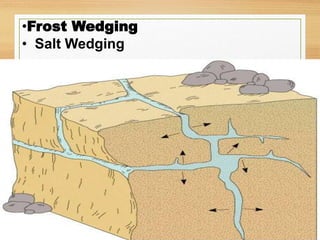
This document discusses exogenic processes that shape the Earth's surface. It describes weathering as the breakdown of rocks at or near the surface through mechanical or chemical means. Physical weathering breaks rocks into smaller pieces through processes like freeze-thaw cycling, while chemical weathering alters rock composition through reactions with water and gases. Erosion then transports weathered materials like sand and soil through agents such as water, wind, and gravity. Mass movement involves large-scale slope movements under gravitational forces, like landslides. Together, weathering, erosion, and mass movement continuously reshape the landscape over time.