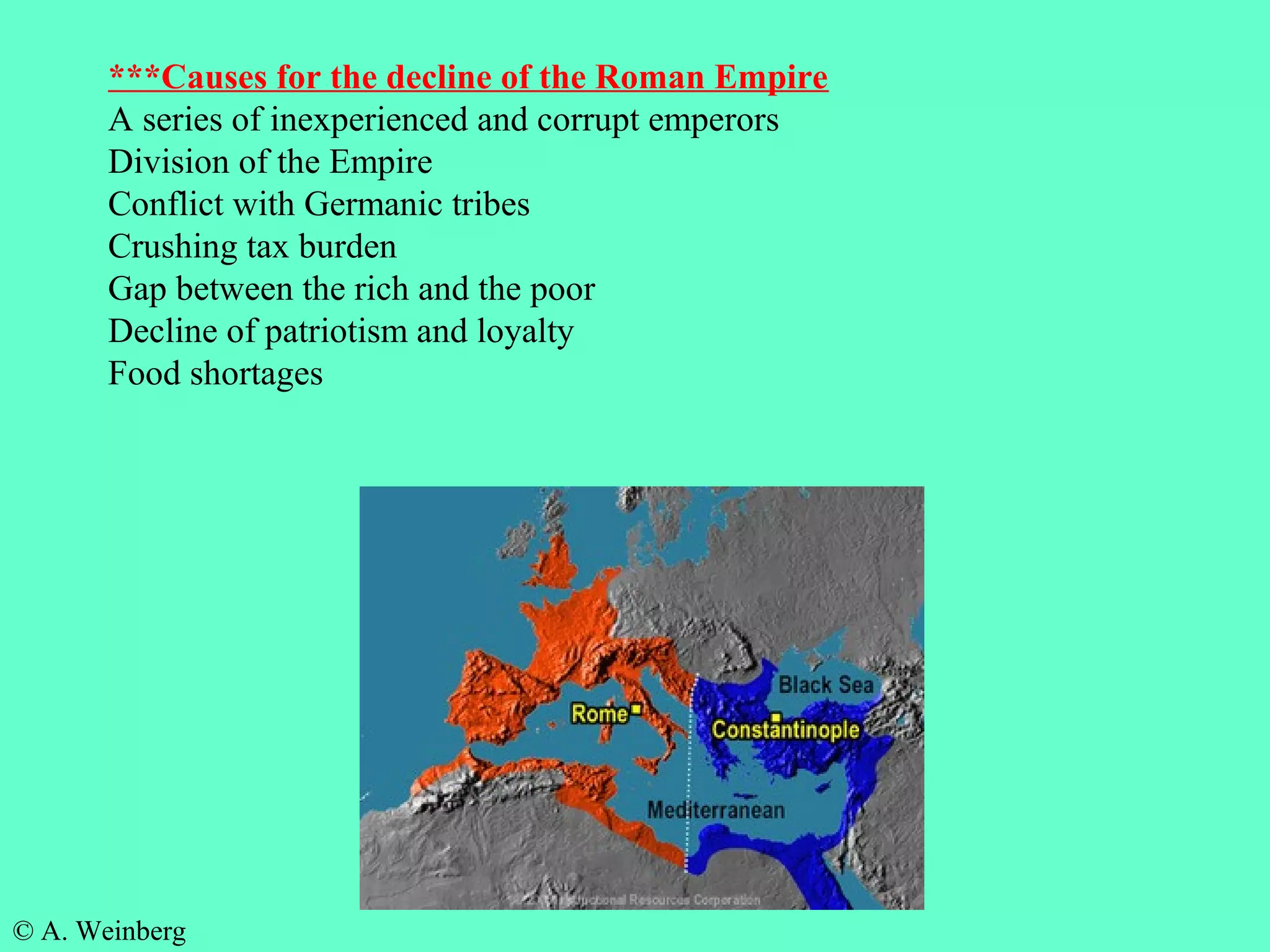
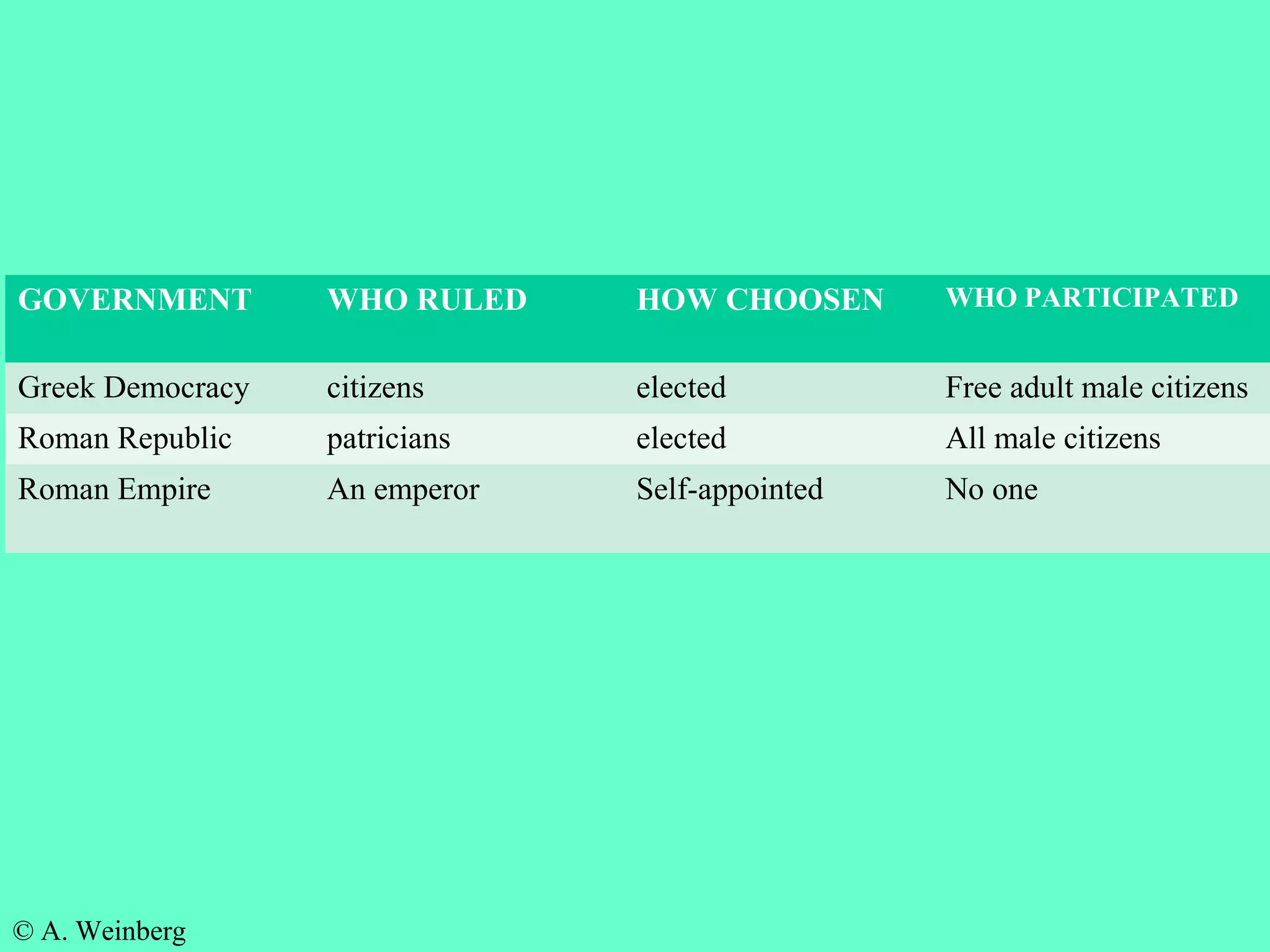
The document provides information about the contributions of Ancient Greece and Rome. It discusses how they influenced architecture through the Greek use of columns and Roman use of arches. It also discusses how they influenced government, with Greece being the birthplace of democracy and Rome establishing a representative democracy. Both civilizations made contributions to sports as well, with the Olympics originating in Ancient Greece.