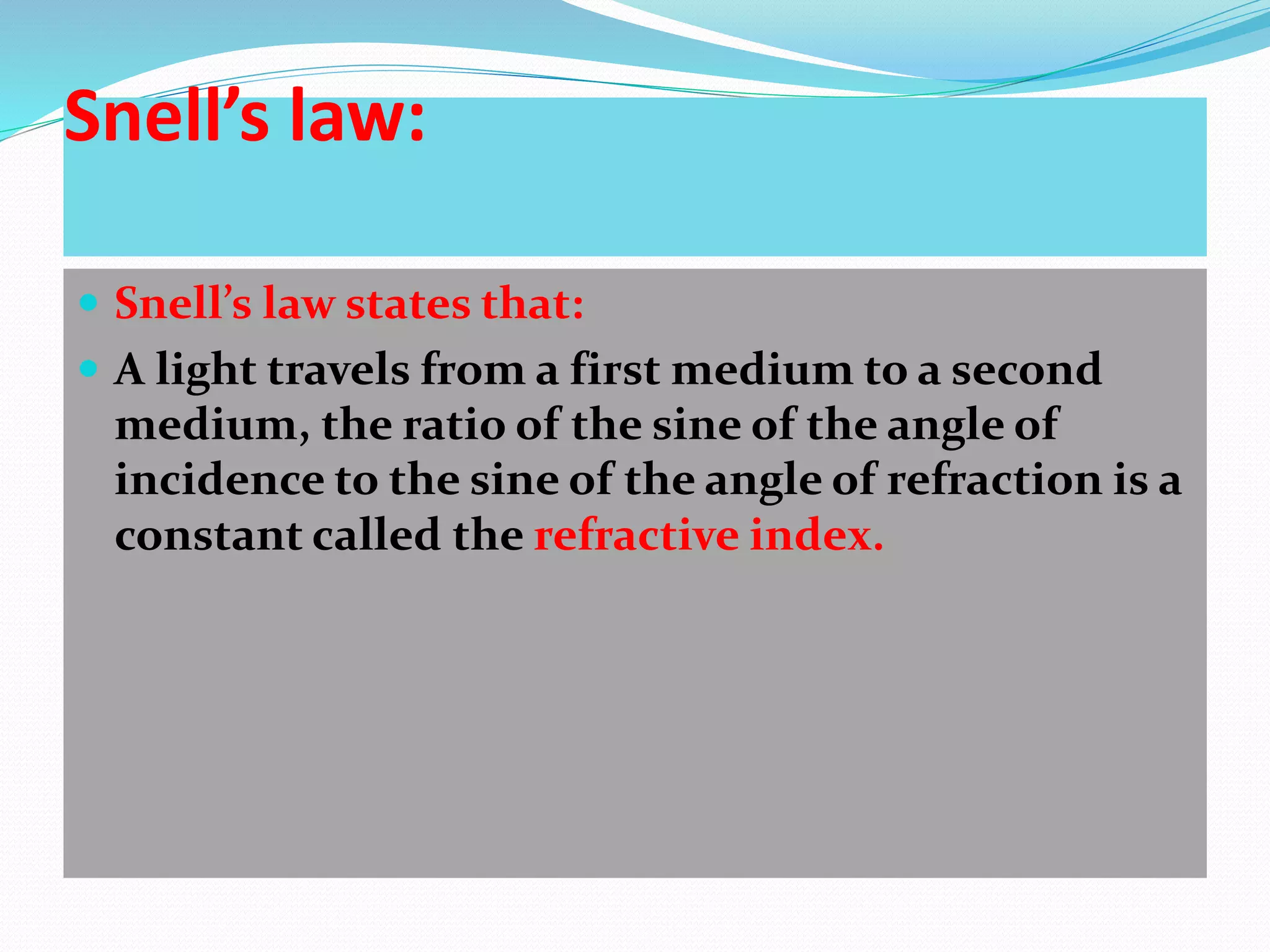
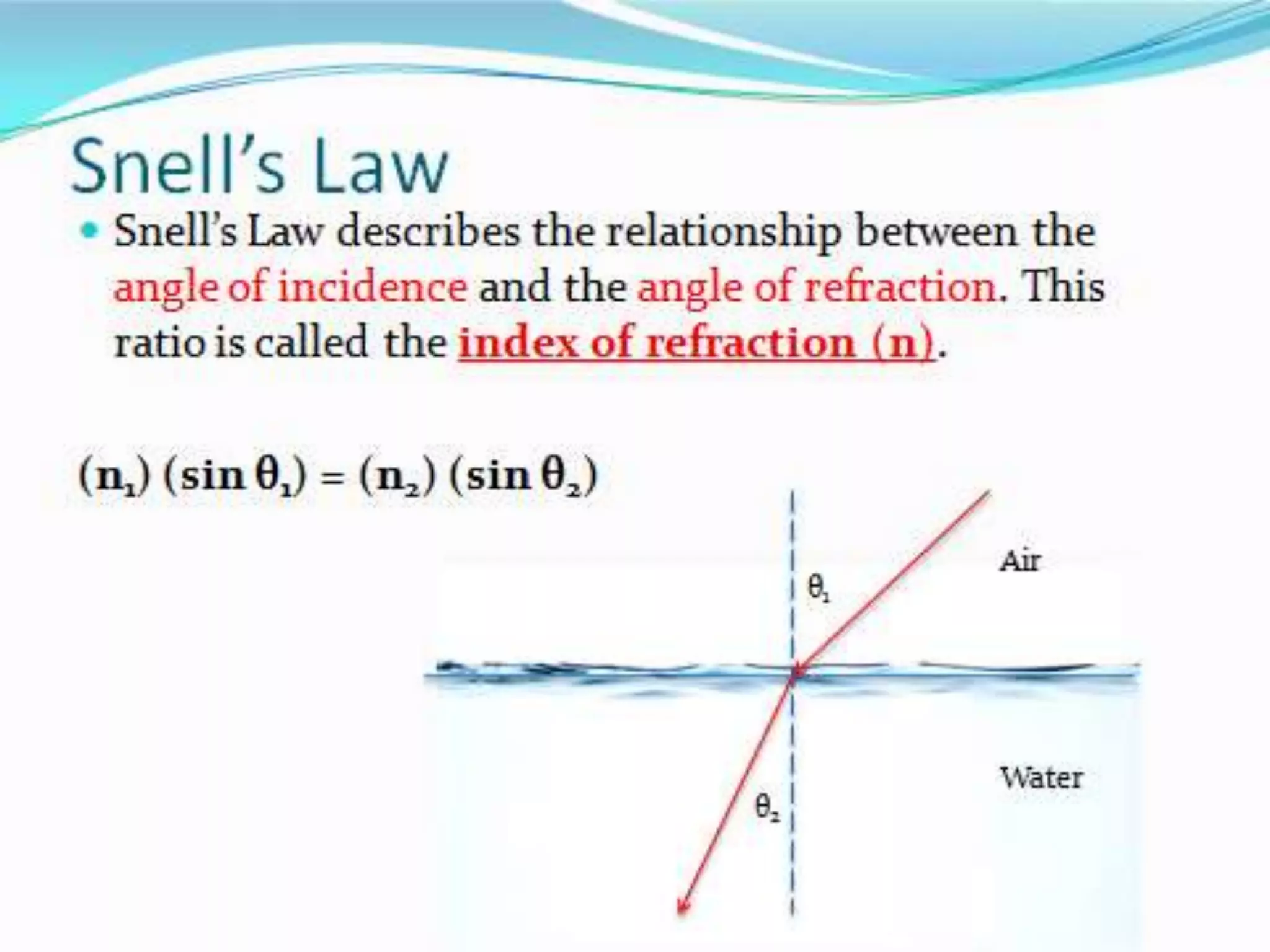
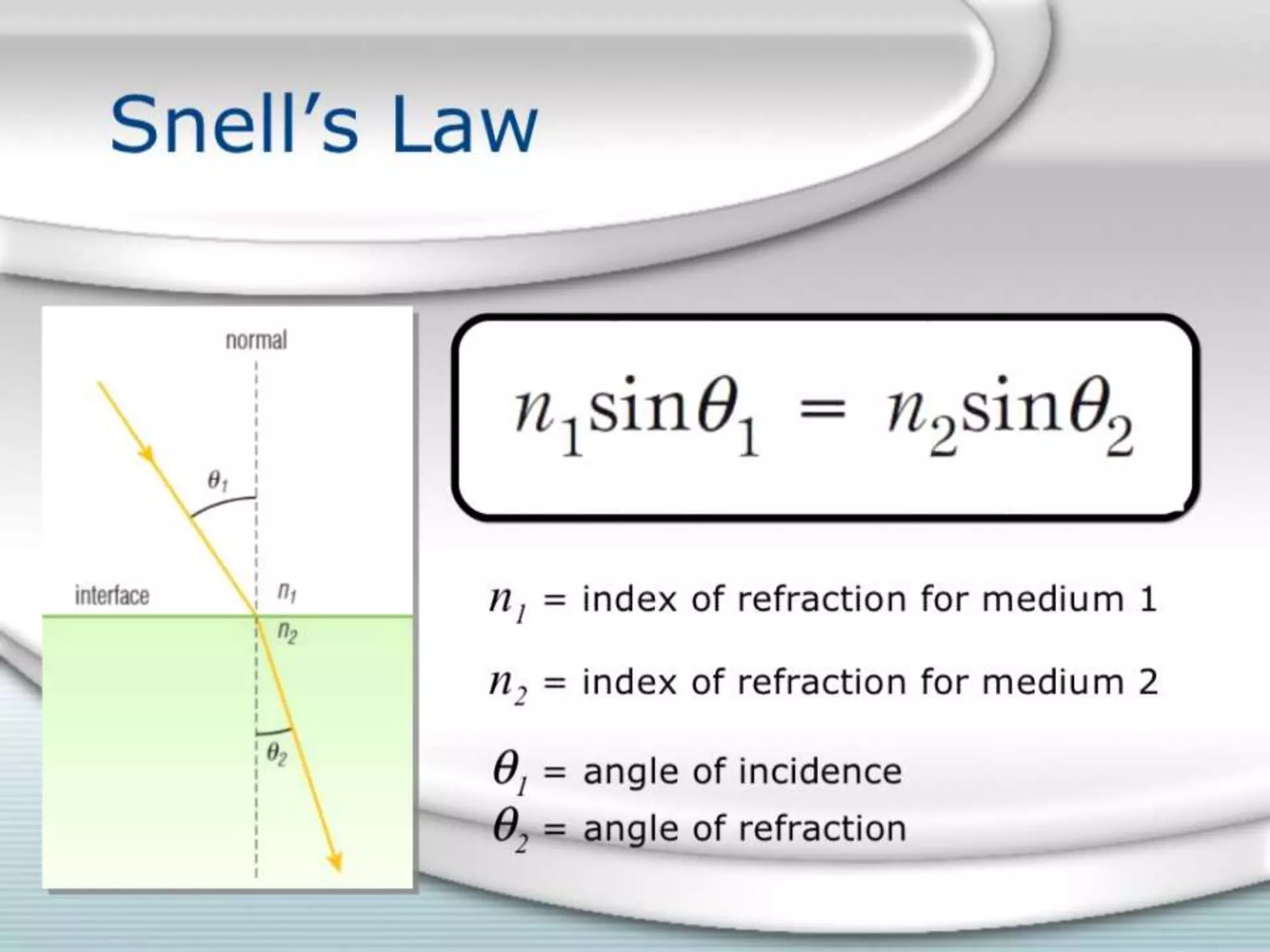
