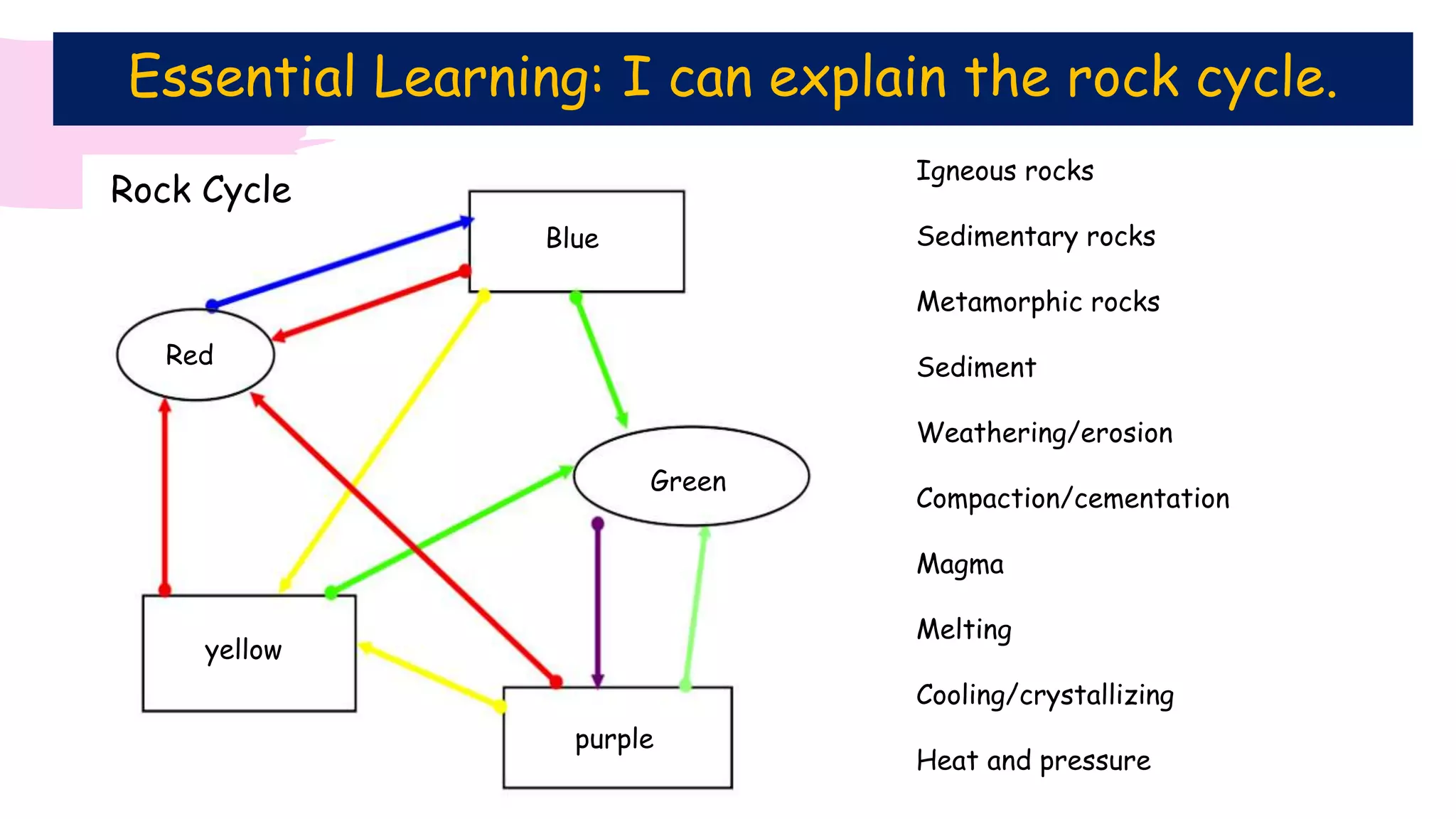
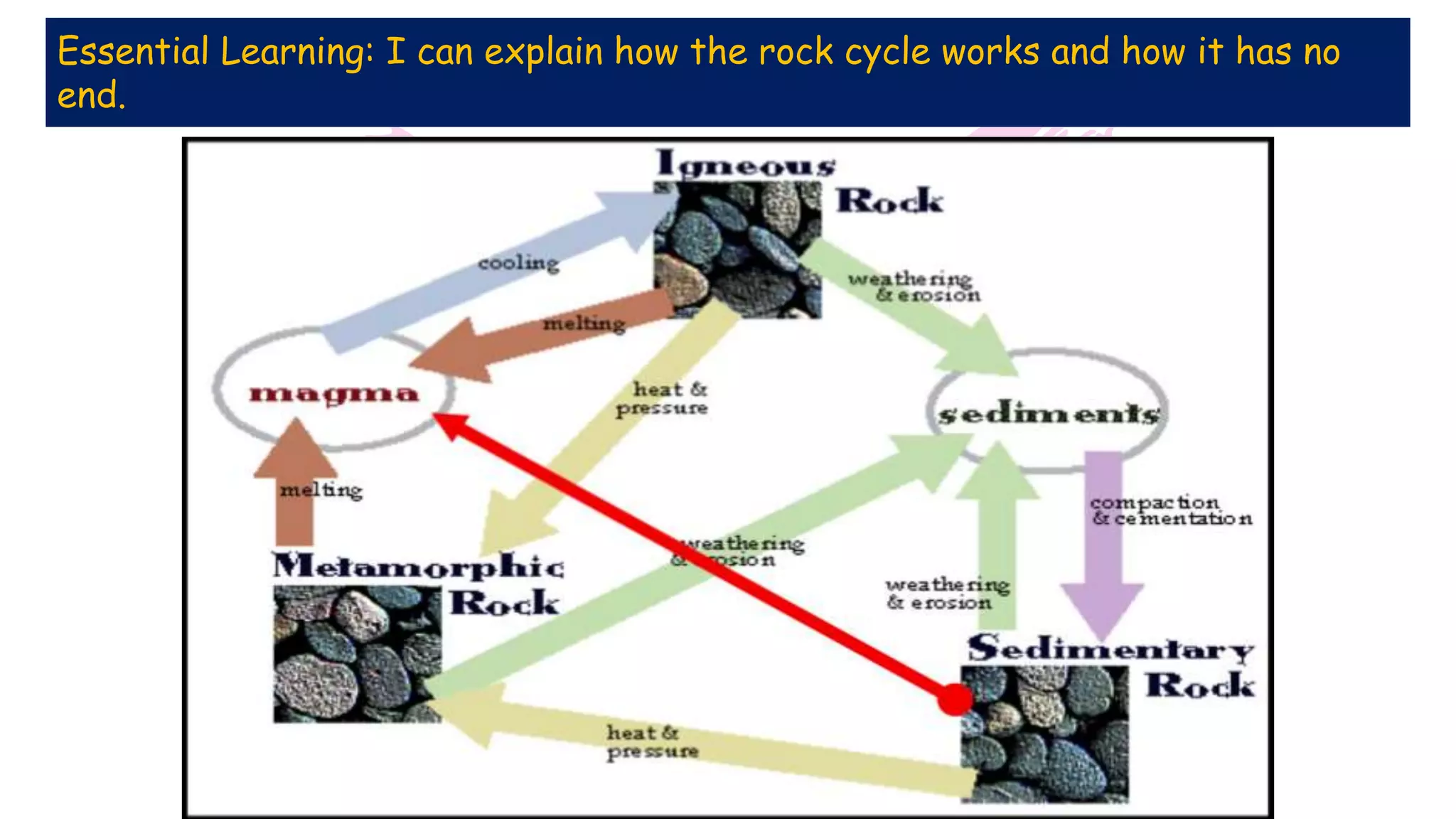
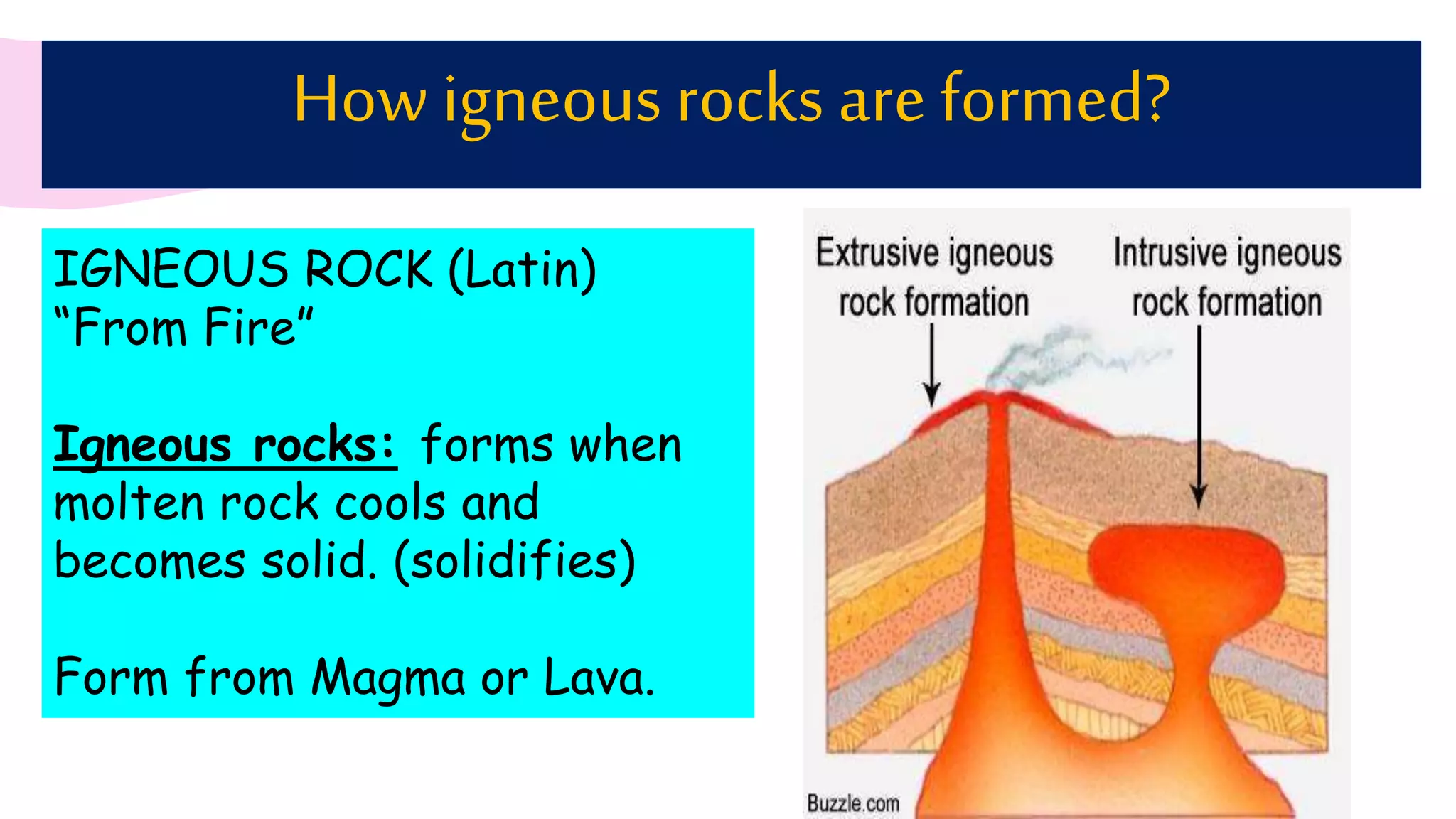
