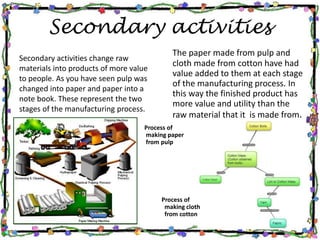
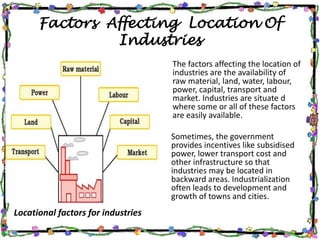
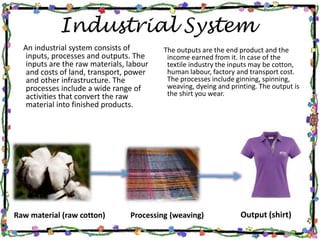
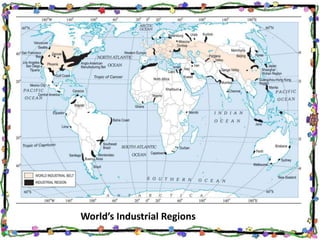
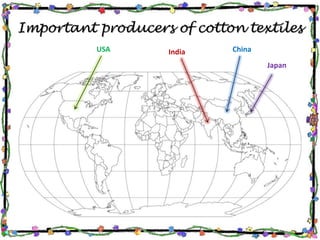
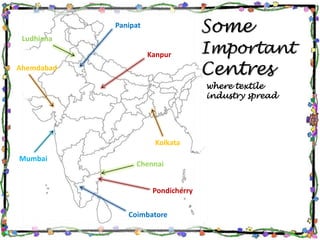
The document discusses the textile industry. It provides details about cotton textile industry centers in important locations like Ahmedabad and Osaka. The key factors responsible for the development of textile industry in Ahmedabad include easy availability of raw cotton, suitable terrain, skilled labor supply, and well-developed transportation network. For Osaka, factors include availability of plain land, suitable climate, labor supply, nearby ports for trade, and water availability from the Yodo river. The cotton textile industry is one of the oldest industries and India and China are major global producers today.