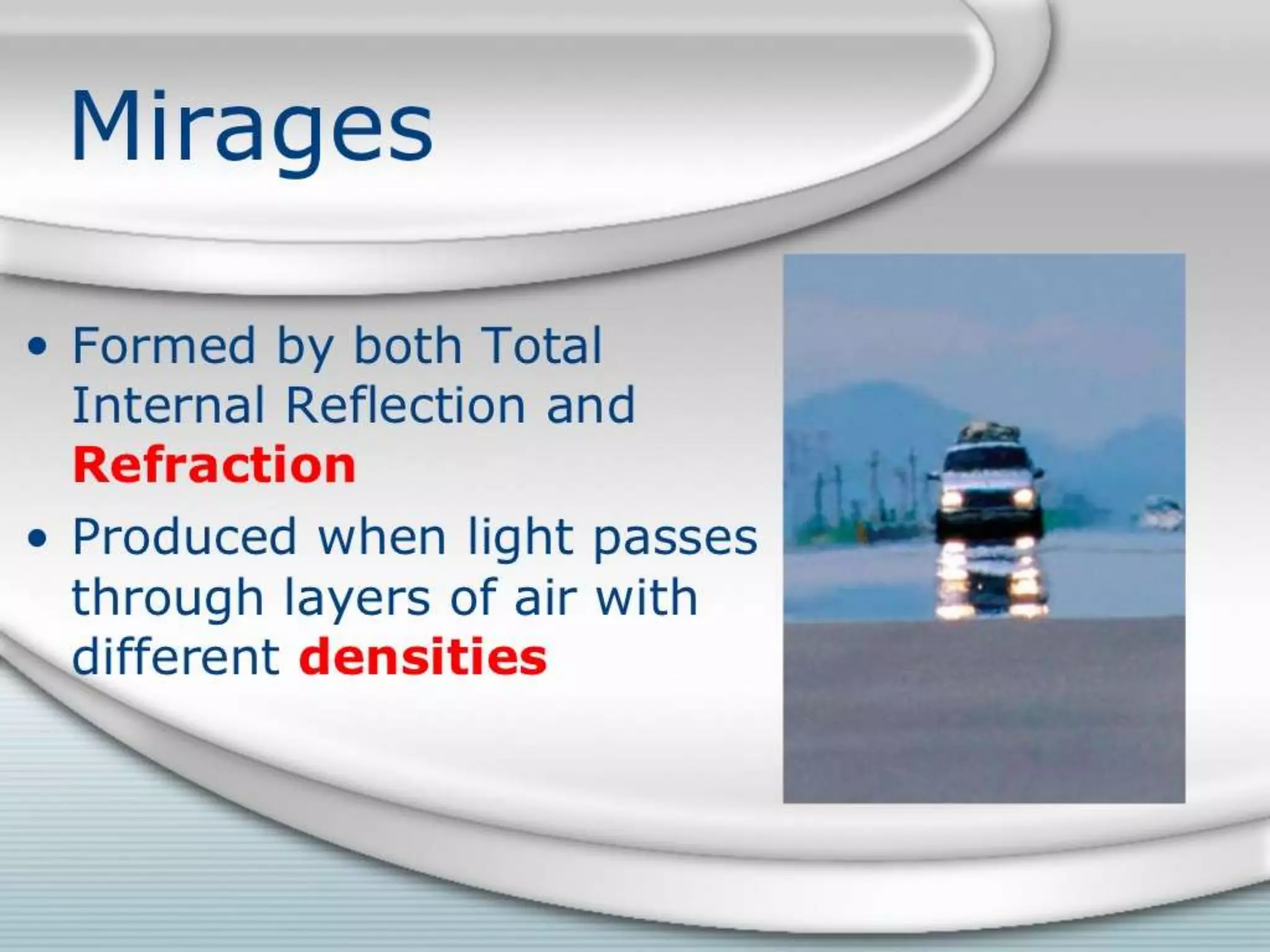
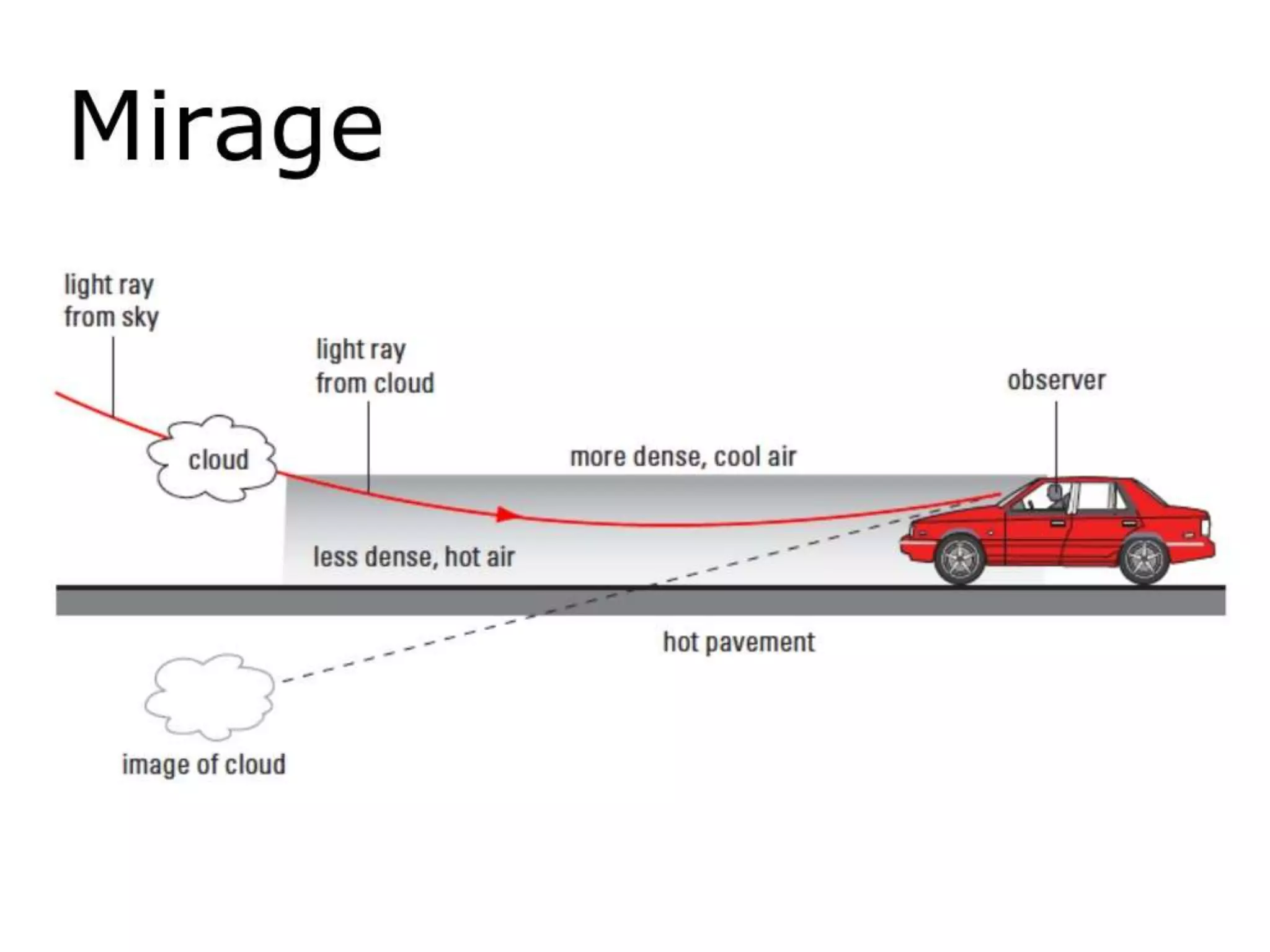
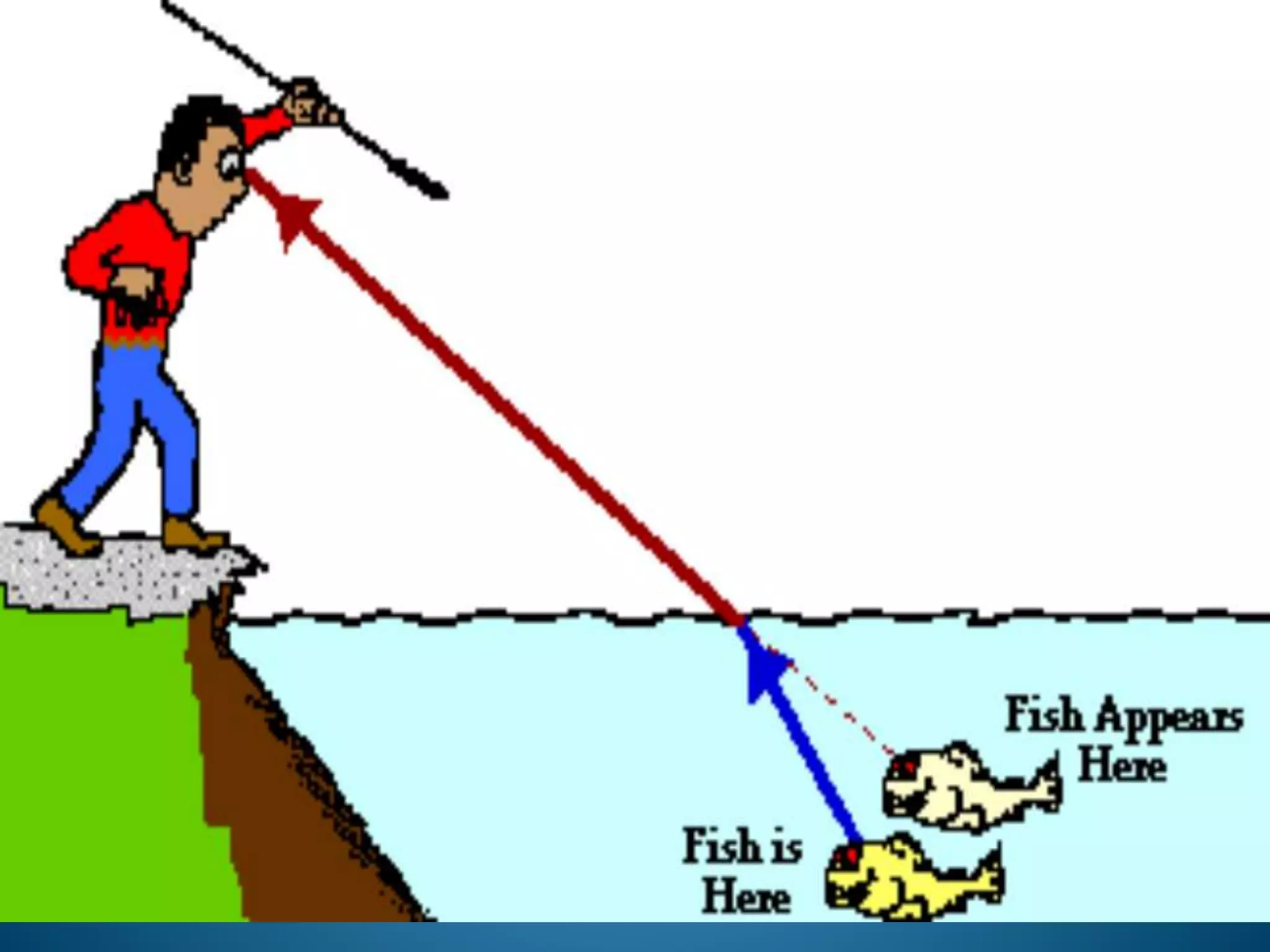