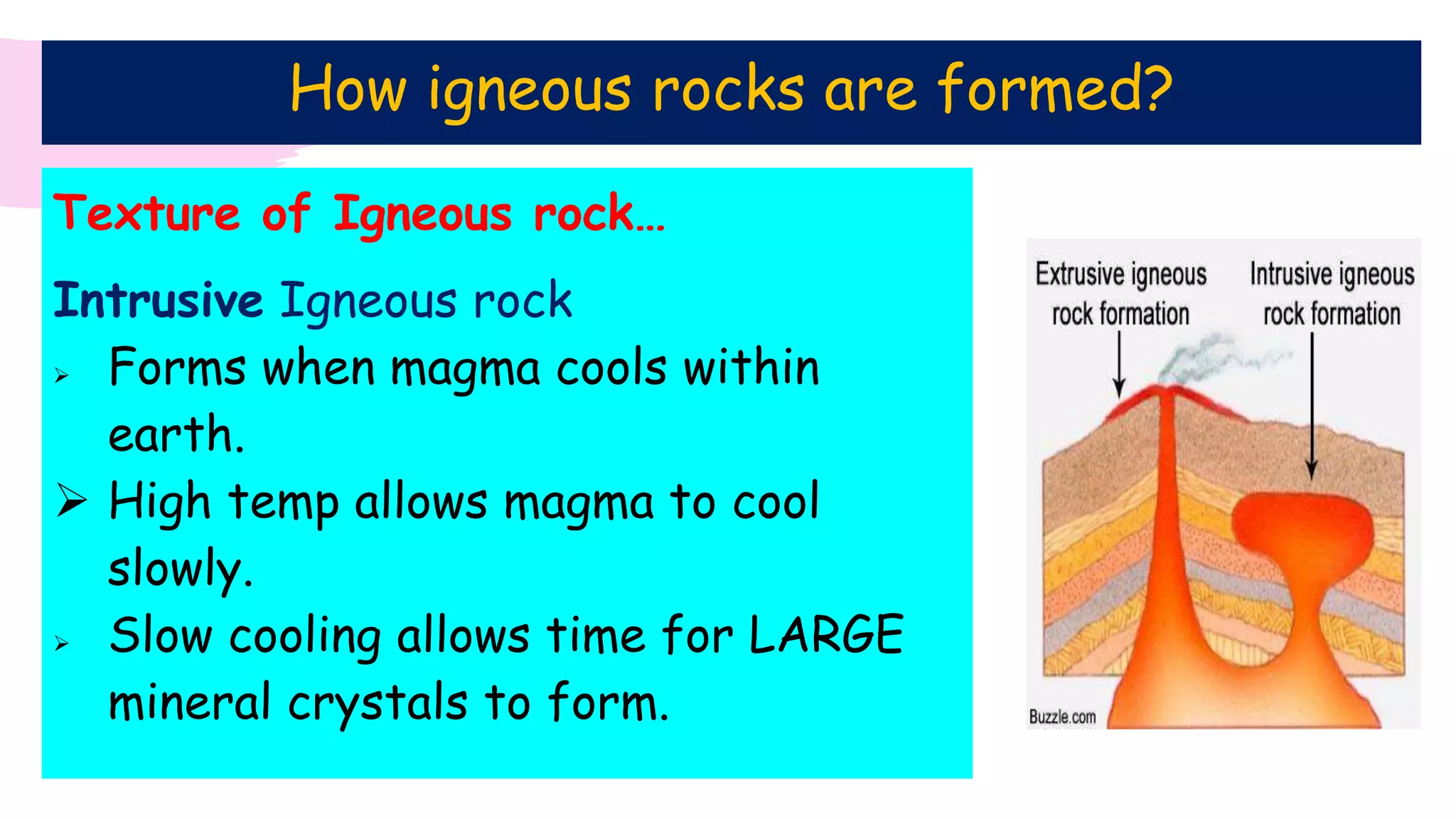
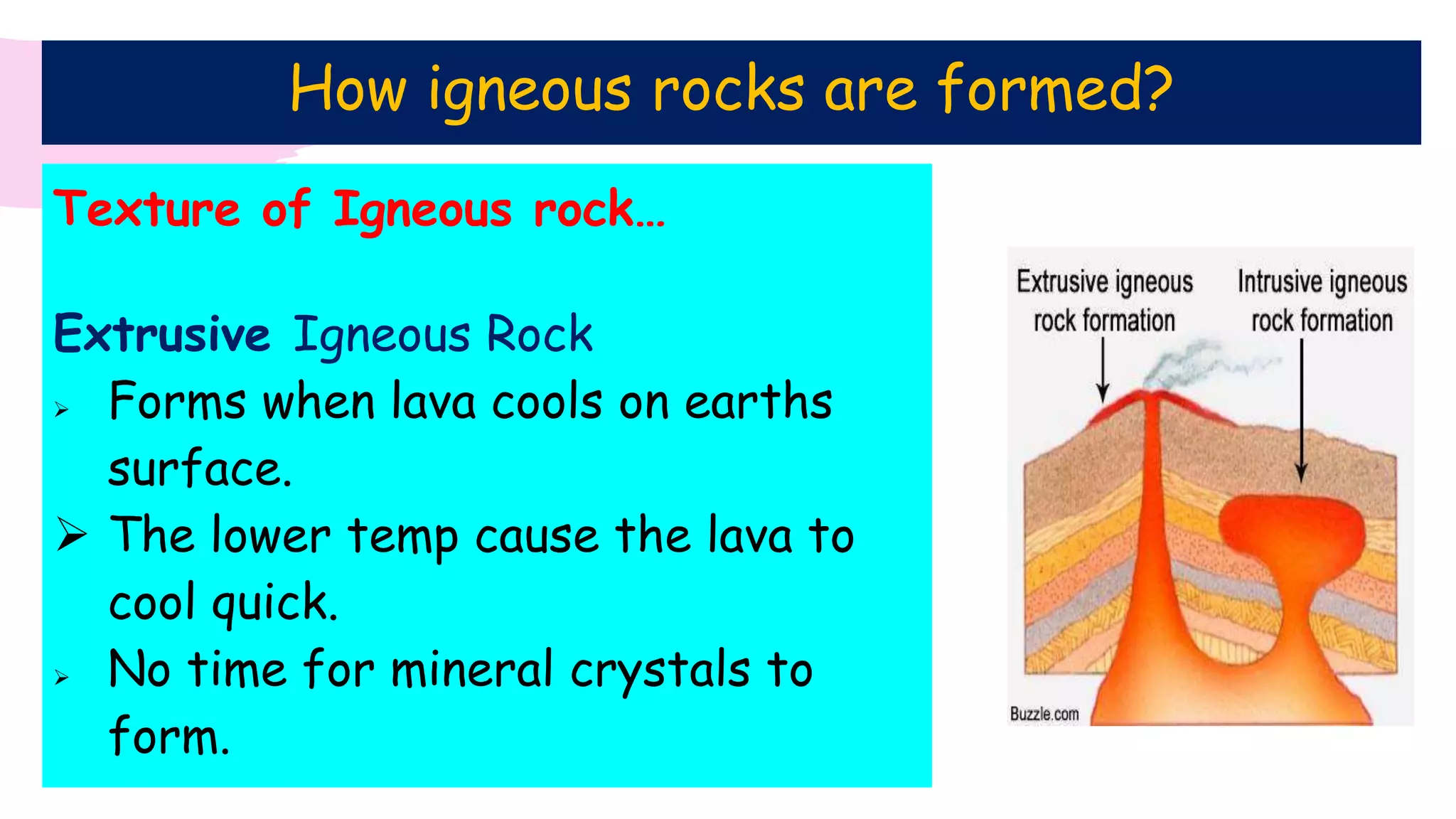
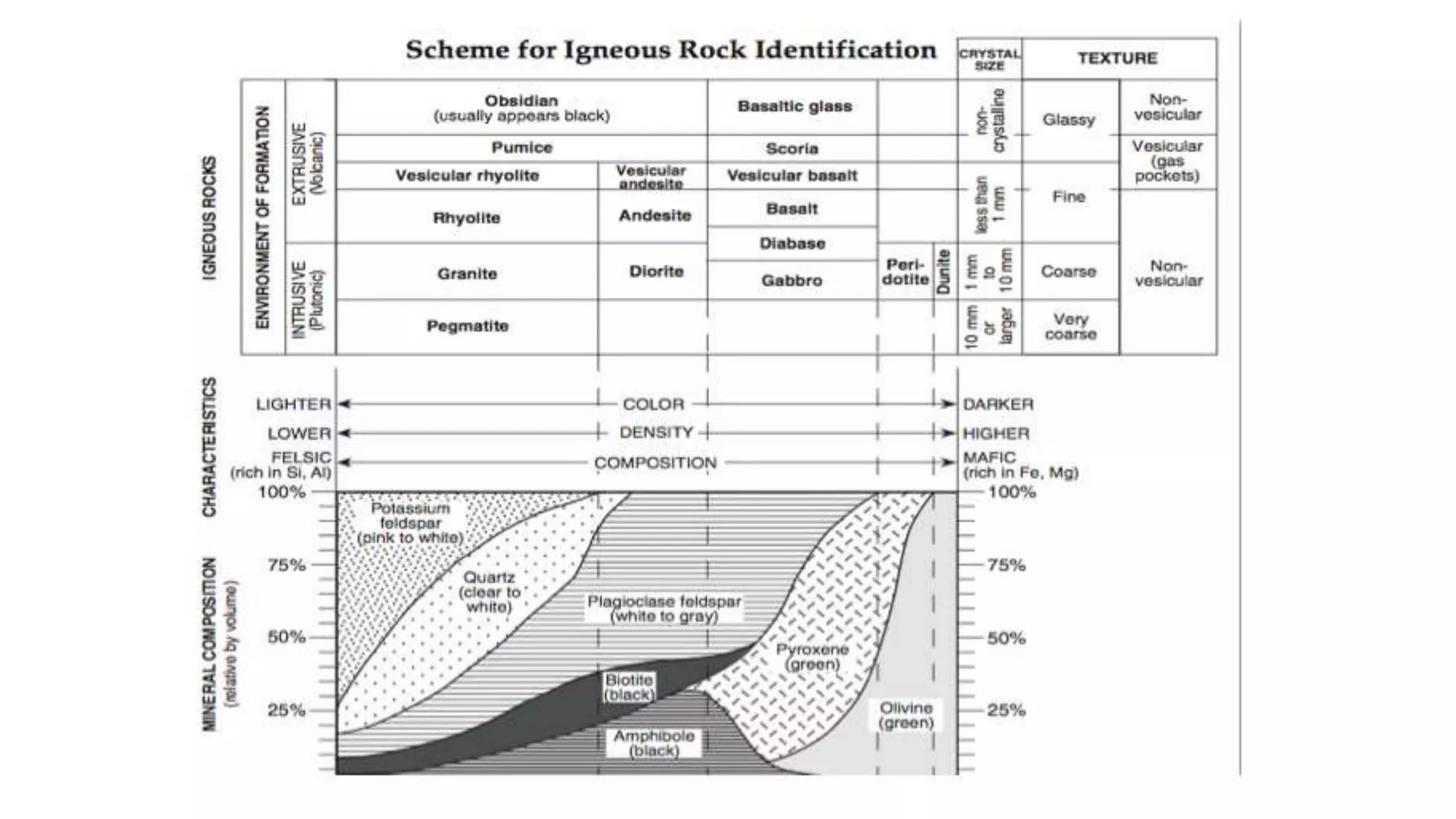
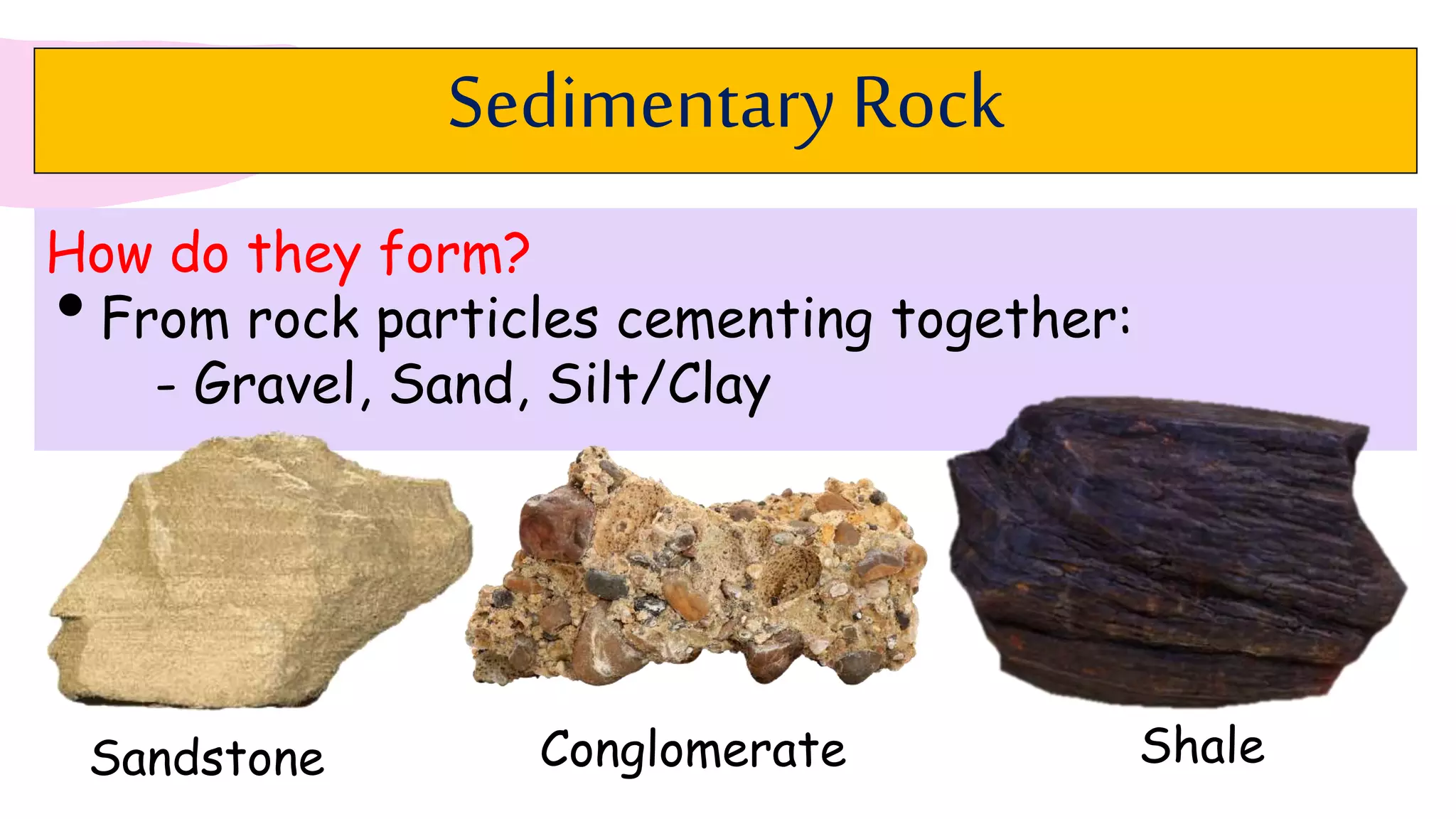
