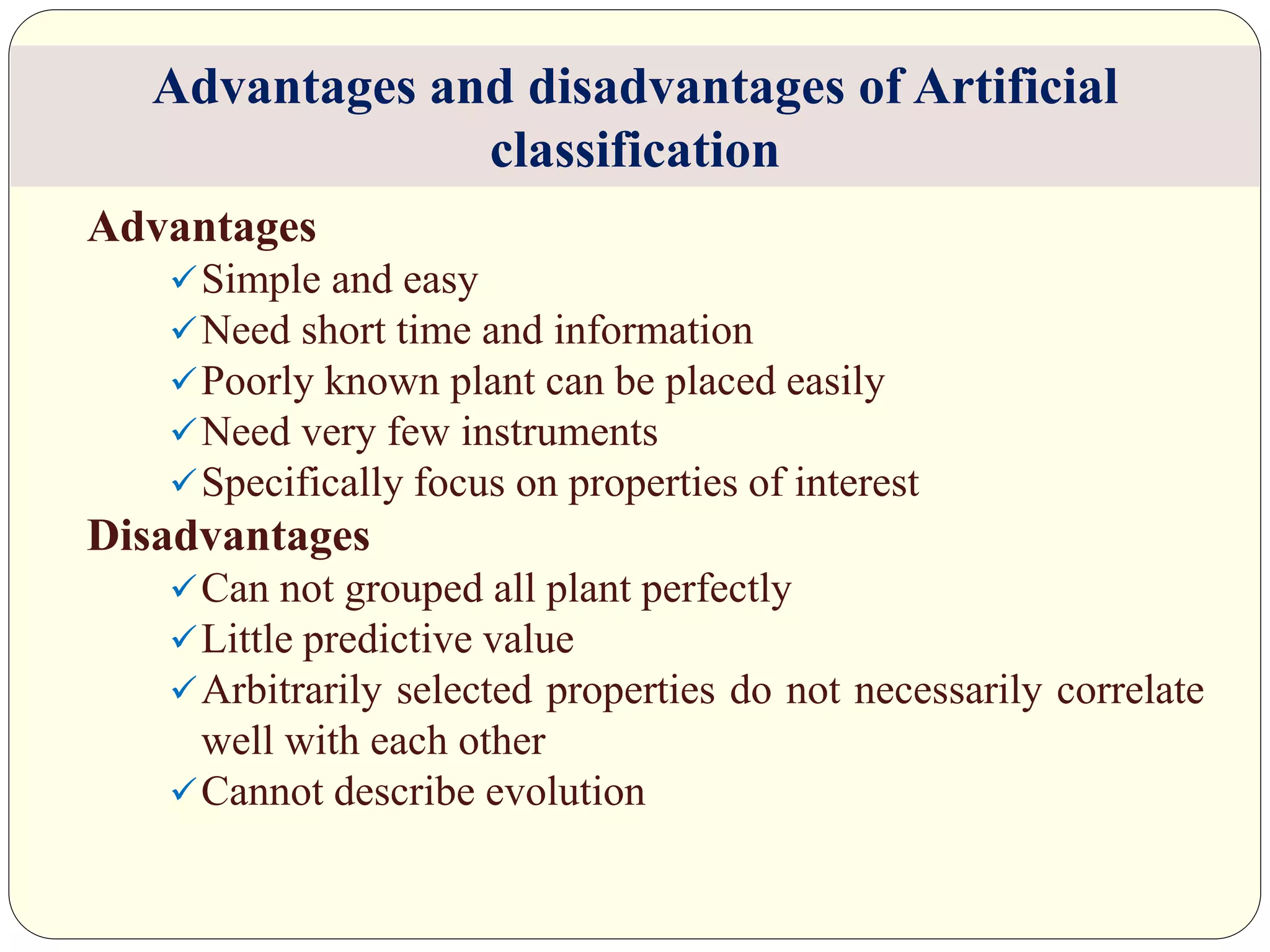
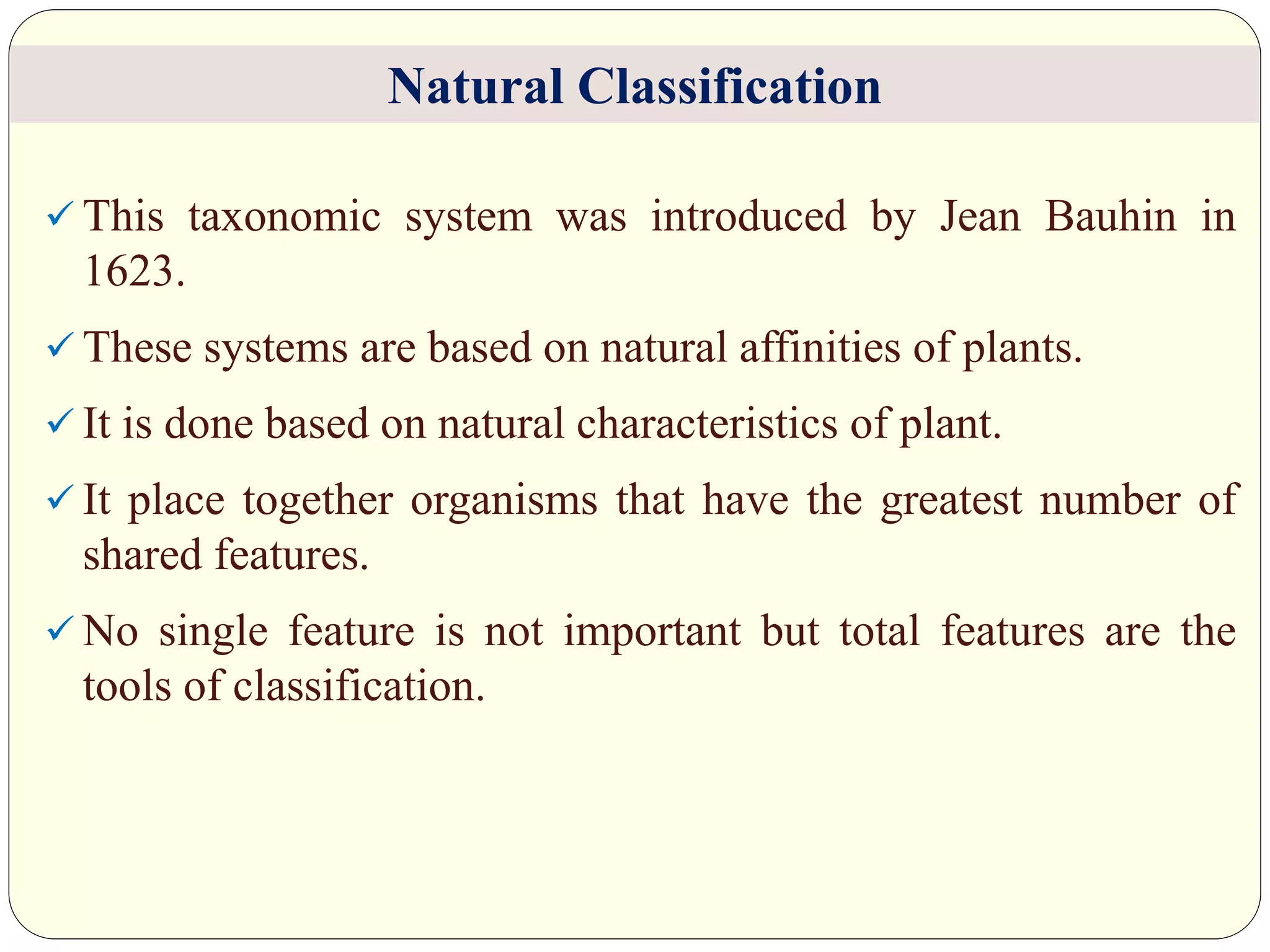
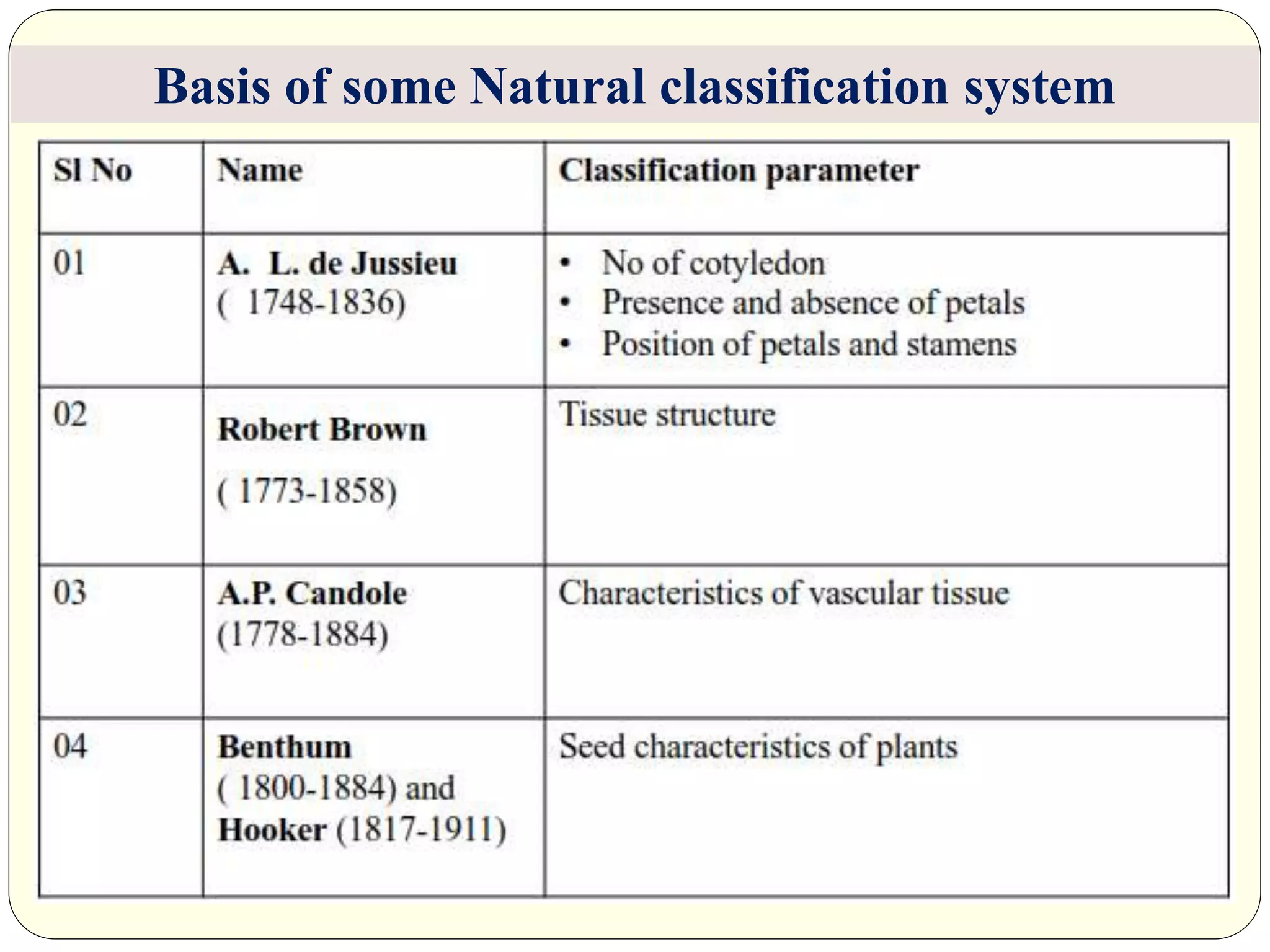
