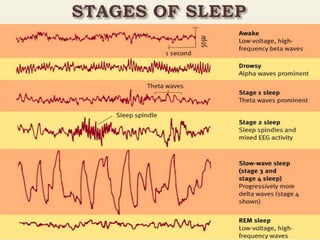
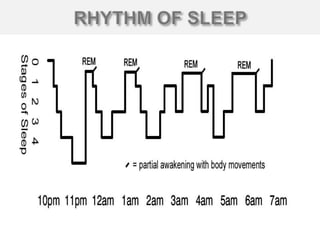
Sleep is one third of human life and is essential for rest, recovery, and memory consolidation. Our understanding of sleep comes from EEG, which measures brain electrical activity and shows different sleep stages. Lack of sleep can impair cognitive and immune functions, while sleep disorders like insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy cause disrupted sleep patterns. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery depending on the disorder.