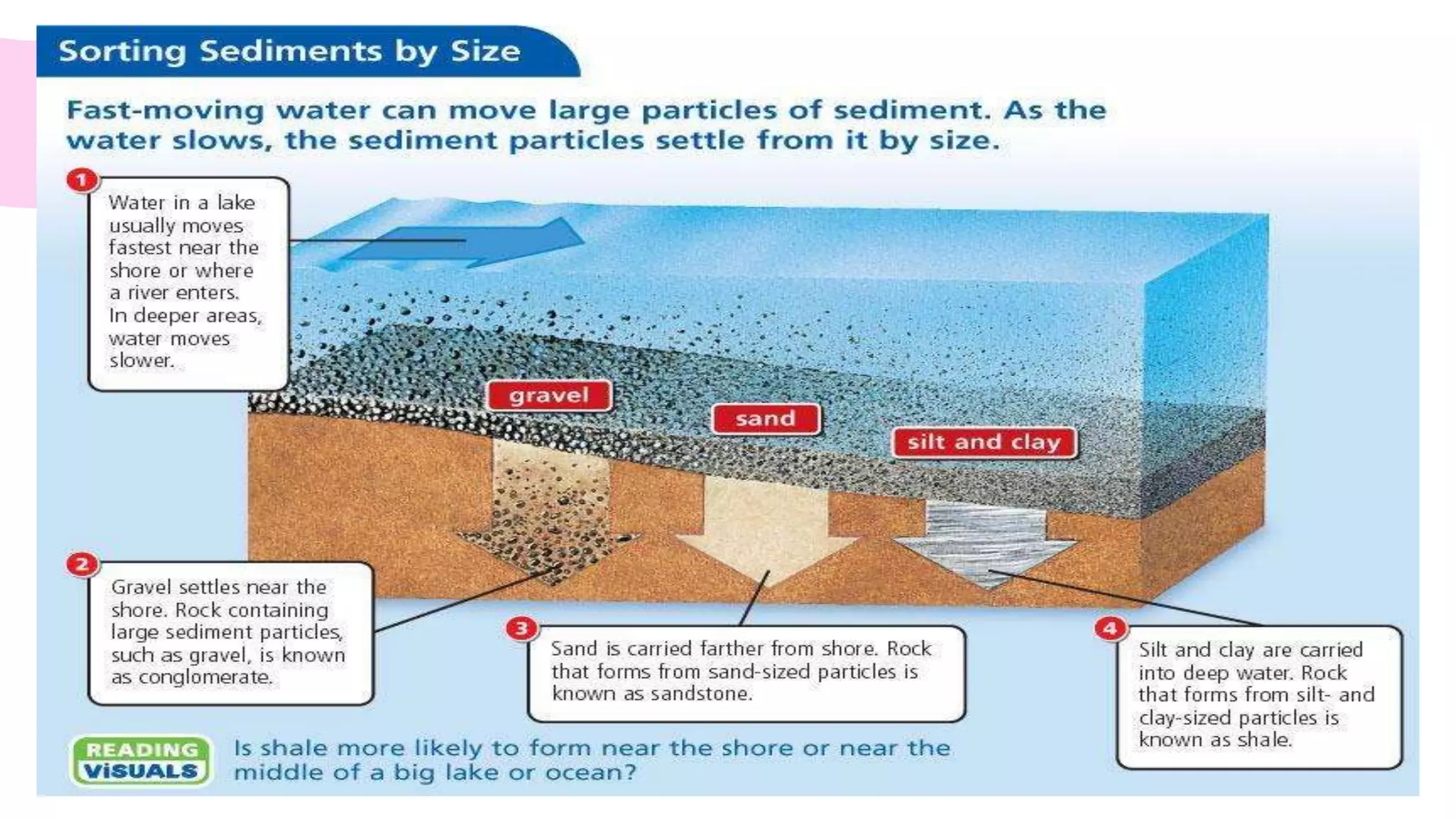
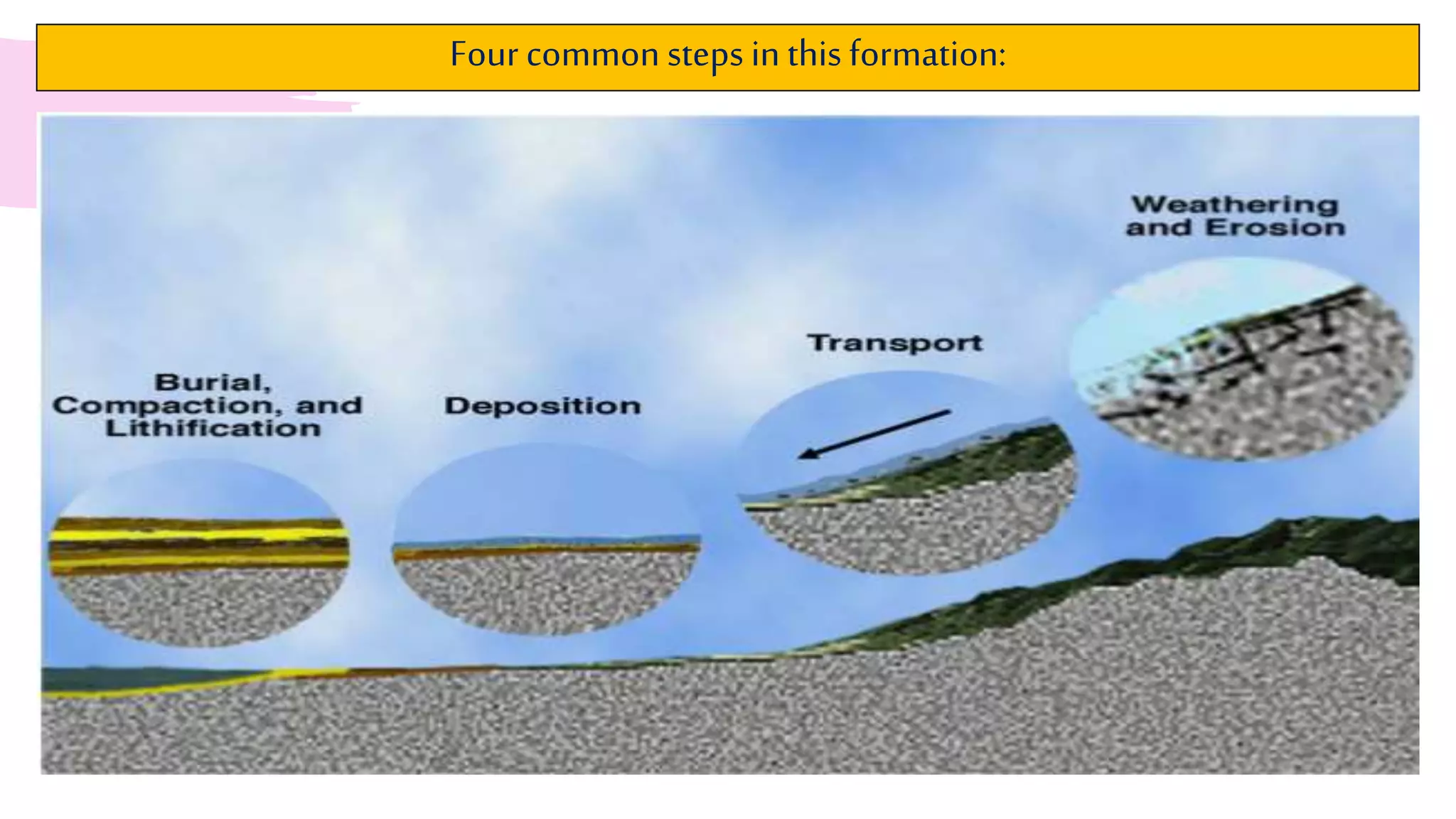
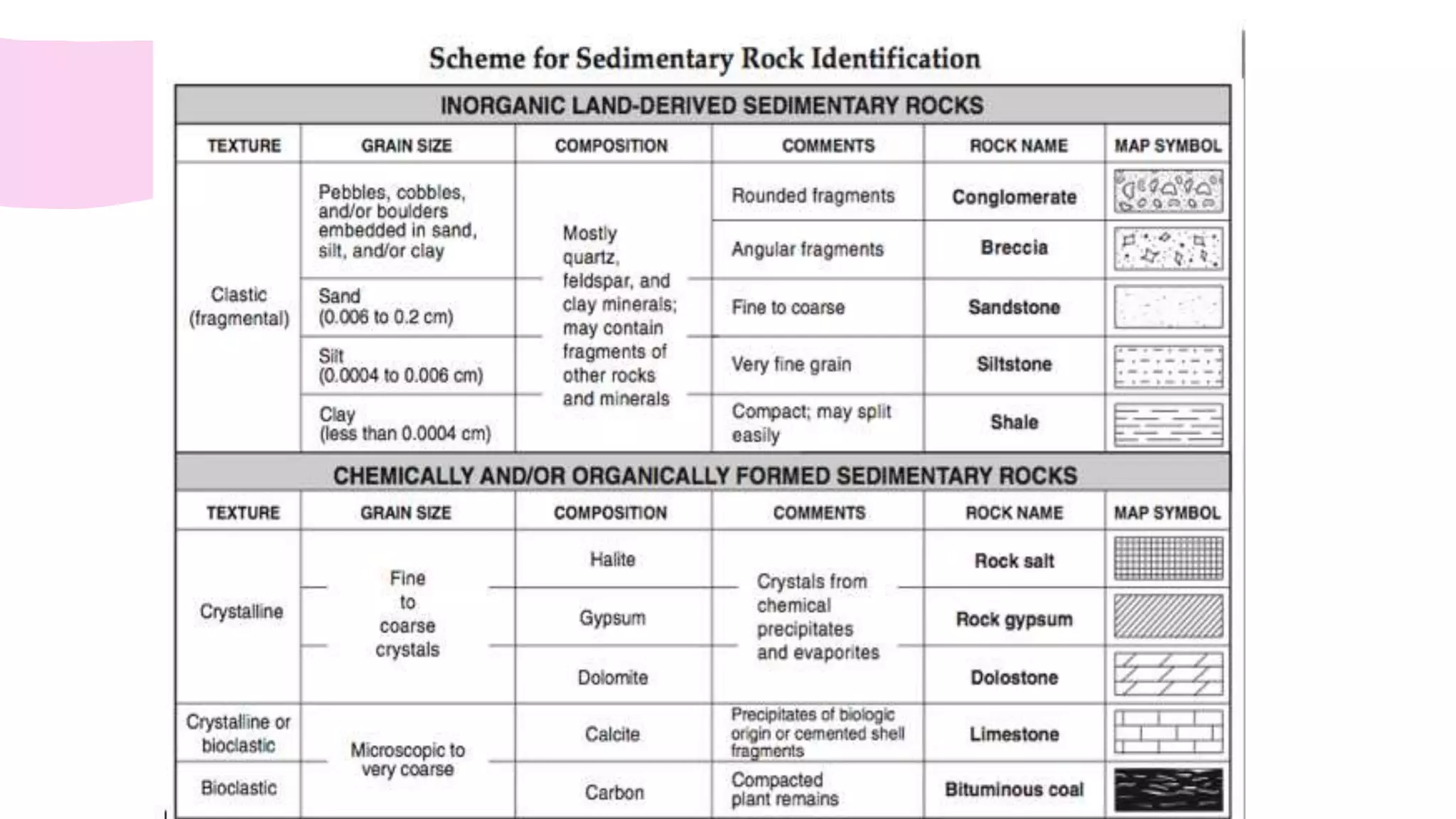
