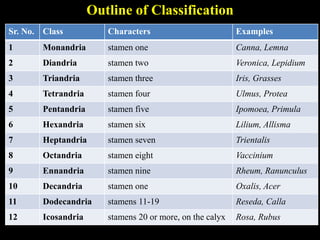
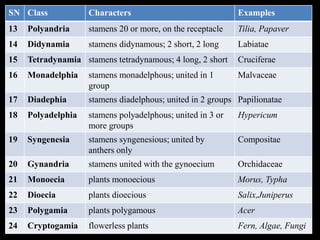
Carolus Linnaeus was an 18th century Swedish botanist known as the "Father of Taxonomy" who developed one of the first comprehensive systems for naming and classifying organisms. He published his system of binomial nomenclature in his influential work Species Plantarum in 1753, establishing standardized scientific names for plants that formed the basis for modern taxonomy. Linnaeus' system classified plants into 24 classes based primarily on their reproductive structures, such as the number of stamens and structure of the pistils, laying the foundation for the modern practice of plant classification.