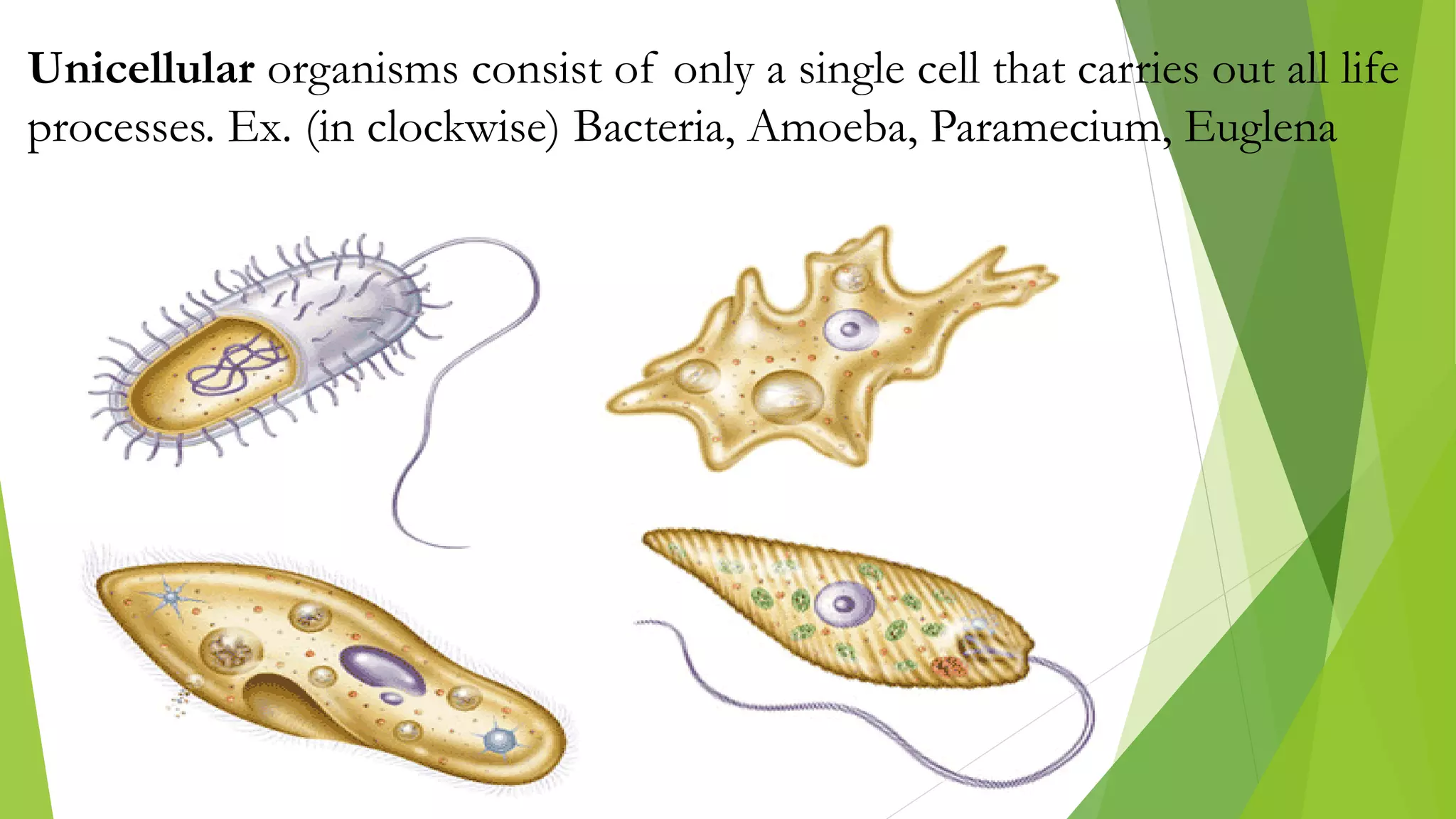
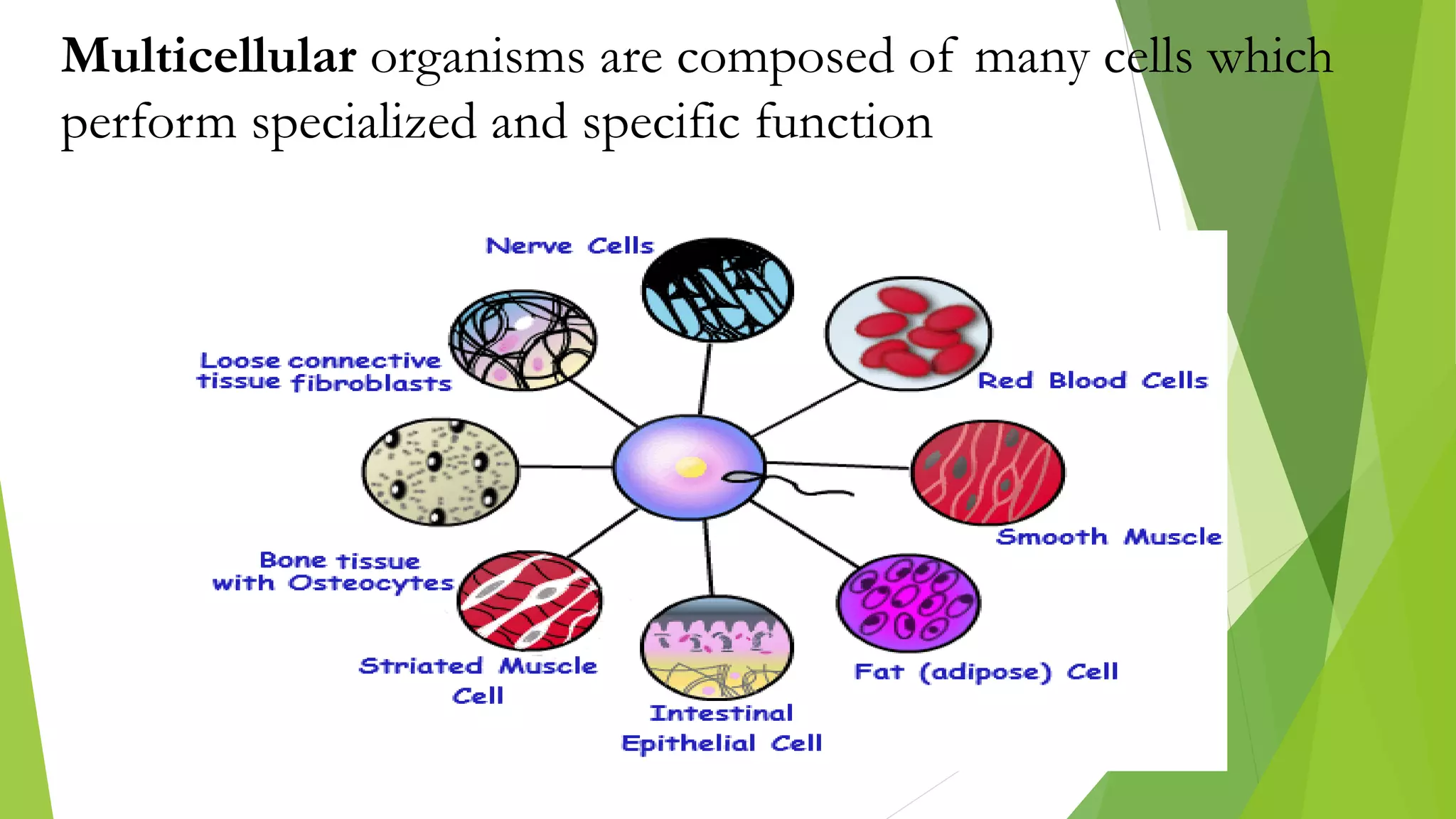
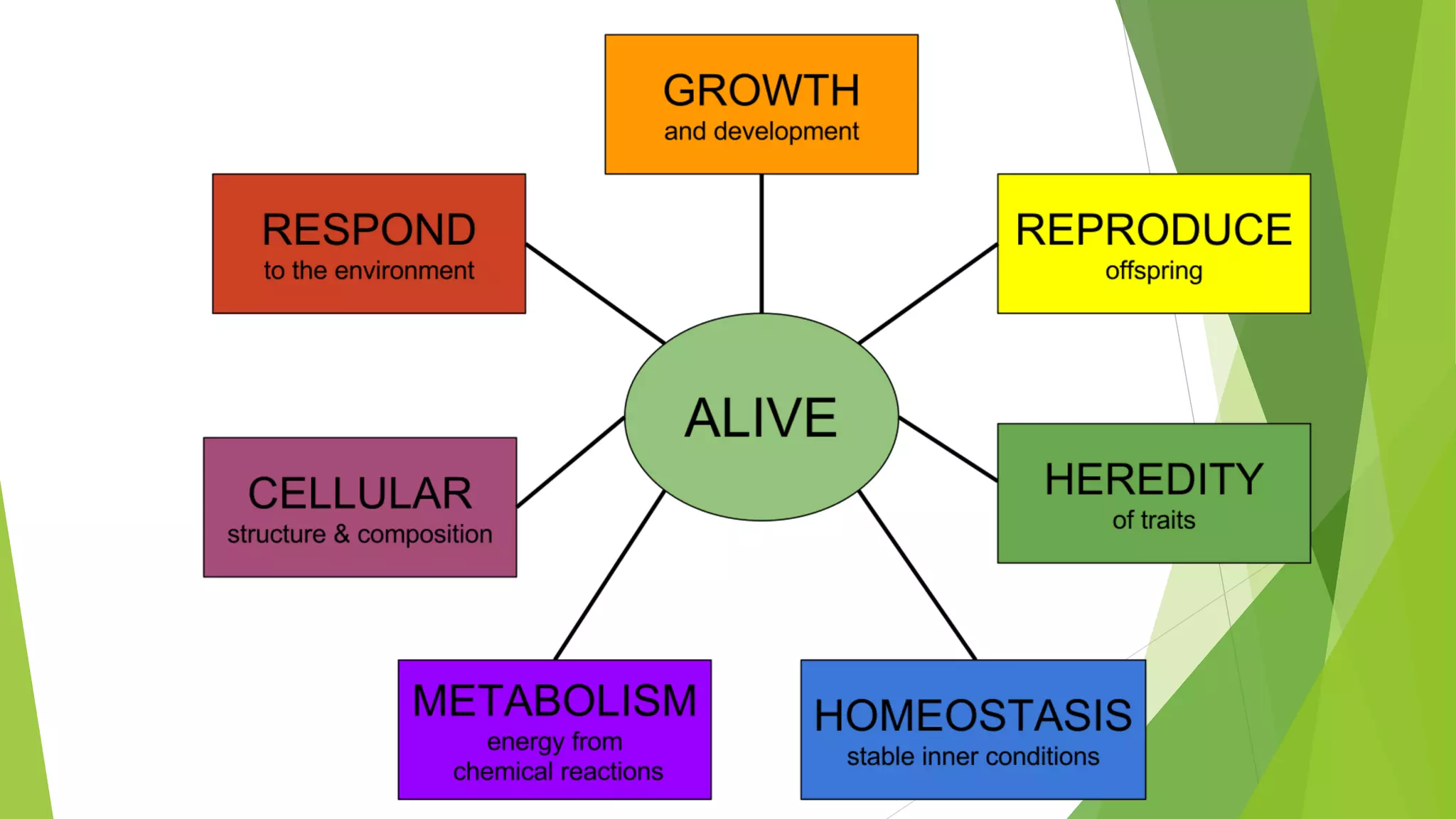
