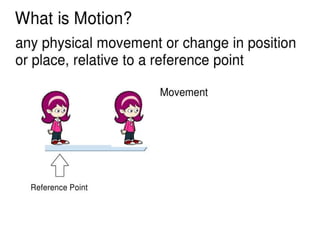
1. Motion refers to the change in position of an object over time. It can be described by quantities like displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc.
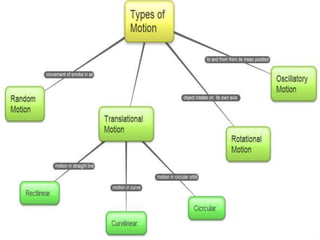
2. Motion can be classified as one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional depending on whether an object moves along a straight line, curved path, or through space.
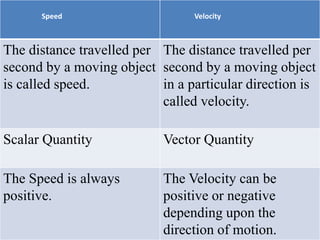
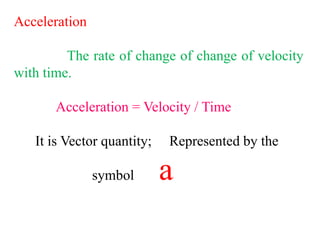
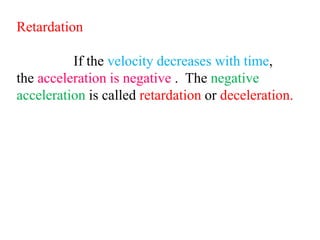
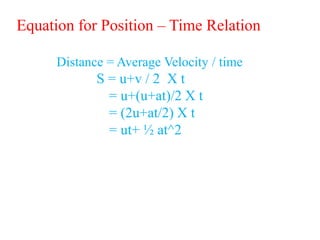
3. Key parameters for describing one-dimensional motion include position, displacement, velocity, acceleration, distance, and speed. Displacement refers to the shortest distance between initial and final positions, while distance depends on the actual path traveled.