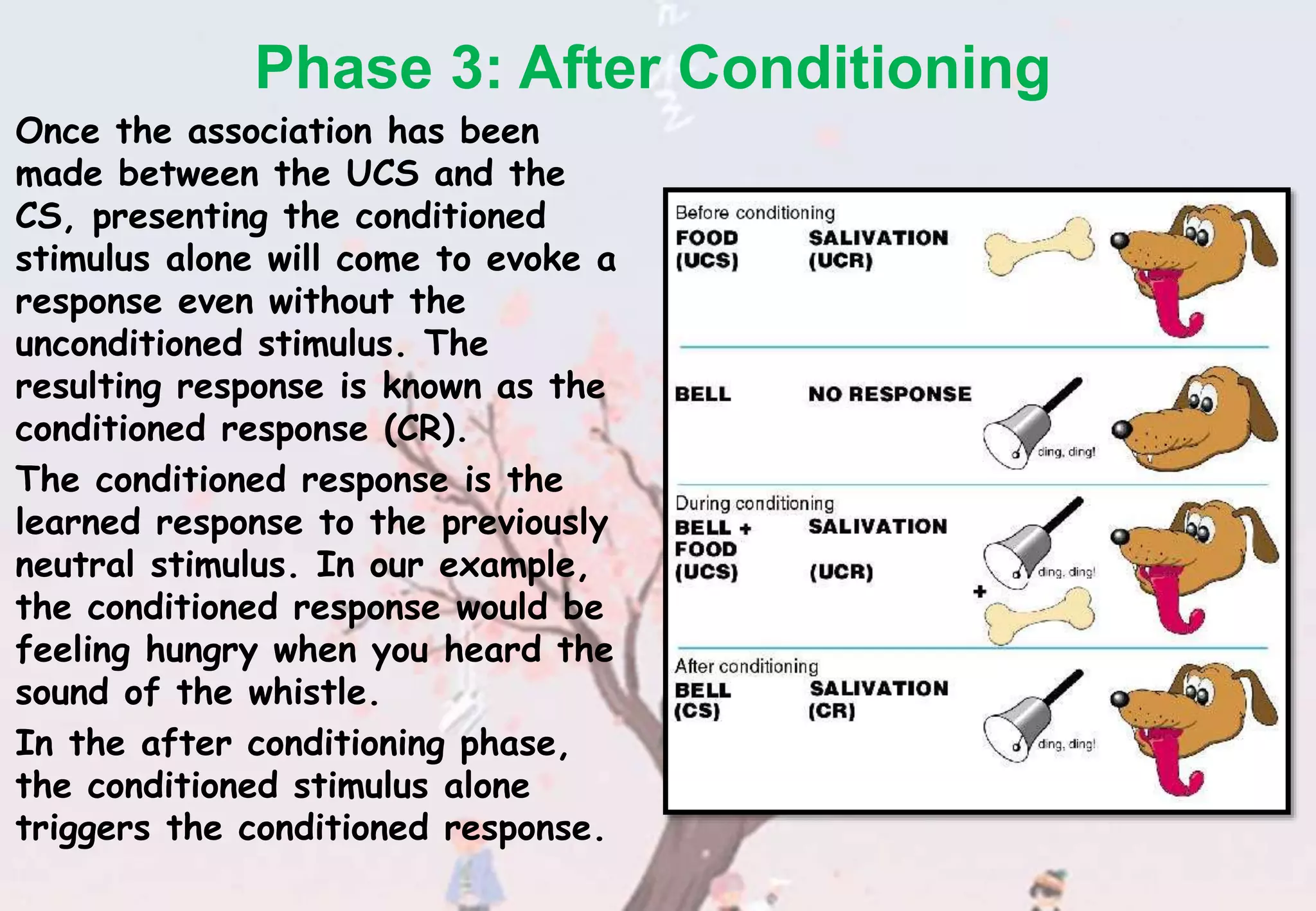
Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience, distinct from temporary changes due to factors like drugs or fatigue. Classical conditioning, a key type of learning, involves pairing a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to create a conditioned response, as demonstrated by experiments like Pavlov's dogs and Watson's work with Little Albert. There are several determinants of classical conditioning, including the timing and type of stimuli involved, which can significantly affect the learning process.