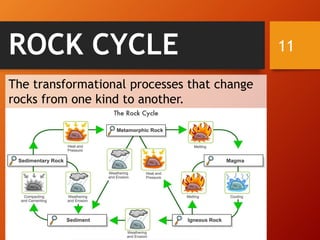
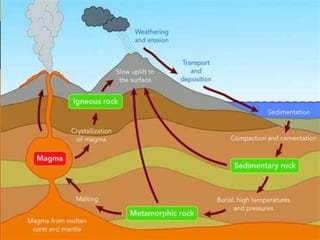
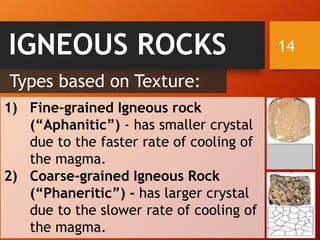
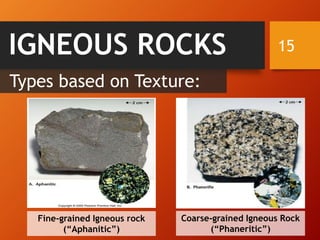
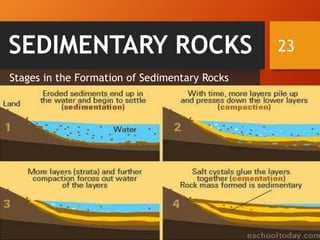
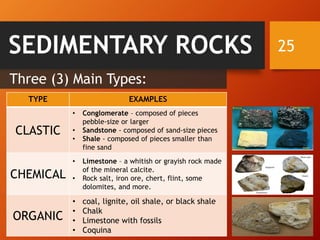
The document classifies rocks into three primary categories: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic, detailing their formation processes and characteristics. Igneous rocks arise from cooled magma, sedimentary rocks are formed from compacted sediments, and metamorphic rocks are transformed from existing rocks due to heat and pressure conditions. Each rock type has further classifications based on texture and composition.