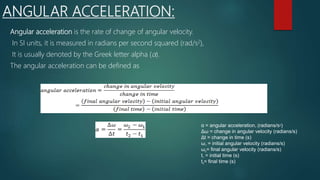
This document provides an introduction to kinematics, which is the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of points, bodies, and systems of bodies without considering the causes of motion. It defines key concepts related to motion such as displacement, velocity, acceleration, and their linear and angular counterparts. Specific types of motion discussed include translatory, rotational, linear, and angular motion. Equations for calculating speed, velocity, acceleration, average speed and velocity are also presented. The document concludes with sections on projectile motion and definitions and equations for angular speed, velocity, and acceleration.