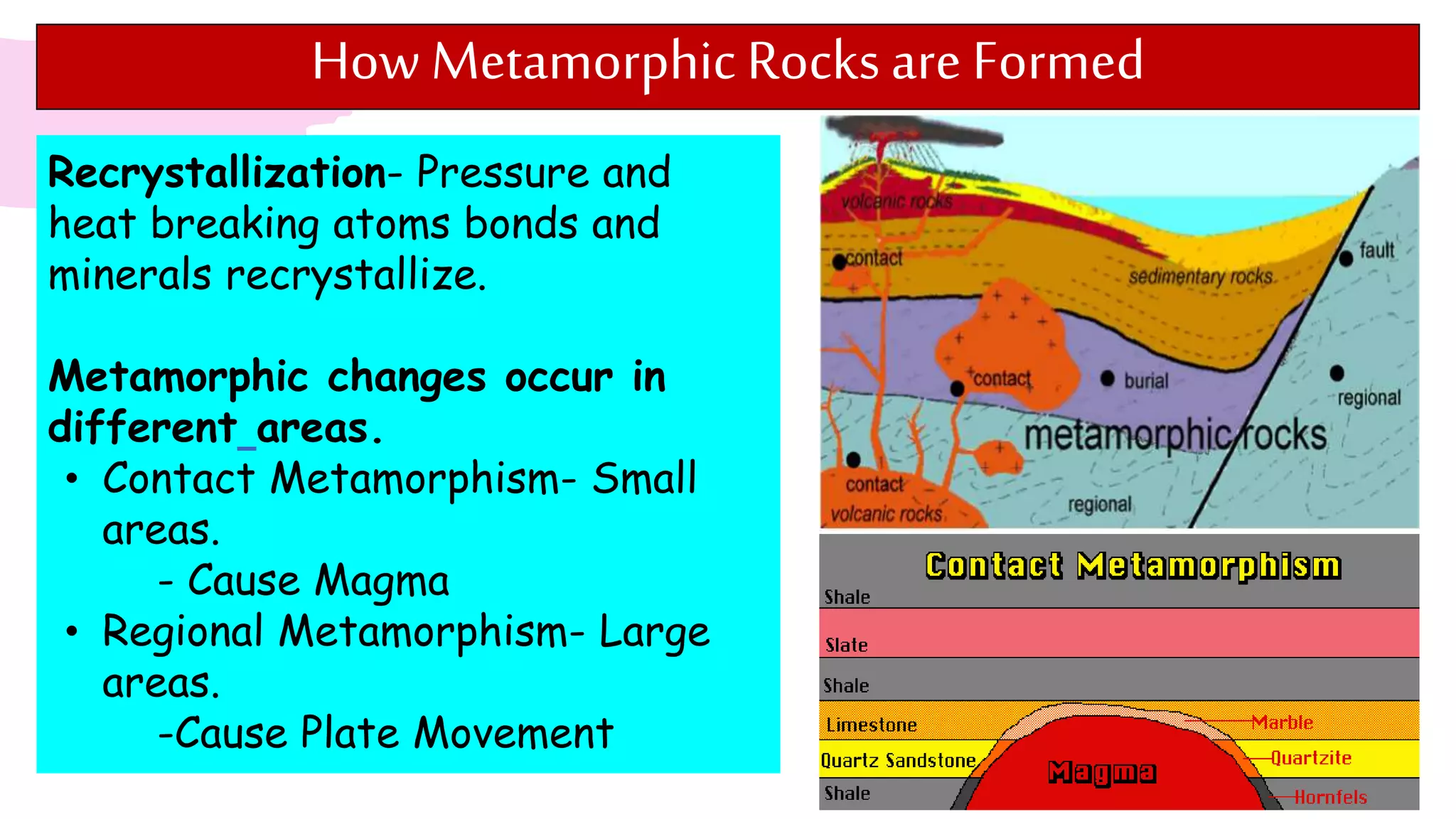
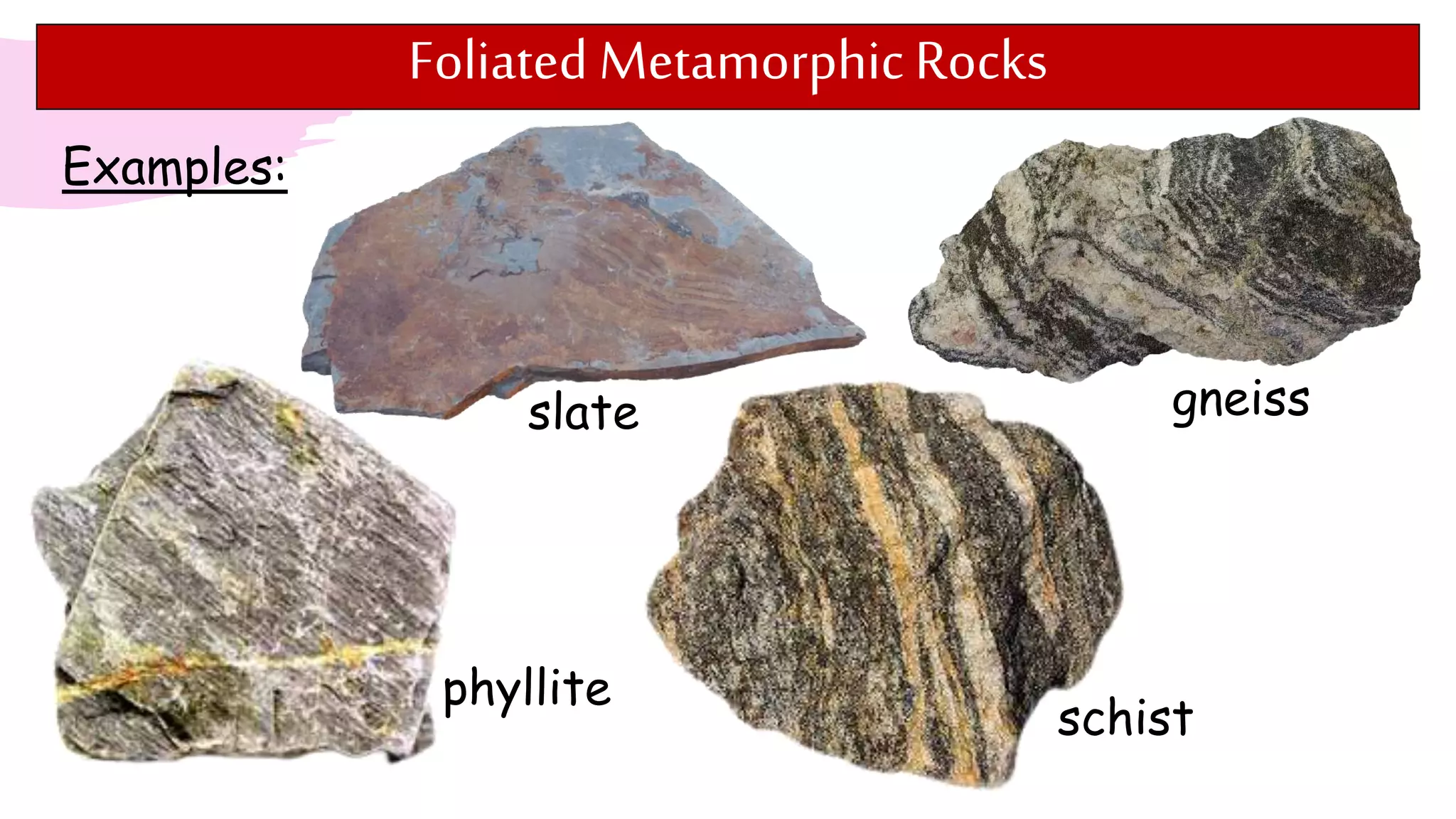
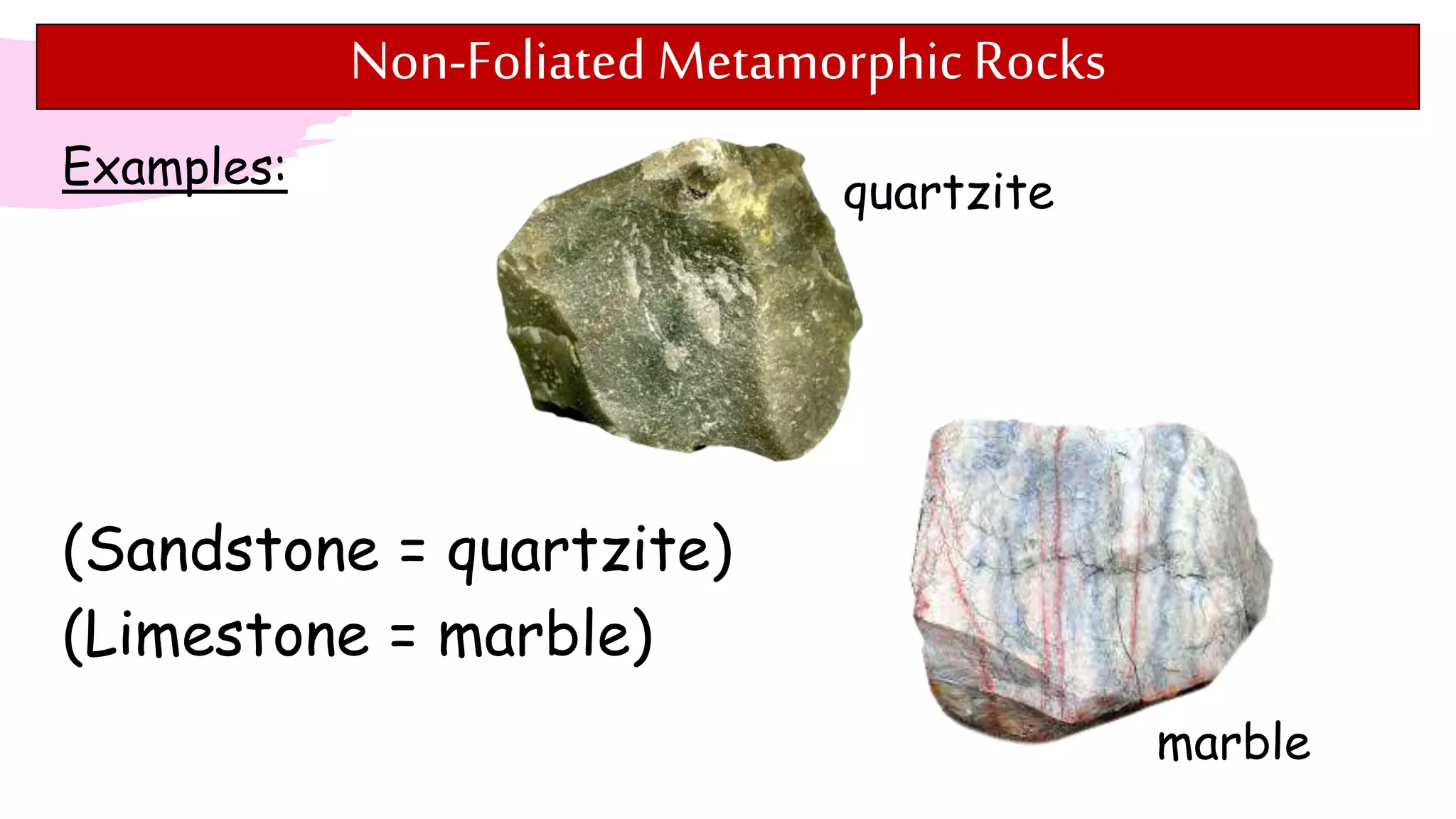
