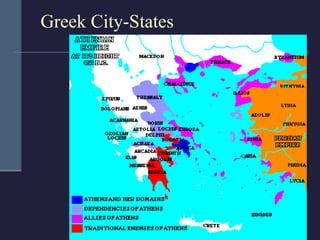
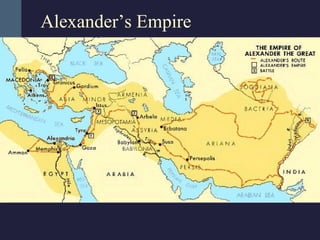
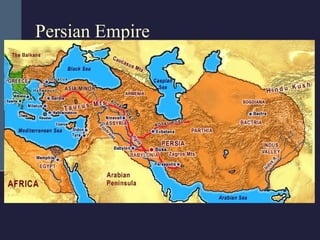
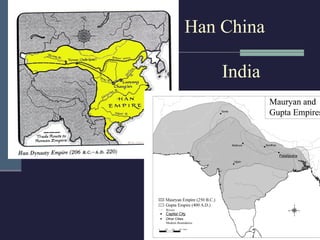
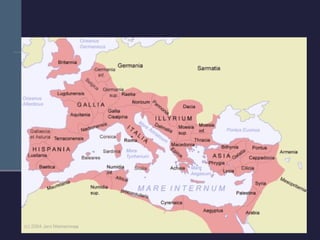
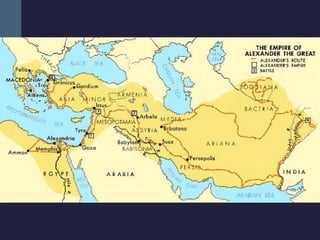
This document summarizes the key political developments of classical civilizations including Greece, Persia, China, India, and Rome. It outlines the rise and fall of major dynasties and empires, noting some similarities like centralized monarchies, bureaucracies, taxation, and use of religion to reinforce political authority. Differences are also highlighted such as Greece having independent city-states while India maintained a caste-structured society.