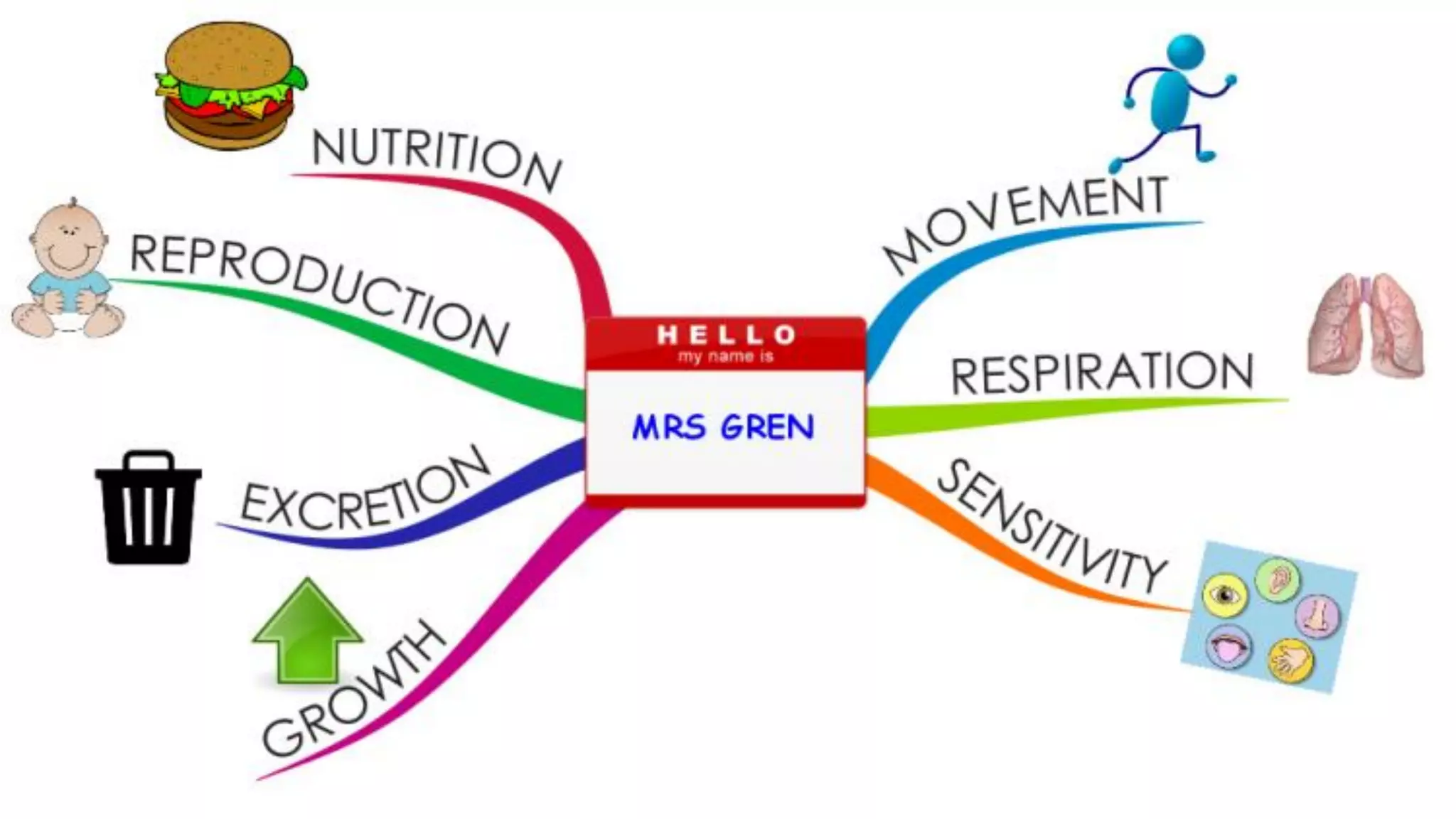
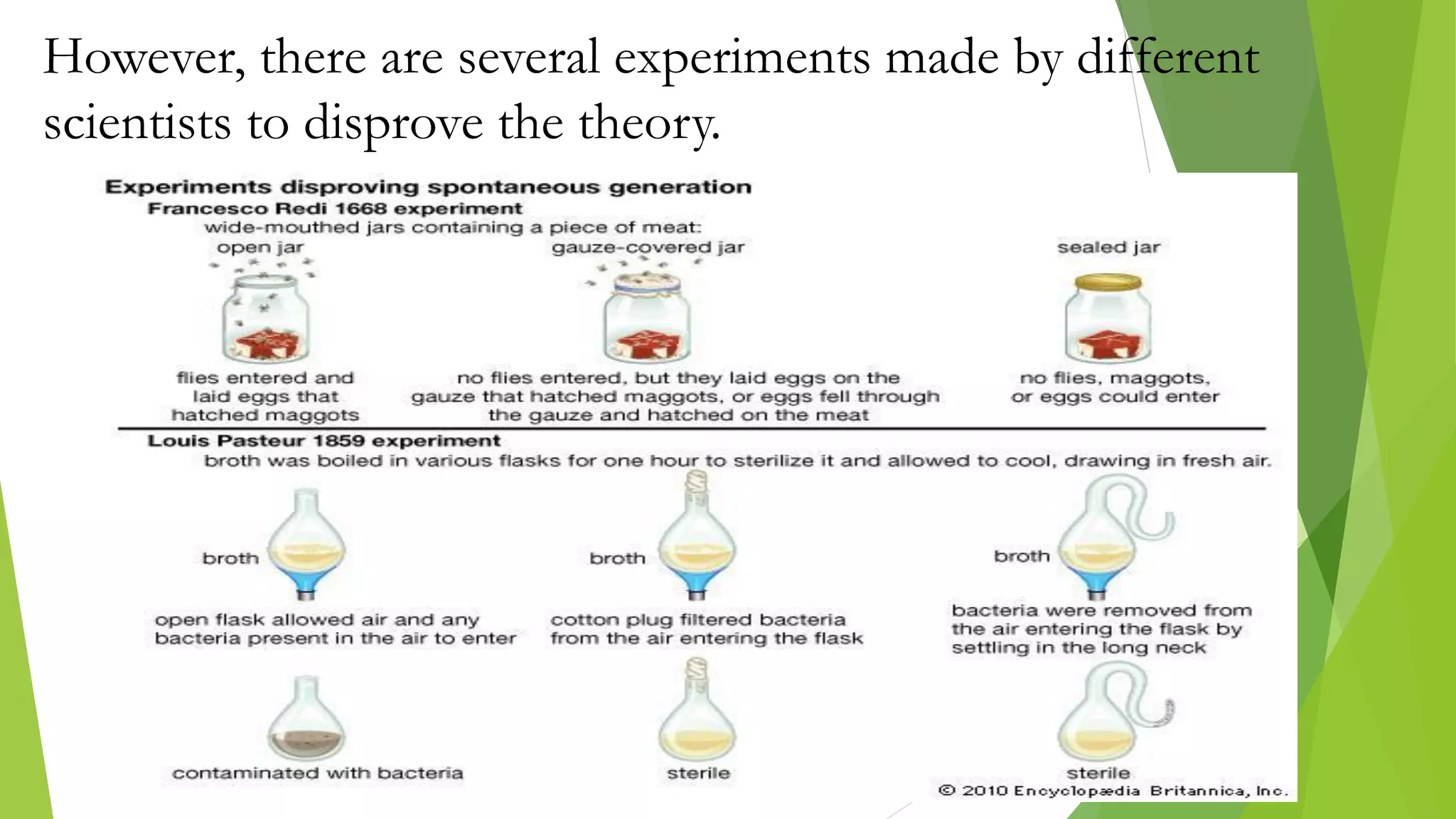
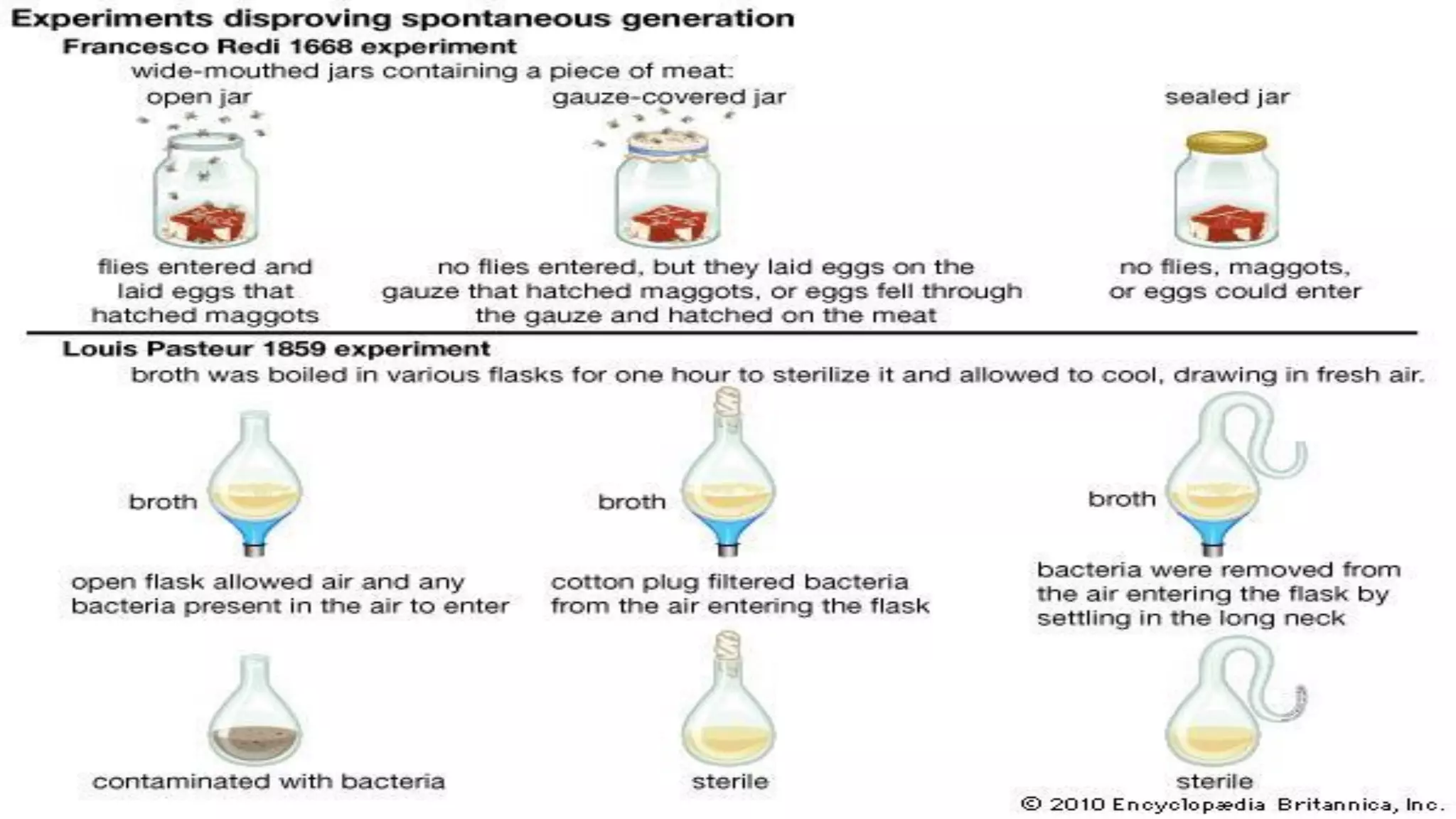