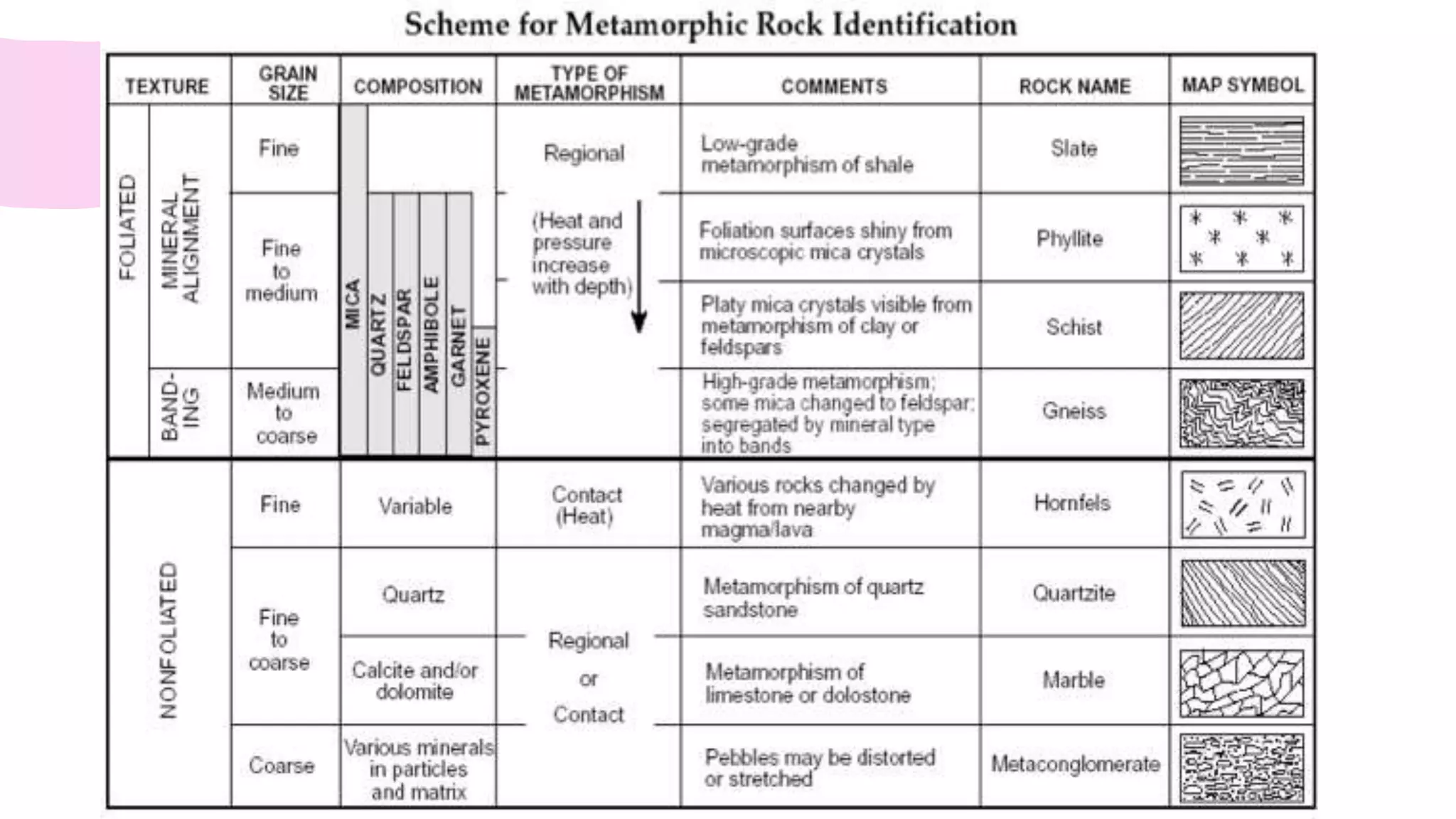
The document provides information about classifying and identifying different types of rocks. It discusses three main types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form when molten rock cools and solidifies. Sedimentary rocks form through the compaction or cementation of sediments. Metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks are changed by heat or pressure. The document also provides guidance on identifying rock samples in hand samples and describes key characteristics of different rock types.