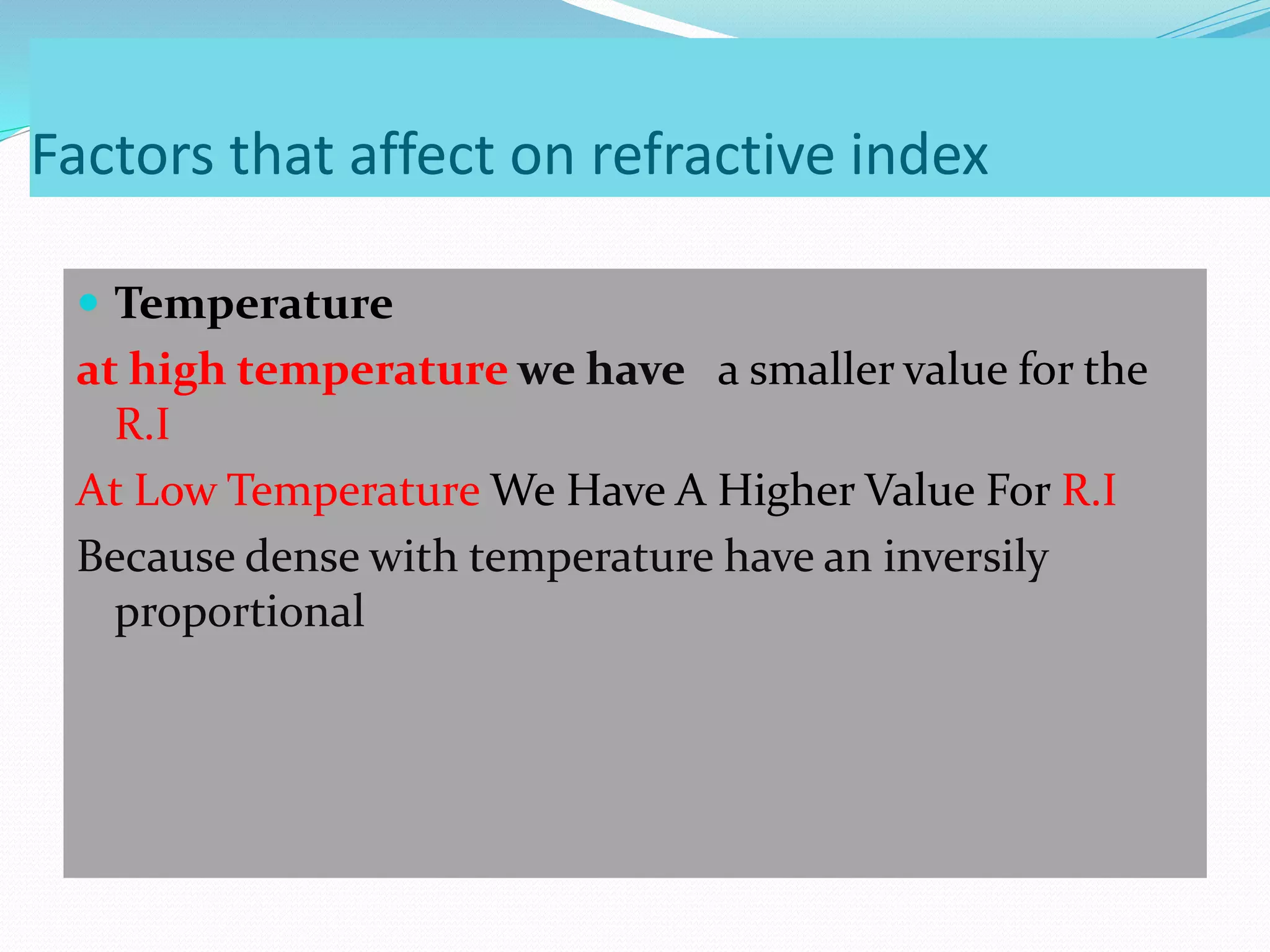
This document discusses refractive index and related concepts. Refractive index is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a substance. It depends on factors like the density, temperature, wavelength of light, and composition of the material. Snell's law describes how light bends when passing from one medium to another with a different refractive index. Refractive index is used in applications like determining the concentration of solutions, calculating lens power, and identifying substances.