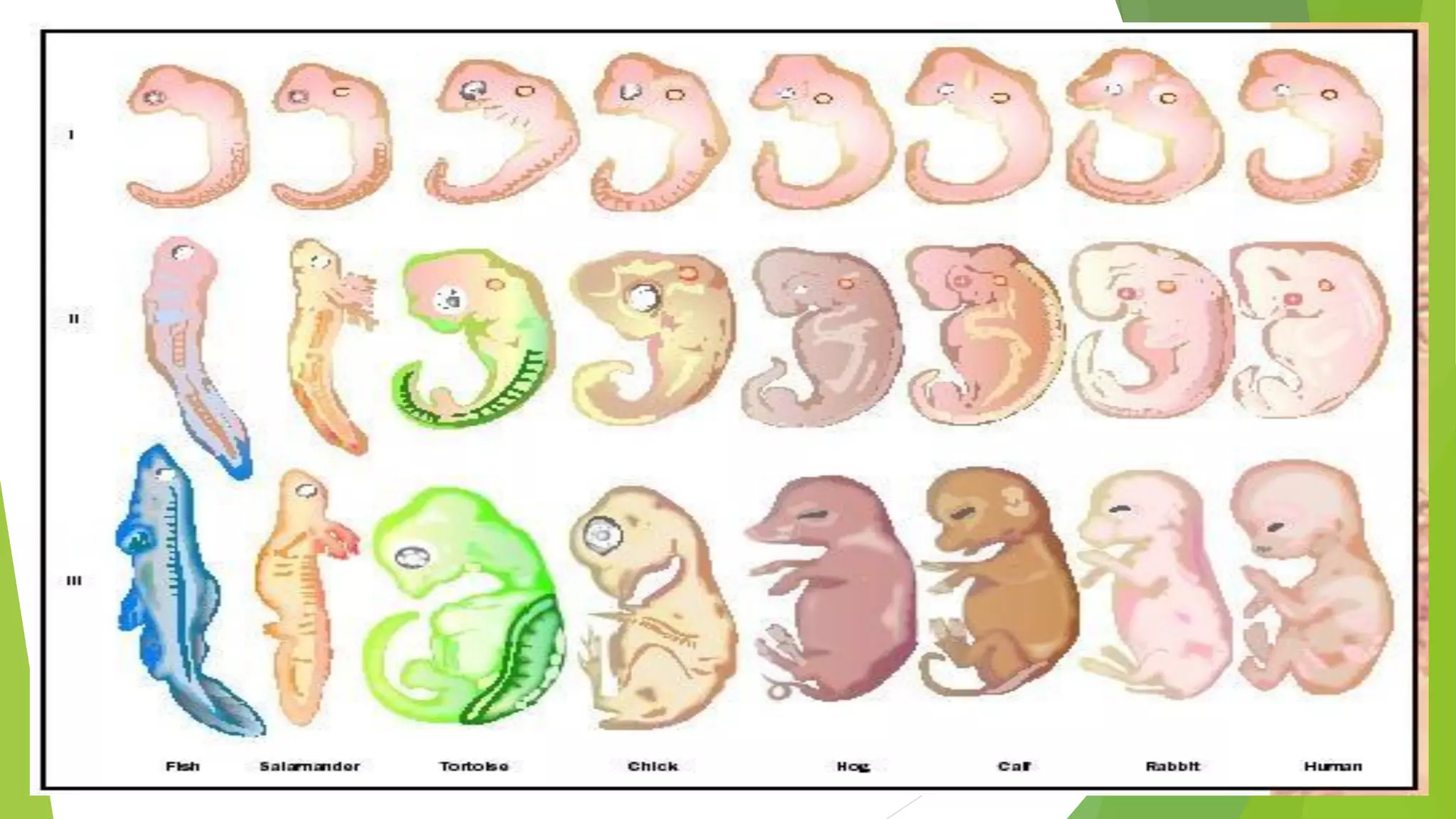
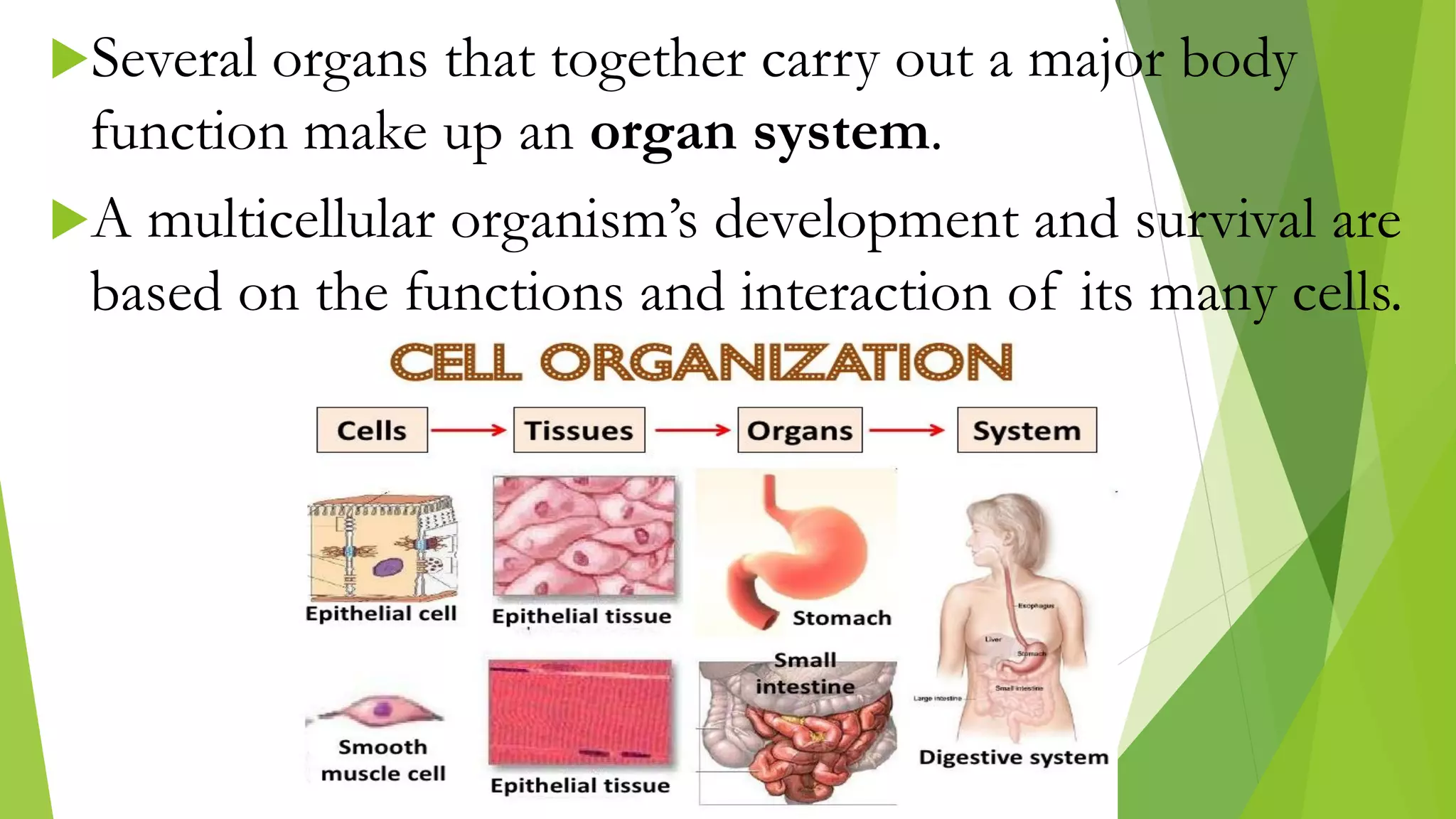
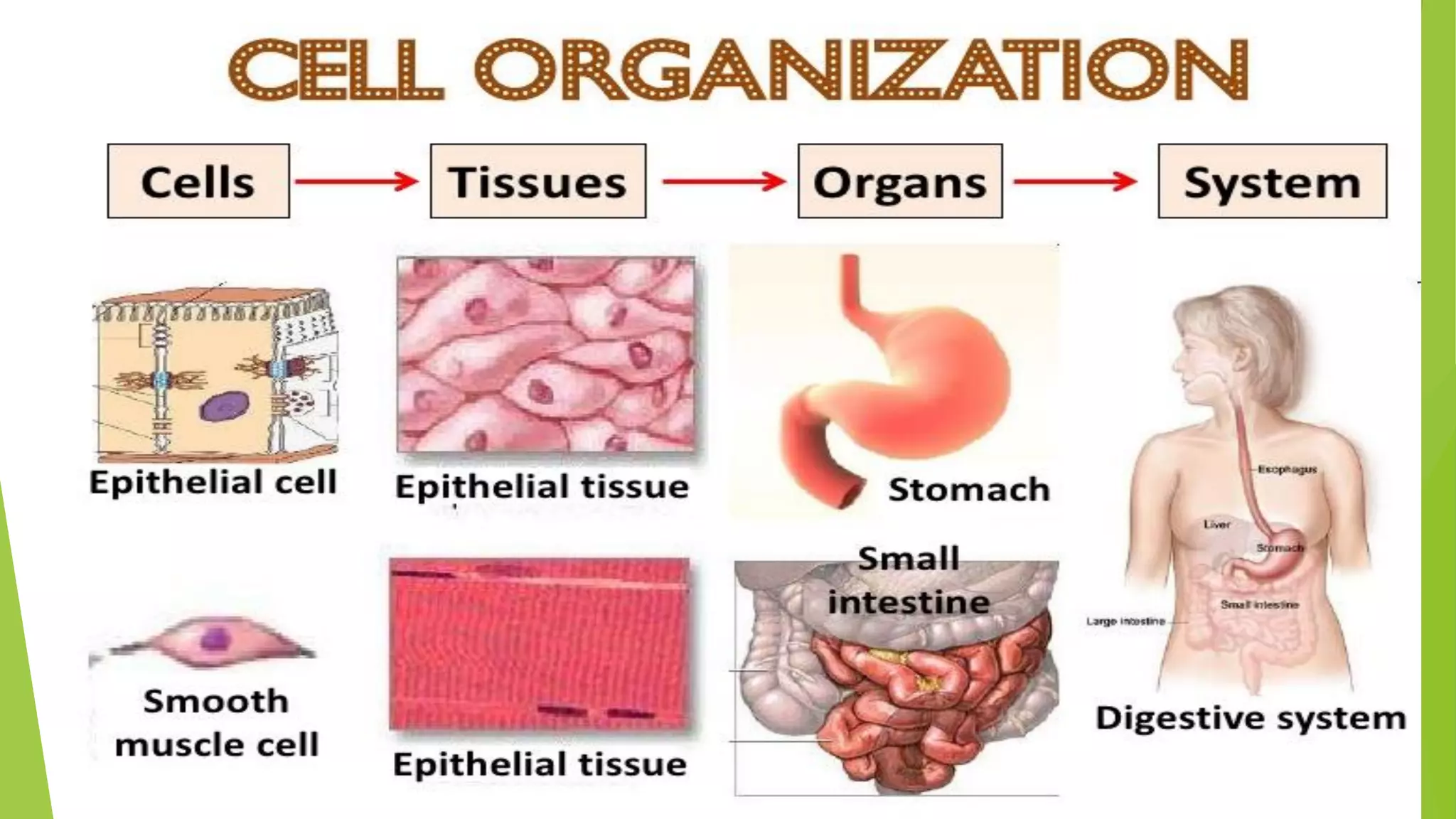
The document provides an extensive introduction to life sciences, discussing the origins and characteristics of life, including cellular organization, metabolism, and reproduction. It explores various theories on the origin of life, such as the special creation theory, spontaneous generation, and abiogenetic synthesis, as well as the importance of biological systems and energy flow in ecosystems. Additionally, it highlights the role of evolution and natural selection in the adaptation of organisms to their environments and the impact of modern biology on society.