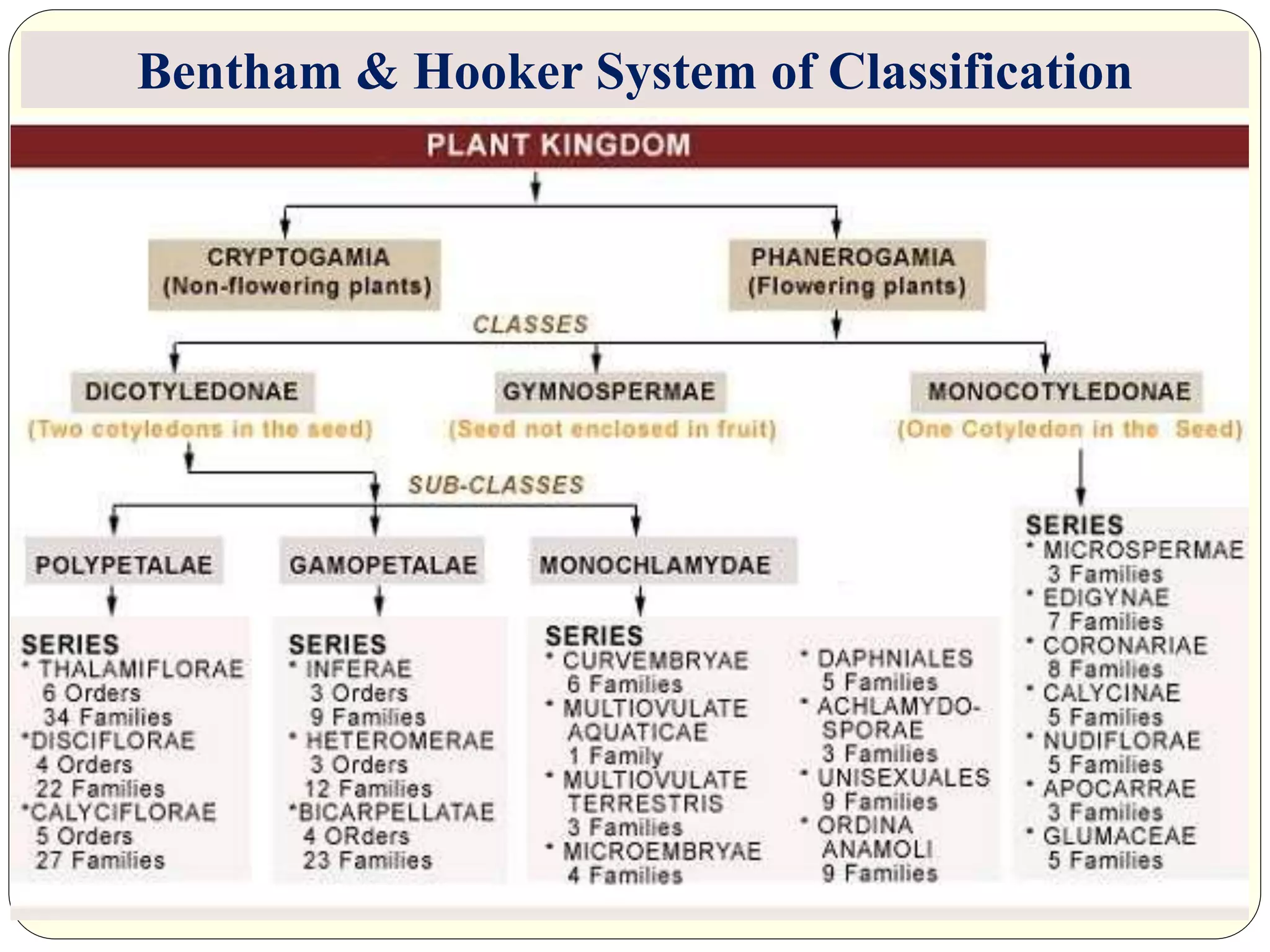
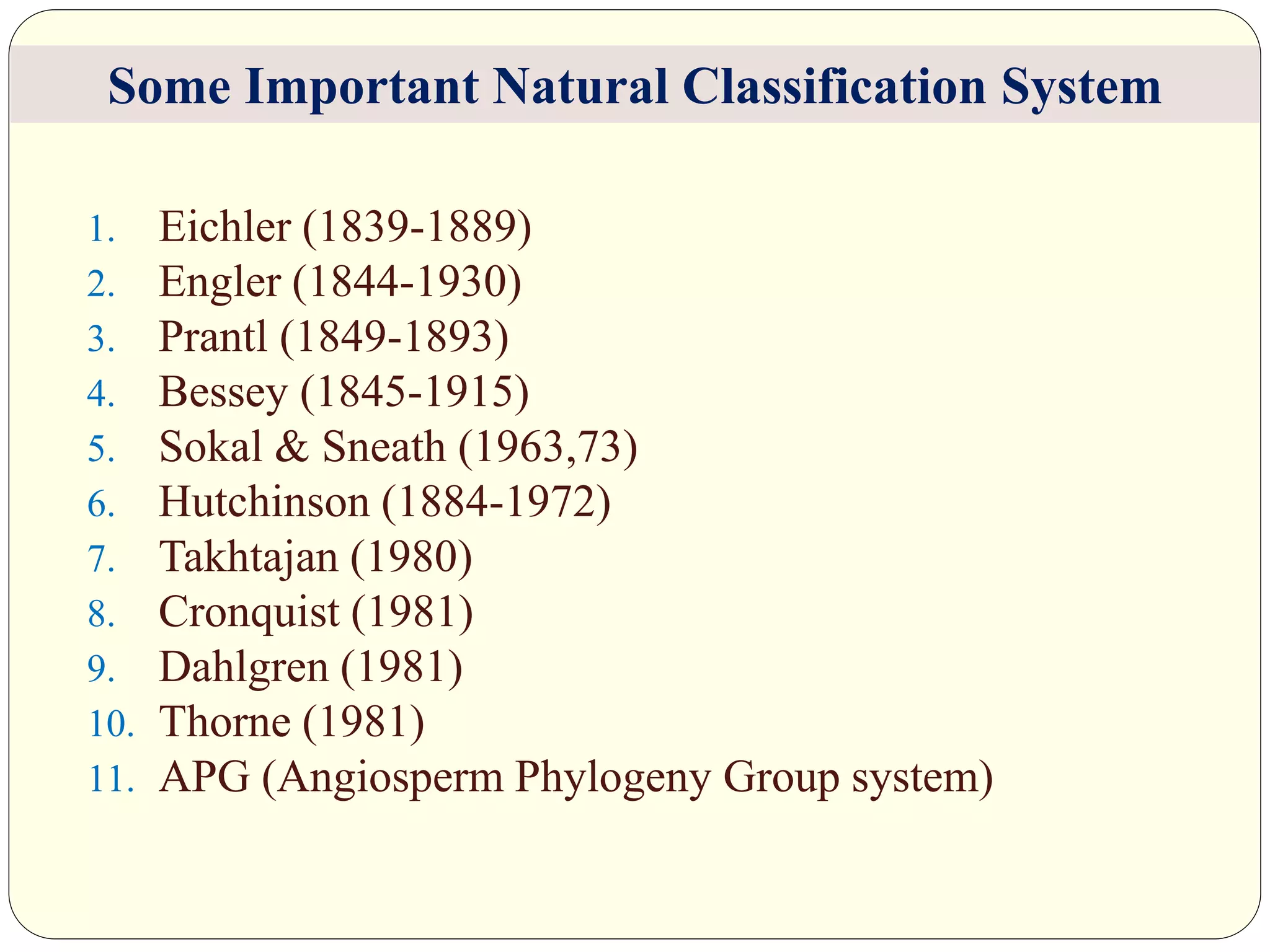
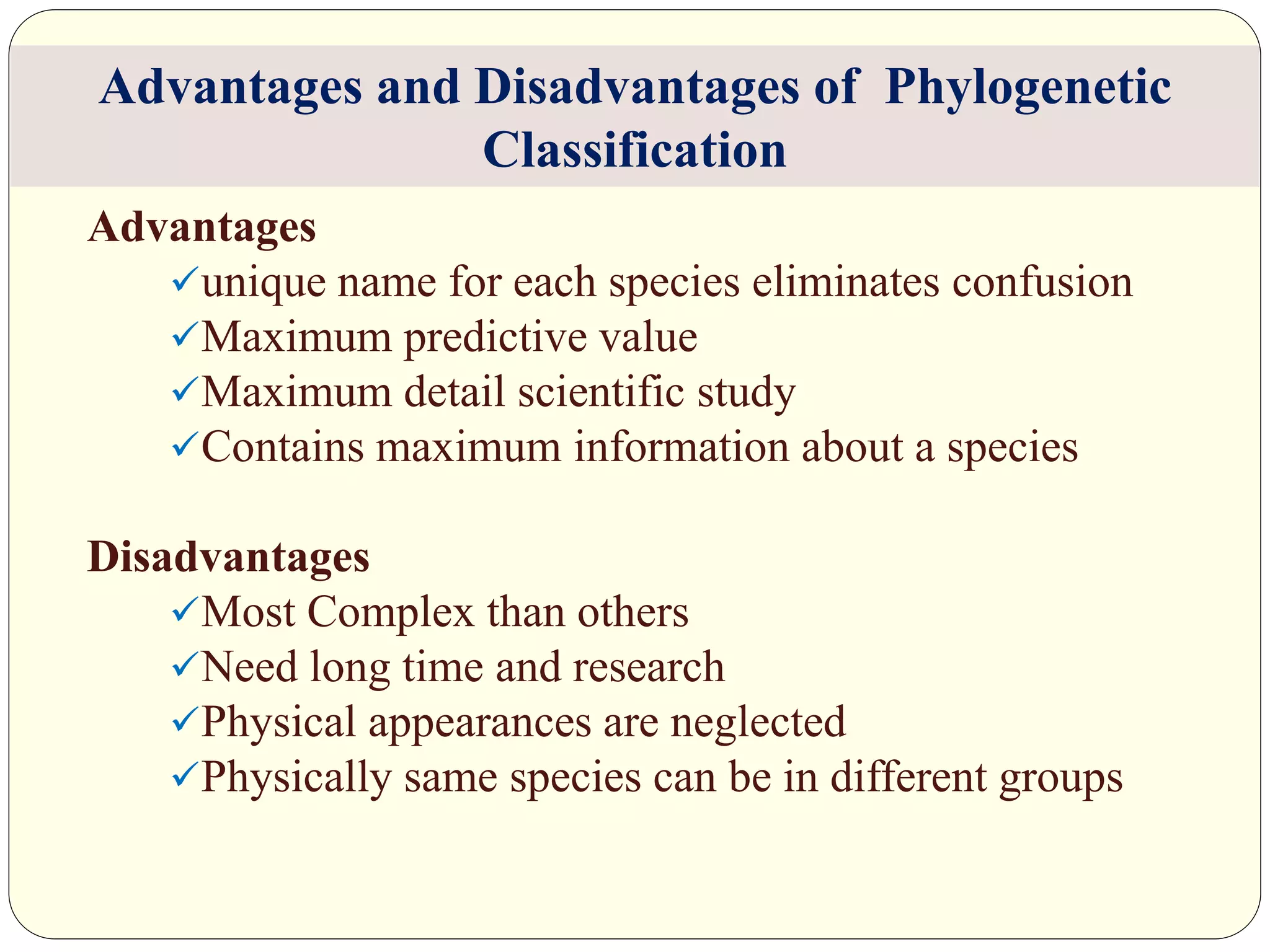
