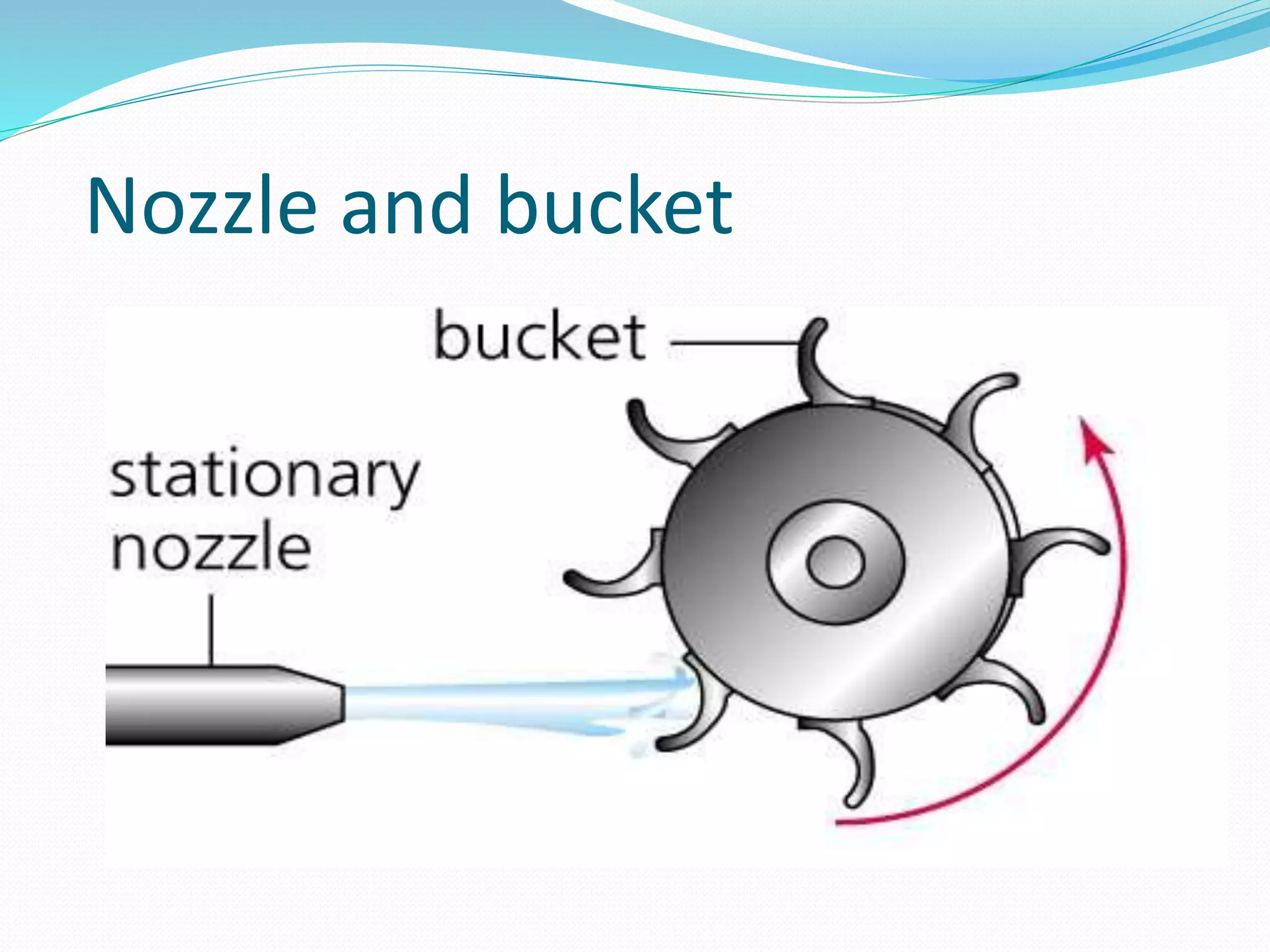
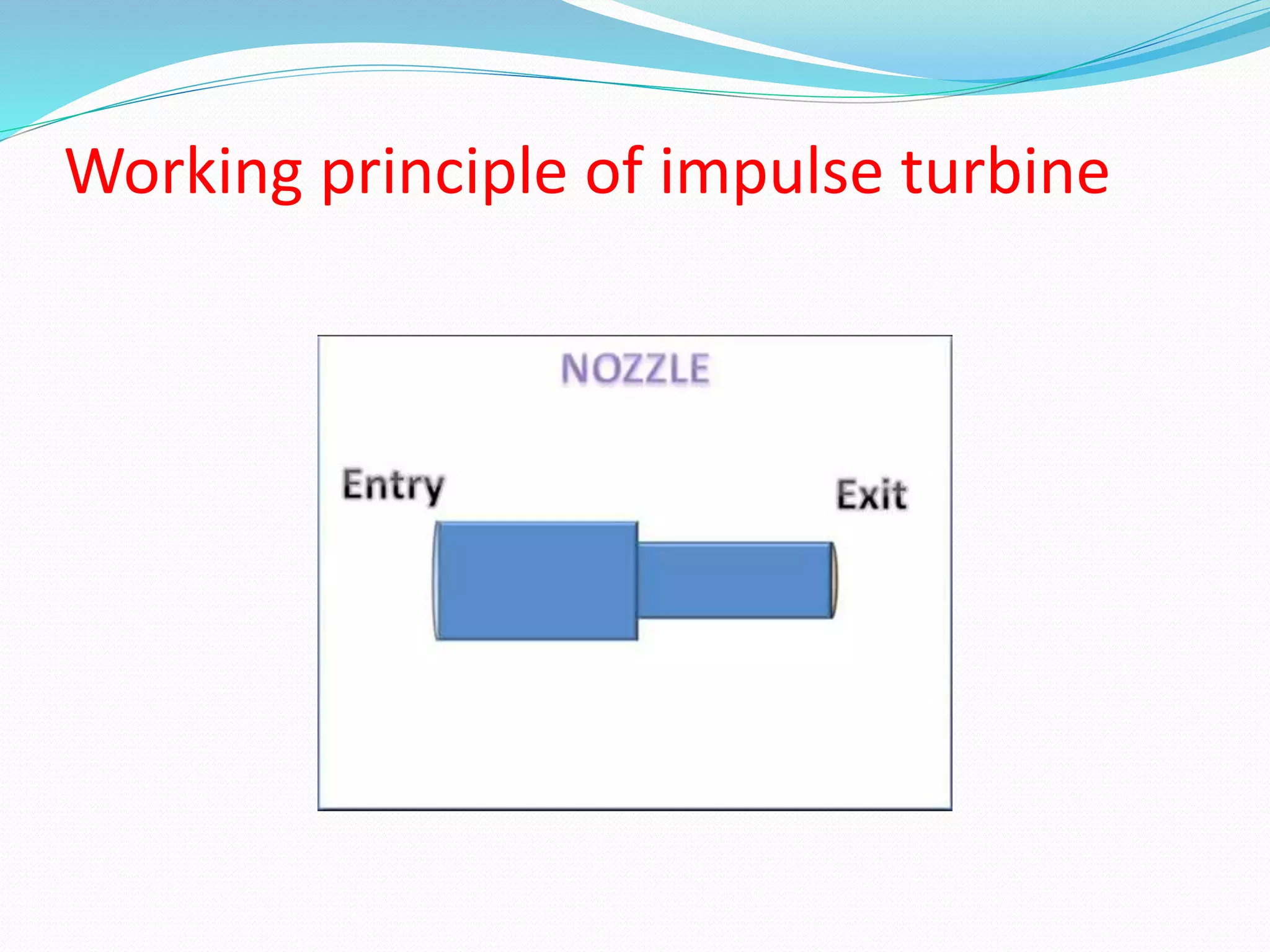
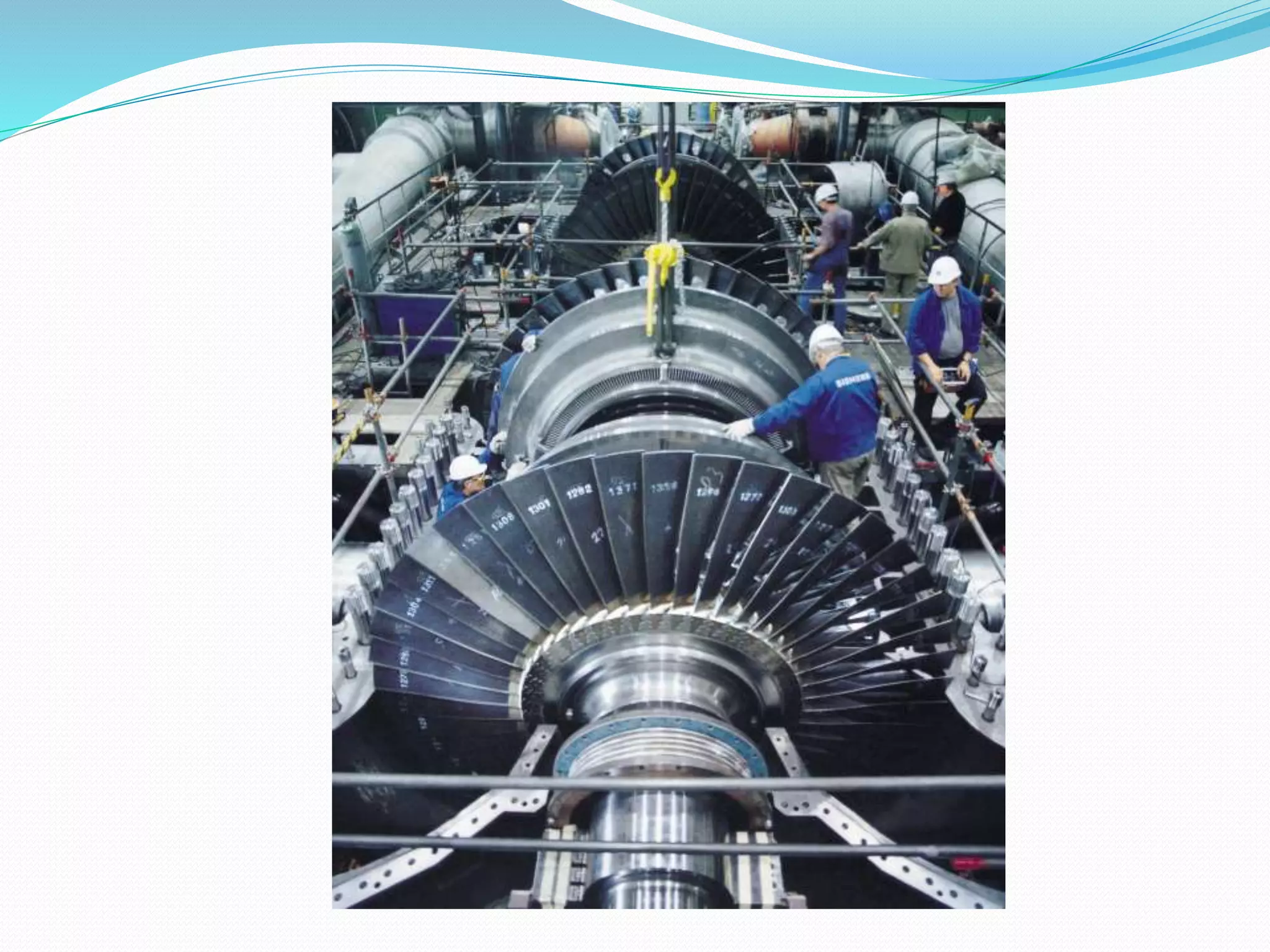
Steam turbines use the momentum of steam to generate rotary motion. They are classified based on the mode of steam action (impulse or reaction), steam flow direction (axial or radial), exhaust conditions (condensing or non-condensing), steam pressure (high, medium, low), and number of stages (single or multi-stage). An impulse turbine operates using the impulse of steam jets which impinge on turbine blades, changing the steam's direction and generating force. It consists of nozzles that direct high velocity steam onto blades attached to a circular runner, and a casing that contains these components.