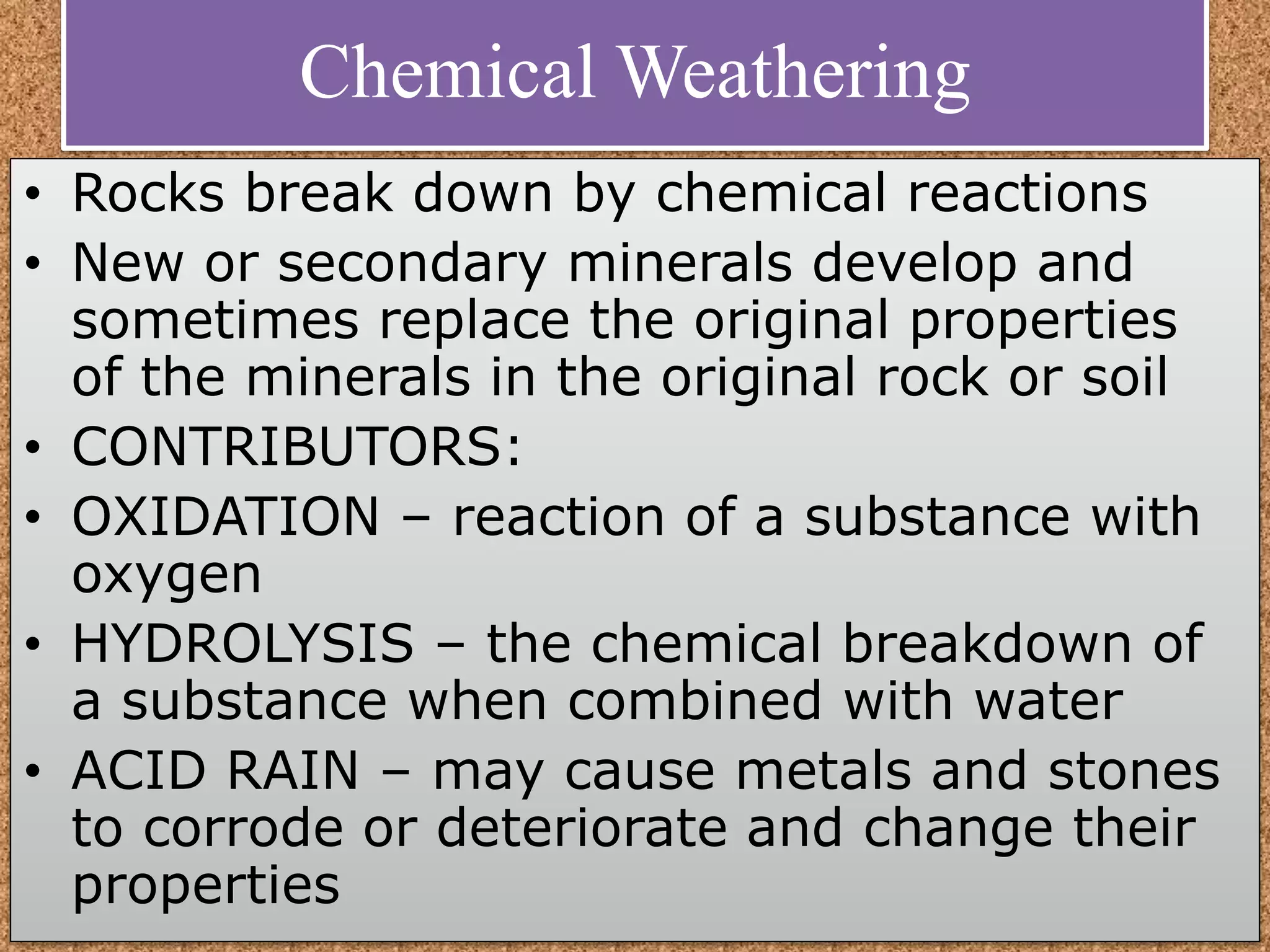
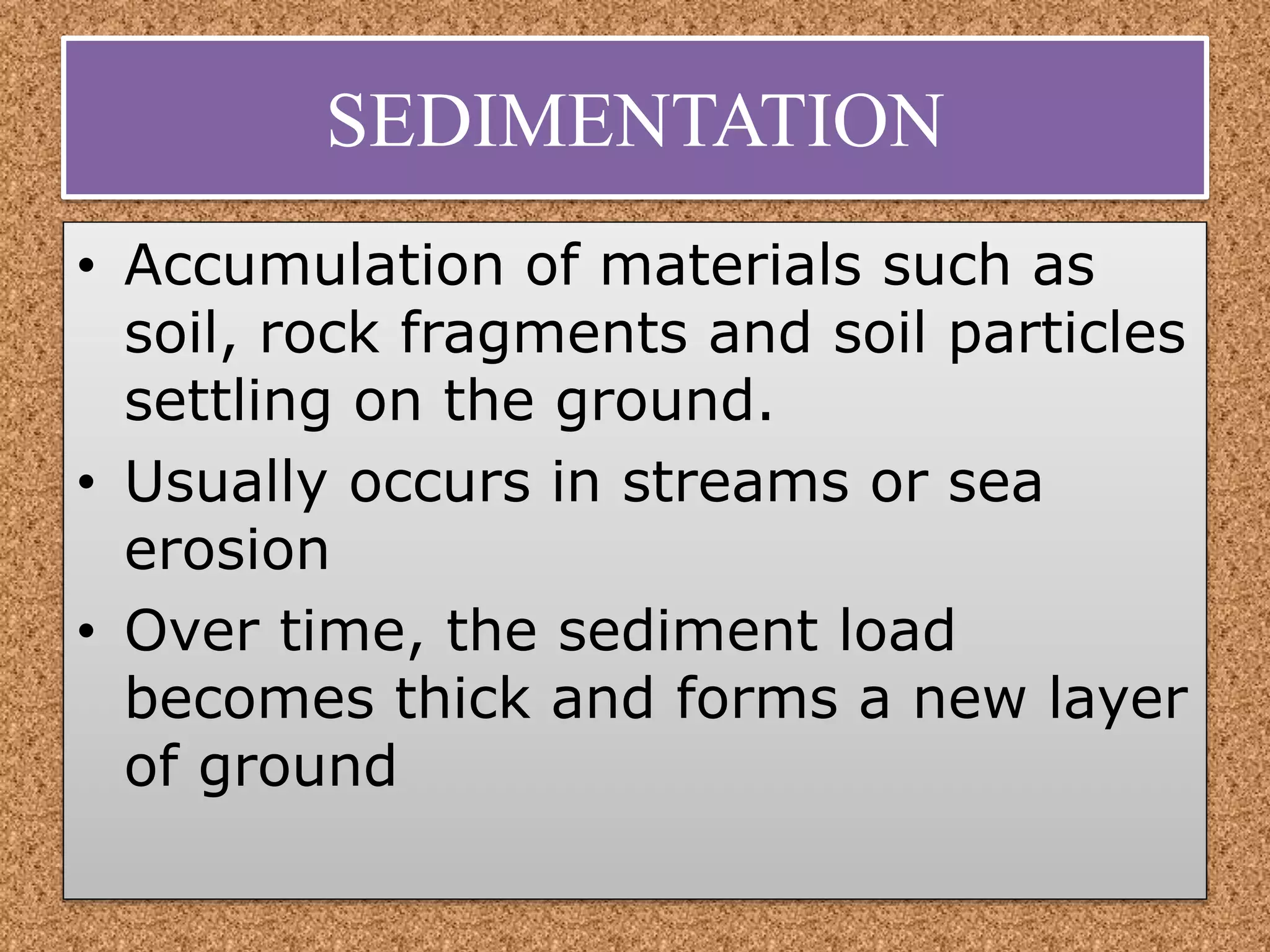
Geologic processes on Earth include exogenous and endogenous processes. Exogenous processes occur near the surface and include weathering, erosion, mass wasting, and sedimentation, which are driven by gravity, water, wind, and organisms. Endogenous processes occur within Earth and are driven by thermal energy in the mantle, resulting in magmatism, volcanism, metamorphism, and mountain building. While these processes shape the landscape and present risks, there may be no completely safe place, as all locations can be affected over millions of years.