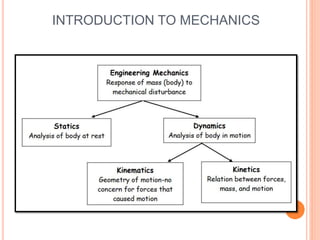
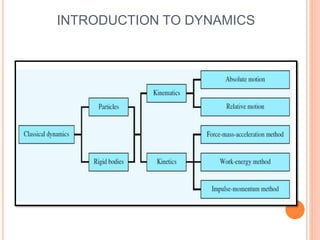
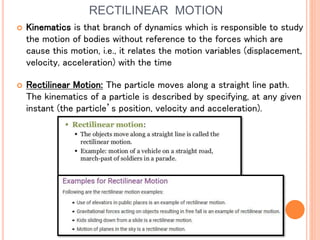
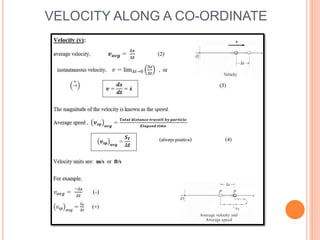
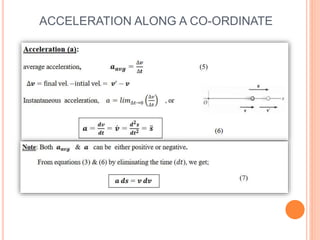
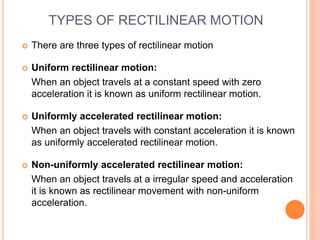
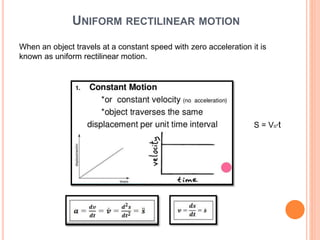
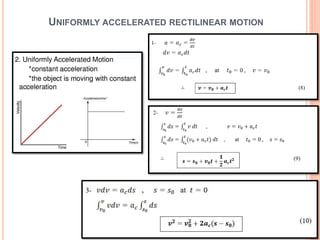
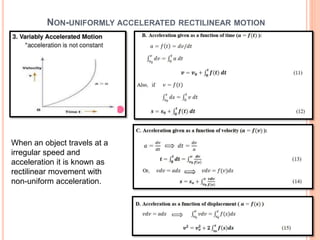
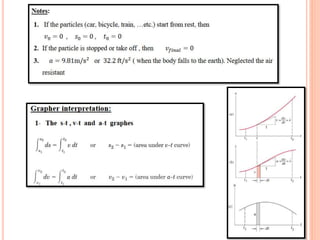
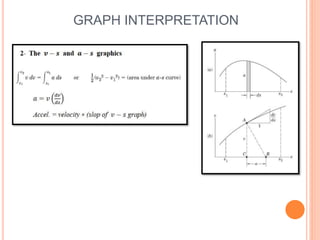
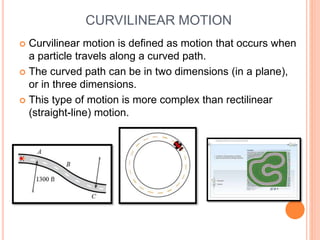
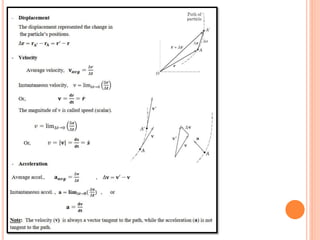
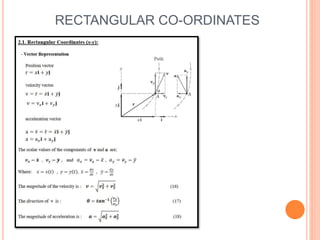
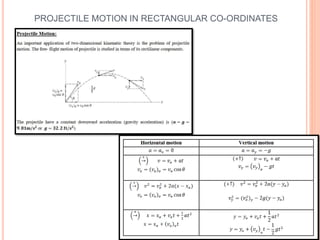
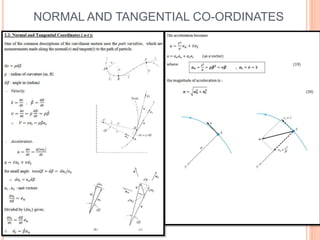
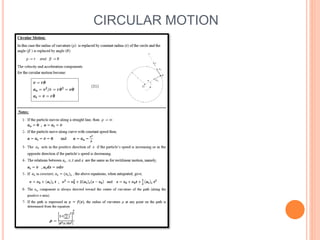
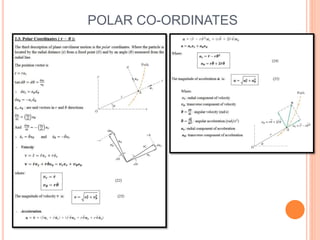
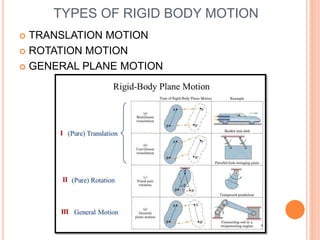
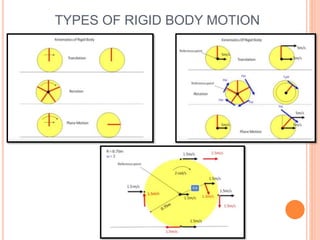
This document provides an introduction to kinematics, which is the branch of dynamics that studies motion without considering forces. It defines important concepts including particles, rigid bodies, and scalar and vector quantities. The three main types of rectilinear motion discussed are uniform, uniformly accelerated, and non-uniformly accelerated. Curvilinear motion along curved paths is also introduced. Coordinate systems for describing motion include rectangular, normal-tangential, and polar coordinates. Rigid body motion types include translation, rotation, and general plane motion.