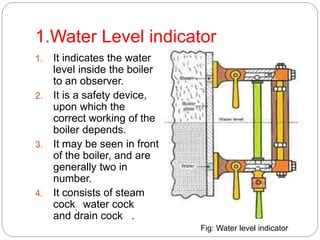
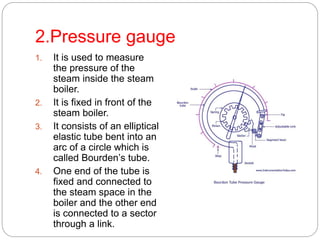
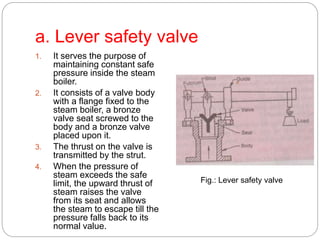
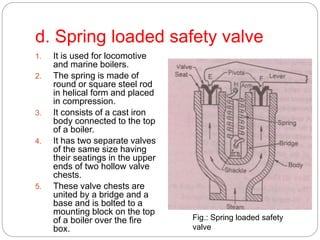
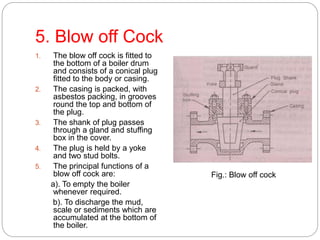
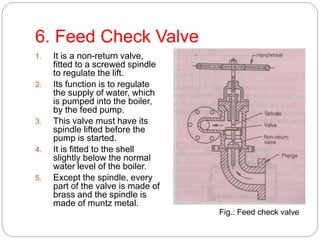
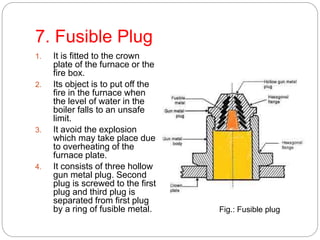
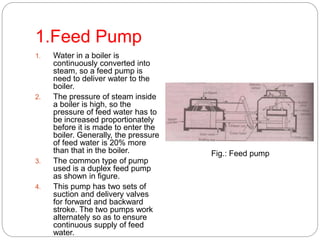
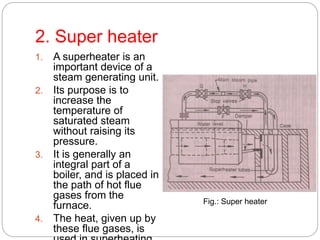
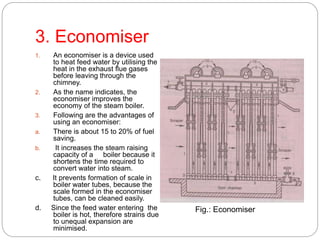
Boiler mountings are fittings that are mounted on boilers for their proper and safe functioning. Some key mountings include water level indicators, pressure gauges, safety valves, stop valves, blow off cocks, feed check valves, and fusible plugs. Safety valves prevent explosions from excessive steam pressure by releasing steam when pressure exceeds safe limits. Boiler accessories like feed pumps, superheaters, economizers, and air preheaters help boilers run efficiently by feeding water, increasing steam temperature, recovering heat from flue gases to preheat feed water and air.