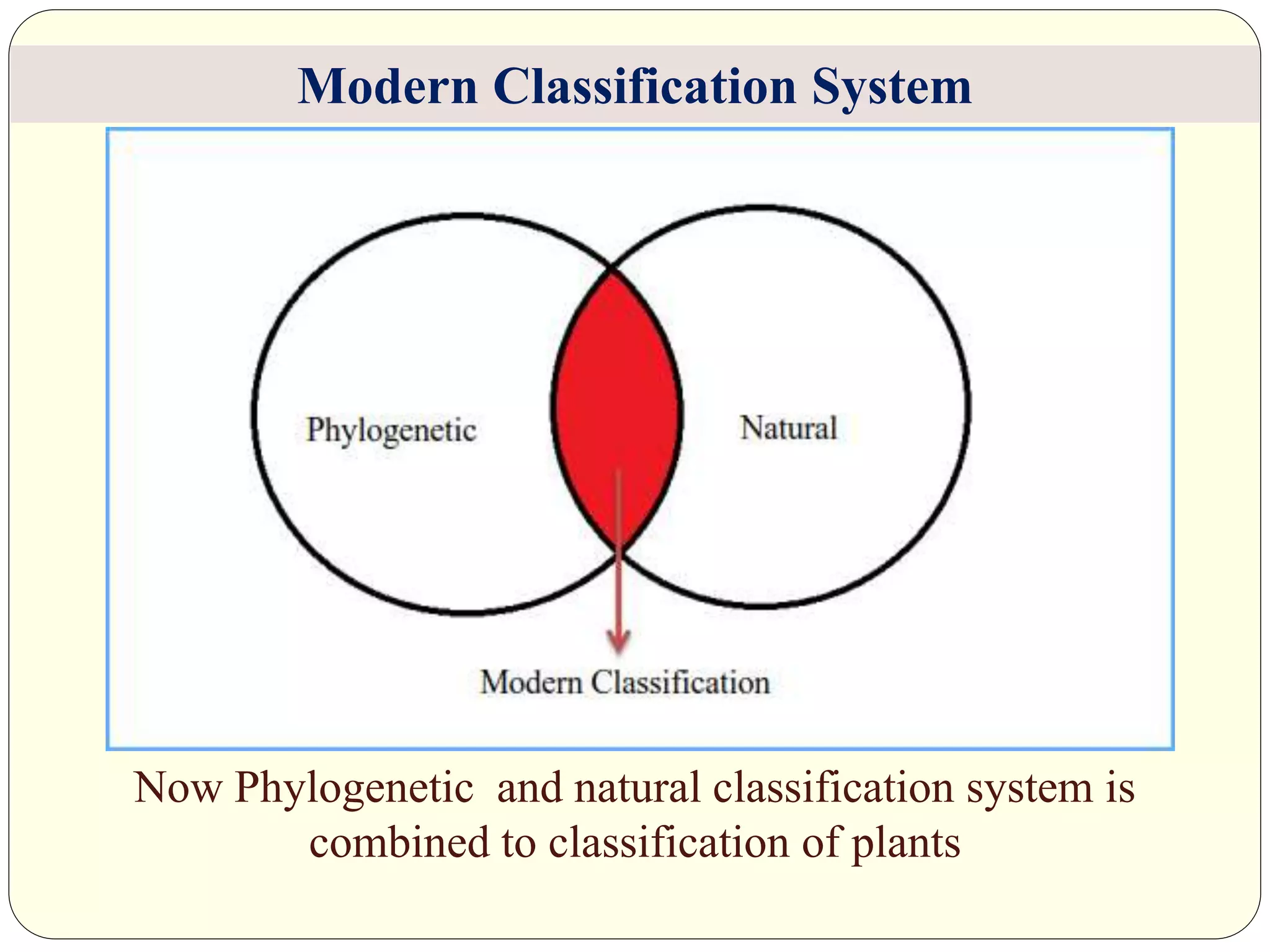
Dr. Ishwar Prakash Sharma discusses the historical development of plant classification systems. Early systems from 2000 BC divided plants based on single characteristics like appearance or habitat. The modern Linnaean system from the 1700s organized plants by their reproductive structures. Later natural systems grouped plants based on overall similarity. The current phylogenetic system, introduced in the 1800s, aims to classify plants based on evolutionary relationships and common ancestry as revealed by modern techniques. The modern combined system incorporates phylogenetic and natural approaches.