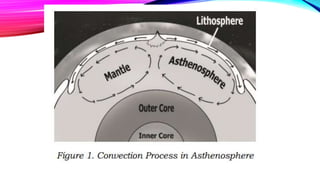
Magma forms deep in the Earth's crust and upper mantle through the process of partial melting. Heat from the mantle causes rocks like quartz and feldspar to melt at temperatures over 650°C. Additional melting occurs through decompression as magma rises to shallower depths and pressure decreases, or through flux melting when water or carbon dioxide are added to already hot rocks. Once a volcano erupts, the magma is called lava on the Earth's surface.